by Lisa Cooke | Mar 25, 2014 | 01 What's New, Beginner, Evernote, Organization, Research Skills
Recently I heard from Jane, a Genealogy Gems Premium subscriber in Canada, who needs a genealogy research plan! She’s researched on Ancestry.ca,  Scotland’s People, the Free English BMD Index, FamilySearch and joined her local society. But she’s not sure where to go next with her research–there just are SO many options! If this sounds familiar, check out her question and the advice I gave her:
Scotland’s People, the Free English BMD Index, FamilySearch and joined her local society. But she’s not sure where to go next with her research–there just are SO many options! If this sounds familiar, check out her question and the advice I gave her:
“I often end up wandering around in circles and mazes as one thing leads to another, and another, and … I am sure you know what I am talking about. I seem to be jumping back and forth between my Dad’s family, my Mom’s family, their families, etc. until there are times that I find myself at a certain point, only to wonder ‘Where was I going with this?’ I’m now wondering if I would be best to take it one person at a time – to find out as much as I can about that person in that point of time, before going on to another. I have started trying to make notes…but find that I end up hopelessly out of order and lost. Any advice would be appreciated! Help!!!”
My Answer: A Genealogy Research Plan to Deal with the Chaos
“You are not along in this genealogical dilemma! It’s easy to let the records start to take over and lead you around. Set a goal or a genealogy research plan – define what it is you want to know. It might be something very specific about a particular ancestor, or it might just be to fill in the blanks on one particular family. Early in my research I focused on one grandparent, and working backwards, I would strive to fill in all the blanks on that person, then their parents, then their siblings. I wouldn’t “leave” that family until I felt that I had filled in as much of the family group sheet as possible. (We have sort of lost track of the “family group sheet“ in this technological age. But it is an excellent tool for keeping you on track and focused on the blanks that need to be filled.)
An additional strategy is to have a process for dealing with information that is a bit off your current track. Often we feel like we have to pursue it or we’ll lose it. I like to use Evernote (free at Evernote.com) to capture data that I’m not ready to deal with right now, but definitely want to pursue later. I create an Evernote “notebook” for that family surname, and a note book called “future research.” Drag and drop “Future Research” onto the family surname notebook which will create a “stack.” Now you can create notes and drop them into the “Future Research” notebook which is inside the applicable family. Add tags to your note like “newspaper,” “death record,” etc. and some good searchable keywords so that the note will be easy to find when you need it. Now you can capture the item, file it away, and stay focused on the task at hand. Whenever you’re ready to ask a new question, open that Future Research notebook. Use what’s there to inspire the next phase of your genealogy research plan.”
More Resources
How to Get Started in Evernote, and the Ultimate Evernote Education
Should Evernote be my Digital Archive?
If you would like to learn more about using Evernote for genealogy, I have a quick reference guide in my store that will work wonders in keeping you organized. It’s available for both Windows and Mac, and in both PDF and laminated print format.
 Your questions are always welcome! Contact me by email, or leave a voice mail at (925) 272-4021 and you may just hear yourself on the show.
Your questions are always welcome! Contact me by email, or leave a voice mail at (925) 272-4021 and you may just hear yourself on the show.
