Combining DNA test types can give you a better picture of your overall genealogical relationship to someone else. DNA expert Diahan Southard shares an example from her family about how she used different DNA tests to solve an adoption mystery.
Combine your autosomal test results with the results of your mitochondrial DNA or YDNA test to make some amazing connections today!
My family recently visited the Jelly Belly Factory in northern California. Of course, at the end of the tour, they funneled us into their gift shop where we felt compelled to buy jelly beans and other sundry treats.
My favorite part of the big box we bought were the recipes on the side. We could turn the already delicious variety of flavors into even more pallet-pleasing options by eating specific combinations of jelly beans at the same time. Like 2 green apply jelly beans + 1 cinnamon jelly bean = apple pie. Who knew!
Naturally, this got me thinking about DNA.
Combining DNA Test Types
Specifically, I was thinking about the power of combining multiple test types to get a better picture of our overall genealogical relationship to someone else.
If you recall, there are three kinds of DNA tests available for genealogists:
- Autosomal DNA
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
- Y chromosome DNA (YDNA)
Much of the focus these days is on how to use the autosomal DNA in our family history research. This may be because the autosomal DNA covers both sides of your family tree, so it is seen as a catchall for our family history. While it is a very powerful tool for our research, it can also be a bit overwhelming to try to determine how you are related to someone else.
Let’s look at an example from my own family history.
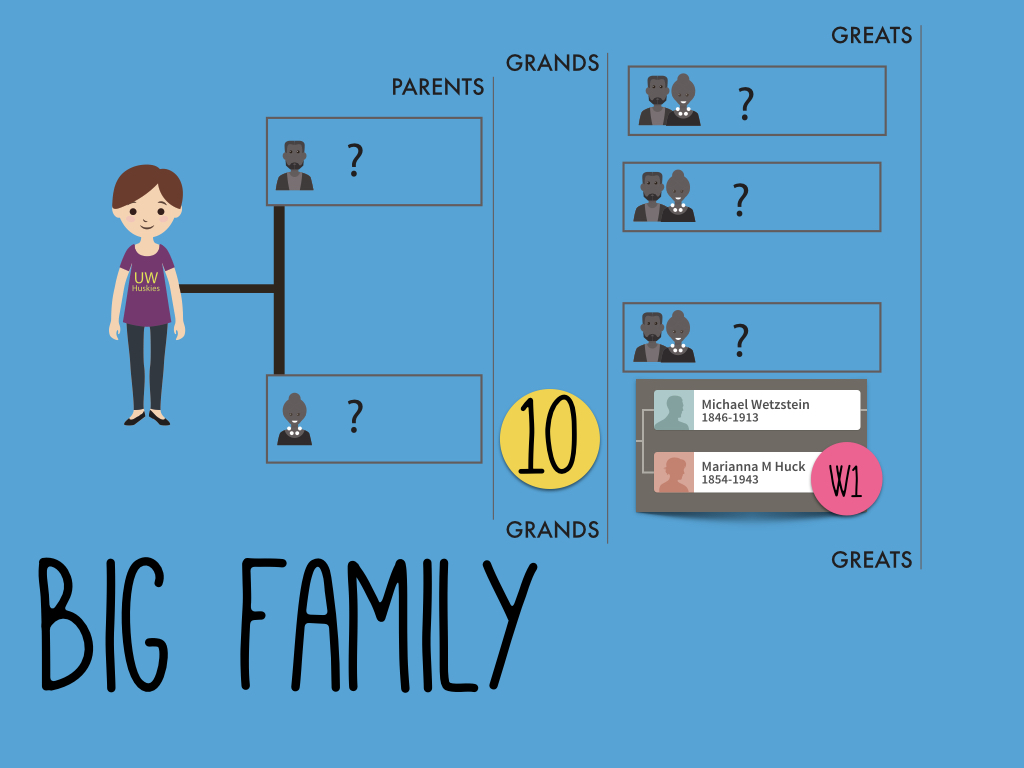
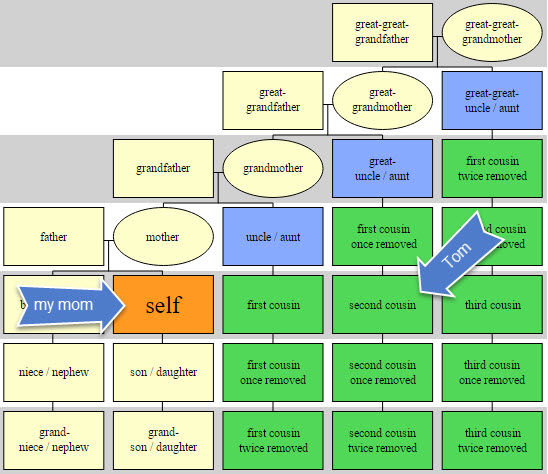
My mom took an autosomal DNA test at 23andMe and matched with Tom. Their predicted genealogical relationship, based on how much DNA they shared, was second cousins.
