by Lisa Cooke | Feb 20, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA, Kids |
DNA testing for kids is a great way to spark their interest in their heritage, while teaching science, math, geography, and more. Consider these reasons and start with the budget-friendly option of an autosomal test.

According to a 2010 study out of Emory University, if we want to encourage kids toward an activity that will positively impact them, we should steer them toward family history. The researchers reported, “Children who know stories about relatives who came before them show higher levels of emotional well-being.”
Now, I know I don’t need to convince you of this. You are already sold on genealogy. But let’s explore how DNA testing might be able to help you share your love of family history with your children and grandchildren.
Why Try DNA Testing for Kids
Since you know this is me, the genetic genealogist talking, you can probably guess what I’ll suggest for getting kids interested in family history. DNA testing is a great way to personally and physically involve them. There is the tangible process of taking the sample at home, and the marvel at how such a simple act can produce the amazing display of our ethnicity results. Since each of us is unique, it will be fun for them to compare with you and other relatives to see who-got-what-from-who. This will naturally lead to questions about which ancestor provided that bit of Italian or Irish, and wham! You’ll be right there to tell them about how their 5th great-grandfather crossed the ocean with only the clothes on his back, determined to make a new start in a new land.

If there are parts of the ethnicity report you can’t explain, use that as a hook to encourage them to start digging and to find out why you have that smattering of eastern European or Southeast Asian. Taking them for a tour of the DNA match page, you can show them how they share 50% of their DNA with their sister (whether they like it or not!) and how they share 25% with their grandparent!
DNA test results give kids a totally unique look at their personal identity with technology that is cutting edge. Looking at their DNA test results can turn into a math lesson, a science lesson, a geography lesson, a lesson on heredity or biology, or a discussion on identity. DNA is the perfect introduction to the wonders that genealogy can hold, especially for children.
A Warning and Caution
As with all DNA testing pursuits, this one should not be taken lightly, even with all of its benefits.
An important word to parents: Be sure to keep unintentional consequences in the forefront of your mind. This includes the possibility of revealing family secrets. Talk with your spouse and make sure you are both on the same page. In the end, this is your decision.
An important word to grandparents and other relatives: DNA testing is a parent’s decision. Even though you’re passionate about preserving the family’s history and the benefits of including children are numerous, you must obtain parental consent if you are not the parent.
More About Autosomal DNA Testing for Kids
 Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 19, 2017 | 01 What's New, MyHeritage
Discoveries pages from MyHeritage make finding matches easier than ever. MyHeritage is known throughout the industry for it’s matching technologies, and they have just gotten even better with this great new user interface.

MyHeritage has just announced their new Discoveries pages. The Discoveries pages provide a unified experience for all matches, organizing them into two main pages: Matches by People and Matches by Source. Now, you can look at all the matches that were found for a particular individual in your family tree, all matches found in a particular collection of historical records, or a matching family tree. Whatever you choose to use, the new pages combine Smart Matches (matches with trees) and Record Matches (matches with records) into the same unified and consistent interface.
MyHeritage also displays the new information that each match provides, and matches are arranged by the value that they add to your family tree. Those matches that add the most value are listed first. This saves you time and allows you to focus on the most valuable matches. You can easily save all new and improved information to your family tree, as well.
The new Discoveries pages are easier to use, more intuitive, and much faster than the previous layout. Learn even more about the Discoveries pages in the official blog post, here.
Don’t Miss a Thing
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 17, 2017 | 01 What's New, Church, Records & databases
Findmypast announces the new catholic church records in their Catholic Heritage Archive this week. This new partnership with British and American Archdioceses will be a monumental help to those searching their early Catholic roots. Also this week, records from Italy and the Netherlands at FamilySearch.