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 24, 2014 | 01 What's New, History, NARA, Photographs
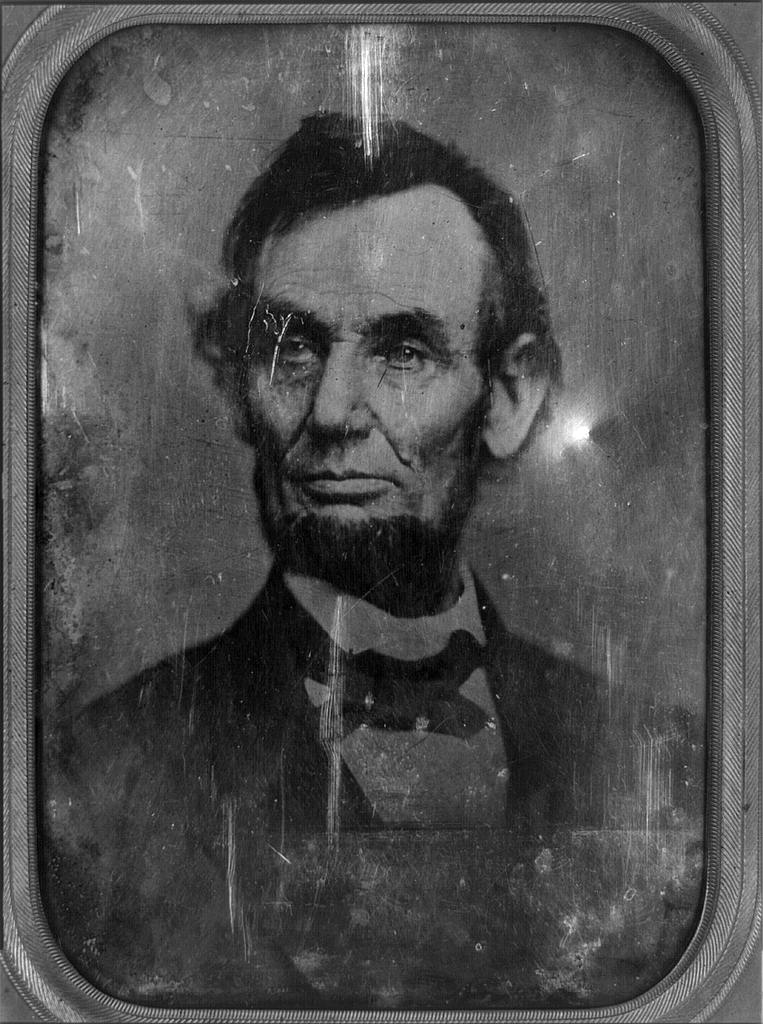

Daguerrotype of a Photograph of Abraham Lincoln, used for the $5 Bill. Original taken on February 9, 1864. Photographer unidentified [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.
Mystery photos are one of a family history researcher’s biggest frustrations. We find them in old albums, between the pages of books or in loose files. It can heartbreaking to wonder whether we’re looking at the face of an ancestor–and to know we may never know for sure.
Well, we’re not alone. Two news stories ran recently about old mystery photos theorized to be two icons of American history: President Abraham Lincoln and singer Elvis Presley!
(Image Right: Daguerrotype of a Photograph of Abraham Lincoln, used for the $5 Bill. Original taken on February 9, 1864. Photographer unidentified [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Mystery Photos: Abraham Lincoln Funeral
The Washington Post recently posted a story about the possibility that some unidentified photos at the National Archives (U.S.) show rare images of Abraham Lincoln’s funeral procession in New York City.
The article gives some great back story how Lincoln’s 2-week+ funeral procession. His body traveled by rail and horse-drawn hearse for 1600 miles from Washington, D.C. back home to Springfield, Illinois. Along the way, there were stops for elaborate funeral processions in several cities. Millions of mourners turned out. The article quotes the man who put together this theory – a retired government accountant who loves historic photos.
Mystery Photo: A Young Elvis Presley?
The Blaze recently reported on an Elvis sighting: well, at least a photo sighting of Elvis. The image in question shows a young teenage boy. There are lots of questions about whether this is really The King before fame changed his life – and American pop music – forever.
These remind me of a genealogy blog post by Lisa Frank. She shares how listening to the Genealogy Gems Podcast led to the discovery of an online video that may belong to her family story. Read her post Could It Be My Ancestor? and chime in with your opinion.
What surprising, poignant or fascinating mystery photos have you found in your family history research? Share them on the Genealogy Gems Facebook page and tell us about them! I look forward to seeing them!
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 19, 2014 | Beginner
 Free Family History has a nice ring to it!
Free Family History has a nice ring to it!
Did you know you don’t have to pay for a subscription to anything to be able to start learning more about your family history?