To begin to understand how they are related, we need to understand which ancestor could be shared by people who are genetic second cousins. To figure it out, you can count backward like this: people who share parents are siblings, sharing grandparents makes you first cousins, and sharing great-grandparents makes you second cousins.
So, if my mom and Tom are true second cousins (meaning there aren’t any of those once-removed situations going on, but that’s a subject for another time), then we should be able to find their common ancestor among their great-grandparents.
Each of us has eight great-grandparents. Because we can’t usually narrow down shared DNA to a single person, but rather to an ancestral couple, we are really just looking at four possible ancestral couple connections between my mom and Tom.
My mom doesn’t have any known ancestors, as she was adopted, so we can only evaluate Tom’s line. Tom was kind enough to share his pedigree chart with us, and he had all four of his couples listed. But how do we know which one is the shared couple with my mom?
Narrowing Down the Results
Now, for those of you without an adoption, you will have some other clues to help you figure out which of the four (or eight, if you are looking at a third cousin, or 16 if you are looking at a fourth cousin) ancestral couples is shared between you and your match. Start by looking for shared surnames.
If that comes up short, evaluate each couple by location. If you see an ancestral couple who is in a similar location to your line, then that couple becomes your most likely connecting point.
What then? Do genealogy! Find out everything you can about that couple and their descendants to see if you can connect that line to your own.
However, in my mom’s case, we didn’t have any surnames or locations to narrow down which ancestral couple was the connection point between our line and Tom’s. But even if we had locations, that may not have helped as Tom is very homogenous. All of his ancestors were from the same place!
But, we did have one very important clue: the mitochondrial DNA. Remember mtDNA traces a direct maternal line. So my mom’s mtDNA is the same as her mom’s, which is the same as her mom’s etc.
At 23andMe they don’t test the full mitochondrial DNA sequence (FMS) like they do at Family Tree DNA. For family history purposes, you really want the FMS to help you narrow down your maternal line connection to others. But 23andMe does provide your haplogroup, otherwise known as your deep ancestral group. These groups are named with a letter/number combination. My mom is W1 and we noticed that Tom is also W1.
This meant that my mom and Tom share a direct maternal line – or put another way, Tom’s mother’s mother’s mother was the same as my mom’s mother’s mother’s mother. That means there is only one couple out of the four possible couples that could connect my mom to Tom: his direct maternal line ancestor Marianna Huck, and her husband Michael Wetzstien.
Now you can only perform this wondrous feat if you and your match have both tested at 23andMe, or have both taken the mtDNA test at Family Tree DNA.
Just as a Popcorn Jelly Belly plus two Blueberry Jelly Bellies makes a blueberry muffin, combining your autosomal DNA test results with your mtDNA test results (or YDNA for that matter) can yield some interesting connections that just might break down that family history brick wall.