By JakobLazarus (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Catholic Church Records in the Catholic Heritage Archive
Findmypast announced their new Catholic Heritage Archive this past week. They are releasing over 3 million exclusive records including sacramental registers for the Archdiocese of Philadelphia from 1757 to 1916 as well as for the British Archdioceses of Westminster and Birmingham from 1657 forward. This builds on last year’s publication of more than 10 million Irish Catholic parish registers.
The Catholic Church holds some of the oldest and best preserved genealogical records and in the past, have been difficult to access.
In collaboration with various Archdioceses of the Catholic Church, Findmypast is helping to bring these records online in one unified collection for the first time ever. Exclusively available on Findmypast, images of original documents will be completely free to view in many cases. Fully searchable transcripts will also be included, providing family historians from the around the world with easy access to these once closely guarded records.
Click “Play Now” below to listen to Sunny Morton’s brief interview with Findmypast about the announcement: [display_podcast]
The next phase of the Catholic Heritage Archive will include records from the archdioceses of New York and Baltimore as well as additional records from Philadelphia. There are over 30 million records in just these three dioceses. The digitization of the whole archive is a monumental undertaking and, when complete, will contain hundreds of millions of records for the USA alone.
Catholic Heritage Archive Holdings for This Week:
United States – Pennsylvania – Philadelphia – Baptisms
The Philadelphia Roman Catholic Parish Baptisms at Findmypast are the first of these record releases from an agreement made with the Roman Catholic Church to digitize their records. These baptismal records will include a name, their parent’s names, and residence at the time of the event.
Additional information may include place of birth, sponsors, minister who performed the ceremony, and notice of marriage. Catholic priests were charged with noting all vital events of their parishioners. If, for instance, a parishioner married outside her home parish, the priest who performed the marriage would contact her priest to confirm she was baptized and to share the details of her marriage, hence the marriage notice in the baptism register.
United States – Pennsylvania – Philadelphia – Marriages
You can now view a transcript and an image of your ancestor’s marriage register from the Archdiocese of Philadelphia in this collection titled Philadelphia Roman Catholic Parish Marriages from Findmypast.
Information contained in these records include the couple’s names, marriage date and location, and you may find dates and locations of the couples’ baptisms.
All Philadelphia Roman Catholic Parish records are from the Archdiocese of Philadelphia, covering Bucks County, Chester County, Delaware County, Montgomery County, and Philadelphia County.
England – Westminster – Roman Catholic Census
Another Catholic records resource from Findmypast includes the Westminster Roman Catholic Census 1893. As well as the typical information you would expect from a census (occupation, address, birth year, etc.), notes detailing the local priest’s opinion on your ancestor’s faith and dedication to the church let you find out if your ancestor was a good or bad Catholic. Scandalous!
England – Birmingham & Westminster – Roman Catholic Church & Parish Records
Four separate collections, also in the Catholic Heritage Archive at Findmypast, include Roman Catholic baptismal, burial, marriage, and congregational records for locales in England. The records released this week are for the areas covering the Birmingham and Westminster archdioceses. The amount of information in each of these record sets will vary on the age of the record, legibility, and the amount of information recorded by the parish priest. You will find both a transcription and a digital image of the record.
England Roman Catholic Parish Baptisms
England Roman Catholic Parish Burials
England Roman Catholic Parish Marriages
England Roman Catholic Parish Congregational Records
United States – Pennsylvania – Vital Records
Provided by the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Findmypast brings you a large collection of vital records. The first is titled Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Births & Baptisms. These records include images from a variety of sources spanning years from the late 1600s to the mid 1900s.
It is important to note this may not be the only place to find births or baptisms—and there may be records included that are not births or baptisms in this material from the Historical Society of Pennsylvania.
The Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Deaths & Burials collection will include records that may contain the following information: decedent’s name, date of death and burial, parish and diocese, and could include additional information such as military service, age, and birth date.
The Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Marriages collection is also a helpful group of records and include marriage records ranging from the early 1600s to the late 1900s. You can view a transcript and the original image.
United States – Pennsylvania – Congregational Records
The Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Congregational Records is a unique collection that may give you insight into your ancestor and the church they attended. Not only will images include lists of past ministers, but you may find additional lists of those persons baptized and confirmed. Some of these records may also be used as a source to discover the names of your ancestor’s parents and spouses.
United States – Pennsylvania – WWII Records