Start to find your family history for free by asking the four questions listed below.
1. What do you already know?
Chances are that you know something about your family already. The most important facts we start with are our relatives’ names and their dates and places of birth, marriage(s) and death. These facts can help you later to distinguish between records about our relatives and others with the same name.
Write down what you know about your “direct ancestors”–your parents, grandparents, great-grandparents, etc.–on a family tree chart like this free fill-in pdf format (these are also called pedigree charts). Then use family group sheets like this one to organize facts about each individual couple (this is where you can list all the children your grandparents had, for example).
2. What do your relatives know?
After filling out what you can, show your family tree chart and family group sheets to other relatives. Ask them if they can fill in some blanks. Remember these tips:
- Try to include a little note about who tells you each piece of information.
- Someone may dispute what you find. Everyone’s memory of an event is different. Don’t argue. Treat their information with respect:. Write it down. Then ask politely if they have any documentation you could see, or why they believe something to be true (who told them, etc).
- Ask whether anything is missing from your charts: a grandparent’s second marriage, a stillborn child or even whether someone’s name is accurate. You or others might know someone by a nickname or middle name.
- Be sensitive to information that might be confidential or not generally well-known, like a birth date that doesn’t appear more than 9 months after a wedding, or a first marriage. Consider asking living relatives if it’s okay for you to share certain facts. Consider only showing part of your charts to a relative.
3. What’s in the attic (or anywhere else)?
We can often find family documents in our own homes and those of our relatives. Look in attics, basements, storage units, safe deposit boxes and  safes, filing cabinets, photo albums, scrapbooks, shoeboxes and other places where papers and memorabilia may be tucked. You’re looking for things like:
safes, filing cabinets, photo albums, scrapbooks, shoeboxes and other places where papers and memorabilia may be tucked. You’re looking for things like:
- certificates of birth, baptism, marriage or death;
- obituaries or other news articles, like anniversaries;
- funeral programs, wedding and birth announcements;
- photos with names or other notes on the backs;
- insurance, pension, military or other paperwork that may mention births or deaths or beneficiary information;
- wills and home ownership paperwork–even outdated ones;
- a family Bible.
When you find family names, relationships, dates and places in these documents, add them to your charts.
4. What’s available online for free?
There are two major types of family history information online: records and trees. Records are documents created about specific people, like obituaries, birth certificates and all those other examples I just mentioned. Trees are a computerized form of other people’s family tree charts and group sheets. It can be tempting to just look for someone else’s version of your family tree. Eventually you will want to consult those. But other people’s trees are notoriously full of mistakes! Instead, start by looking for records about the relatives you already have identified.
I suggest that you start your search at FamilySearch.org because it’s totally free. At most other sites, you’ll have to subscribe or pay to see all the search results. At FamilySearch, you just need to create a free user login to get the most access to their records.
After logging in, click Search. Choose a relative you don’t know a lot about. Search for that name. Use the different search options to add more information–even a range of dates and a state/province or country–so you don’t have to wade through thousands of near-matches.
The most common records to find on FamilySearch for many countries are census and vital records.
- A census is a tally of residents, voters or another target population. Entries often include details about a household: who lived there, how they were related, how old they were, where they were born, etc. You can often extract family information from census listings, though some things (like ages or name spellings) may not be totally accurate.
- Vital records are official records of someone’s birth, marriage or death. In these, you’ll often find important dates and places as well as names of parents, spouses or others important to the family. They aren’t always totally accurate, and you may only be able to see an index of the record (not the actual document).
As you find search results, compare what they say to what you’ve already learned. How likely is it that this record belongs to your family? Consider how many people seem to have the same name in that location and time period (for example, how many are mentioned in the 1880 U.S. census in that state?). Don’t just look at the search results list: click through to look at the full summary of the entry and, if you can, the original record itself. You may find additional details in these that can confirm whether this record belongs to your relative. You may even find out about new people: your great-grandparents’ parents, for example. Write it all down or begin building a family tree right there on the FamilySearch website (because it’s totally free: learn more about that here.) And one of the greatest keys to long term success is citing your sources. It’s imperative that you make careful note of where you got the resource so that you can find and refer to it again later, and back up your research if it is ever called into question.