Get your mtDNA and YDNA tested at Family Tree DNA
If you are considering testing your YDNA and/or your mtDNA, then Family Tree DNA is the place for you!
Even if you aren’t trying to solve an adoption mystery, you can utilize these additional tests to break down other brick walls in your genealogical research and learn more about your heritage. You can take their Family Finder autosomal test, YDNA, or Mitochondrial (mtDNA) full sequence test. Click here to shop now!

About the Author: Diahan Southard has worked with the Sorenson Molecular Genealogy Foundation, and has been in the genetic genealogy industry since it has been an industry. She holds a degree in Microbiology and her creative side helps her break the science up into delicious bite-sized pieces for you. She’s the author of a full series of DNA guides for genealogists.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
This article was originally published on April 17, 2017 and updated on April 5, 2019.






So did you find your mother’s parents?!
Carol,
Thanks for asking! We did find my mom’s mom! We have been warmly welcomed by her family (she passed away in 2001). And we are pretty sure her father was one of three brothers.
Great article, even two years later!
Just one question…
I have taken the Autosomal tests at both 23andMe and AncestryDNA.
Then, because I learned that my dad was a posthumous birth (of course after everyone with answers have passed) but with myself being his only child and a female, I have no way of testing for his Y-DNA!
So I took the mtDNA at Family Tree, in hopes of strengthening which leads came from my maternal side.
So that being said… Do I need to also take the Family Tree Autosomal (Family Finder) test? or is there a way upload my other test results on the Family Tree site?
(Because I don’t see that option)
Can both tests be uploaded to GEDmatch maybe?
Thanks.
We have many articles including some that address transferring raw data. You’ll find them here: https://test.lisalouisecooke.com/category/dna-2/
Or go to our home page genealogygems.com and select “DNA” from the category menu under “Start Learning.” You’ll also find quick reference guides including “Organizing Your DNA” which addresses working with results from multiple sites at https://www.shopgenealogygems.com/collections/dna-guides-print
I have a confusing situation. My daughter did 23and me and had a match come up as her cousin, so then my son did the same and the same woman was a match as his 1st cousin as well. This woman, who is my age 53, could not be their cousin. Therefore I did 23 and me and she matched as my half-sister, I suspected this as my father was often unfaithful to my mother. After all of this my father admitted to an affair and she was most likely his daughter. My sister was given up for adoption by her mother. MY sister and I share 19.7% DNA more than cousins but a little less than expected for half-siblings. My children both share 8.7 and 9.6% with her. My father did 23 and me and only matched 31%. I emailed 23 and me and their response was “you half-sister and you must not share the same father as their DNA does not fall within the percentage of a parental match, but your children came up as cousins because cousins and half-nieces/nephews share the same amount of DNA as cousins. Here’s the thing that makes zero sense and they refuse to answer How can she be my half-sister, my children’s half-aunt but not my father’s daughter? They are saying he is her uncle, my father had two much older (22 and 21 years) sisters, and one brother who was sterile due to a childhood illness. Is there any way my father could be her father and have the dna percentage come out that low?
Dear Krystal,
This may be a long-shot, but there have been cases where a chimera effect has occurred.
Sometimes it happens when a person has a bone marrow transplant.
It also has occurred when a twin, in utero, absorbs another twin and the host takes on the DNA of the absorbed twin. Sounds very weird and kind of gross, however, it has been proven. I am no scientist, but it sounds like a possibility here.
There are posted articles about it. Please read up on this very unique phenomenon.
I hope you will let us know the outcome. Best wishes!
Hi, I hope you can help with my question. Through Ancestry DNA I have found “an immediate family member”. In contacting this person we have found that we both were adopted. She is a couple years older than I am. We don’t have much more to go on in trying to figure out which parent we share. In looking over our matches, we seem to have basically the same names coming up in “first cousins”. I have been in touch with one of those who is also adopted. My question is how do we go about determining who we come from. Or any other avenues to,pursue. Thank you in advance.