 People who research their family history often describe it as a puzzle with lots of different pieces. You will need to assemble a lot of puzzle pieces–information about each relative–to begin to see the “bigger picture” of your family history. You’ll start to sense which pieces may belong to a different family puzzle. You may put together a picture that is unexpected, or has some shadows and sadness. There will likely also emerge heroic, beautiful and touching images.
People who research their family history often describe it as a puzzle with lots of different pieces. You will need to assemble a lot of puzzle pieces–information about each relative–to begin to see the “bigger picture” of your family history. You’ll start to sense which pieces may belong to a different family puzzle. You may put together a picture that is unexpected, or has some shadows and sadness. There will likely also emerge heroic, beautiful and touching images.
Ready to learn more?
Up next, read:
7 Great Ways to Use Your iPad for Family History
How to Find Your Family Tree Online
Best Genealogy Software
Search the SSDI for Your Family History
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 18, 2014 | 01 What's New, Certification, Family History Podcast, Research Skills, Source Citation
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
Originally published 2009
Republished March 18, 2014
[display_podcast]
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-2009. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 23: The GPS in Action: Using the Genealogical Proof Standard
In episode 20, we talked about using the Genealogical Proof Standard (GPS), the powerful research process used by the professionals. This process ensures the quality, accuracy and success of our research. Researching by these standards now may save you going back and re-doing some of your hard work later down the road.
In today’s episode I’m going to help you put the GPS into concrete action with an example from my own research. And I have some downloadable free tools that will help you do the job! In this episode we also follow up with a listener question on how to export your family tree from Ancestry.com—see below for an updated link.
The GPS in Action
Wouldn’t it be nice to have a worksheet that prompts you through the GPS process and helps you keep track of everything and stay organized? Well, I wanted something like that myself. I think we need more than just a blank form: we need and want a detailed worksheet that not only gives the area to record our findings, but also buy medication online usa incorporates all the key areas of the Genealogical Proof Standard so that we can be sure we aren’t missing anything.
I didn’t find something like this online so I created it myself. Click on the Research Worksheets, under Links below, for both a filled-out sample version and a blank version that you can save to your computer.
According to the Board of Certification of Genealogists the 5 keys elements of the Genealogical Proof Standard are:
- a reasonably exhaustive search
- complete and accurate source citations
- analysis and correlation of the collected information
- resolution of any conflicting evidence
- a soundly reasoned, coherently written conclusion
I’ve incorporated these elements while keep in mind Mark Tucker’s process map worksheet (see Links section below) into my Research Worksheet.
The Research Worksheet is divided into the following sections:
- Research Objective
- Known Facts
- Working Hypothesis
- Research Strategy
- Identified Sources
- Final Conclusions
In your conclusion which is called a Proof Argument you should:
- Explain the problem
- Review the known sources which you identified on your worksheet
- Present the evidence with source citations and the analysis of those sources
- Discuss any conflicting evidence. This important because it may generate another search that needs to occur, or put to rest questions about evidence that on first glance looks conflicting.
- And finally summarize the main points of your research and state your conclusion.
Updates and Links
How to download your GEDCOM from Ancestry.com
Research Worksheet: Example
Research Worksheet: Blank Form
Correspondence Log
Mark Tucker’s GPS Flowchart
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 17, 2014 | 01 What's New, Libraries, NARA
National Archives (US) facilities are closing or restructuring in three locations. But steps are being taken to maintain access (local or online) to the

National Archives, Washington, D.C. Wikimedia Commons Image by Edbrown05.
treasure trove of research materials at these facilities.
A recent press release states, “As part of ongoing budget adjustments, Archivist of the United States David S. Ferriero announced the permanent closure of three National Archives facilities. This year, the National Archives facility in Anchorage, AK, will close and two facilities in the Philadelphia, PA, area will be consolidated to a single site. Within the next two years, two Archives’ facilities in Fort Worth, TX, also will be consolidated to a single site. These closures and consolidations will result in estimated annual cost savings of approximately .3 million.”
“The National Archives budget is devoted primarily to personnel and facilities, both of which are essential to our mission,” the Archivist stated. “I recognize these cuts will be painful; however, we are committed to continuing to provide the best service to our customers and best working conditions for our staff nationwide.”
Here’s the scoop on each of the affected locations:
National Archives – Anchorage, AK, facility closing:
The National Archives’ facility in Anchorage, AK, will close permanently in FY 2014. The employees who work there will be offered positions at other National Archives facilities, with the National Archives paying relocation expenses. The less than 12,000 cubic feet of archival records in Alaska will be moved to the National Archives at Seattle, WA, where the National Archives will digitize these records so that they remain available to Alaskans through the internet. In addition, we will move approximately 7,500 cubic feet of records center holdings to Seattle, WA.
National Archives – Philadelphia, PA, facility consolidation:
The National Archives currently maintains two facilities in Philadelphia—a records center and archives at Townsend Road, and a small “storefront” archival facility at 900 Market Street in the city center. These facilities are in the same commuting area, and archival records are currently moved between the two for research use. The Market Street facility will close in FY 2014, and those employees will move to Townsend Road or telework locations. The less than 5,000 cubic feet of archival records stored at Market Street will be moved to Townsend Road, where the majority of the archival records already are stored. The Townsend Road facility’s research room will be modified to better provide appropriate access to researchers, and community outreach programs will continue.
National Archives – Fort Worth, TX, facility consolidation:
The National Archives currently maintains two facilities in Fort Worth: a combined records center and archives at John Burgess Drive, and a smaller “storefront” facility at Montgomery Plaza. The National Archives will permanently close the Montgomery Plaza facility in FY 2016. All employees at the Montgomery Plaza location will move to John Burgess or telework locations. No original records are stored at Montgomery Plaza, and researchers will have continued access to archival records through the research room at John Burgess Drive.
What’s at National Archives facilities for family history researchers? Learn more here.
 Scotland’s People, the Free English BMD Index, FamilySearch and joined her local society. But she’s not sure where to go next with her research–there just are SO many options! If this sounds familiar, check out her question and the advice I gave her:
Scotland’s People, the Free English BMD Index, FamilySearch and joined her local society. But she’s not sure where to go next with her research–there just are SO many options! If this sounds familiar, check out her question and the advice I gave her:
 Your questions are always welcome! Contact me by email, or leave a voice mail at (925) 272-4021 and you may just hear yourself on the show.
Your questions are always welcome! Contact me by email, or leave a voice mail at (925) 272-4021 and you may just hear yourself on the show.

 Free Family History has a nice ring to it!
Free Family History has a nice ring to it! safes, filing cabinets, photo albums, scrapbooks, shoeboxes and other places where papers and memorabilia may be tucked. You’re looking for things like:
safes, filing cabinets, photo albums, scrapbooks, shoeboxes and other places where papers and memorabilia may be tucked. You’re looking for things like: People who research their family history often describe it as a puzzle with lots of different pieces. You will need to assemble a lot of puzzle pieces–information about each relative–to begin to see the “bigger picture” of your family history. You’ll start to sense which pieces may belong to a different family puzzle. You may put together a picture that is unexpected, or has some shadows and sadness. There will likely also emerge heroic, beautiful and touching images.
People who research their family history often describe it as a puzzle with lots of different pieces. You will need to assemble a lot of puzzle pieces–information about each relative–to begin to see the “bigger picture” of your family history. You’ll start to sense which pieces may belong to a different family puzzle. You may put together a picture that is unexpected, or has some shadows and sadness. There will likely also emerge heroic, beautiful and touching images.