Screenshot from Findmypast of the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, WWII Casualty Cards.
The Historical Society of Pennsylvania, Word War II Casualty Cards collection is a group of records created by the Army so if something happened to a local soldier, the newspaper wouldn’t have to scramble for information. These records are particularly relevant in light of the fire at the National Archives and Records Administration in the 1970s when most World War II personnel files were destroyed.
Netherlands – Miscellaneous Records
We have brought you many collections from Findmypast, which require a subscription. However, these next few collections are brought to you by FamilySearch and are free to access.
Netherlands, Archival Indexes, Miscellaneous Records collection has been updated this week at FamilySearch. These records include many record sources, such as civil registration, church records, emigration lists, military registers, and land and tax records. These records cover events like birth, marriage, death, burial, emigration and immigration, military enrollment, and more. These indexes were originally collected, combined and published by OpenArchives. For the entire index collection and more information visit www.openarch.nl.
Italy – Trapani, Civil Registration
FamilySearch brings you updates to the Italy, Trapani, Civil Registration (State Archive), 1906-1928 collection. This collection consists of civil registration of births, marriages, and deaths within the custody of the State Archive of Trapani. Availability of records is largely dependent on time period and locality. This collection of civil registrations records covers the years 1906-1928 and may also include:
- Residency records
- Marriage banns
- Indexes
- Marriage supplements
- Miscellaneous records
Learn More about Institutional Records Research
 From schools and orphanages to prisons, hospitals, asylums, workhouses, and more, there’s a good chance one or more of your ancestors might be found on record in one of the many types of institutions. In this Premium eLearning video, Institutional Records Research Methods, Lisa Louise Cooke presents methods for finding your ancestors in institutional records, from establishing a workflow and investigating clues found in the census and other records to resources and strategies for digging up the records. This 40-minute video includes a downloadable handout and is available right now to all Premium eLearning members. Click here to sign up!
From schools and orphanages to prisons, hospitals, asylums, workhouses, and more, there’s a good chance one or more of your ancestors might be found on record in one of the many types of institutions. In this Premium eLearning video, Institutional Records Research Methods, Lisa Louise Cooke presents methods for finding your ancestors in institutional records, from establishing a workflow and investigating clues found in the census and other records to resources and strategies for digging up the records. This 40-minute video includes a downloadable handout and is available right now to all Premium eLearning members. Click here to sign up!
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 16, 2017 | 01 What's New, Genealogy TV, Who Do You Think You Are? |
TLC’s Who Do You Think You Are? is back with eight new one-hour episodes bringing more unexpected turns, and surprising discoveries of great historical significance. Read more to find out who you’ll see and some of the hidden family secrets revealed.

7th Season of WDYTYA
Communists, secret agents, and abolitionists are just a few of the family secrets uncovered in this season of Who Do You Think You Are. The line-up of celebrities include:
Jessica Biel making a surprising discovery that changes what she thought knew about her heritage.
Julie Bowen, of Modern Family, uncovers the story of two relatives whose moral codes are from opposite ends of the spectrum.
Courteney Cox will trace her maternal line back seven centuries to the Medieval times to discover royalty in her lineage and an unbelievable tale of family drama.
Jennifer Grey uncovers new information about the grandfather she thought she knew, learning how he survived adversity to become a beacon of his community.
Smokey Robinson searches for answers behind the mystery of why his grandfather disappeared from his children’s lives, and finds a man tangled in a swirl of controversy.
John Stamos digs into the mystery of how his grandfather became an orphan, and learns of tensions between families that led to a horrible crime.
Liv Tyler learns that her family is tied into the complicated racial narrative of America.
Noah Wyle unravels the mystery of his maternal line, uncovering an ancestor who survived one of America’s bloodiest battles.
Tune in on Sunday, March 5th, 2017 10/9c and be a part of their journeys. Also, you can enjoy this sneak peak in the video below:
Sharing Your Own WDYTYA Experience
 Have you recently found an amazing discovery that has altered how you feel about your family’s history? We would love to hear about your experiences on our blog, here in the comments section, or on our Facebook page. After all, everyone has a story to tell.
Have you recently found an amazing discovery that has altered how you feel about your family’s history? We would love to hear about your experiences on our blog, here in the comments section, or on our Facebook page. After all, everyone has a story to tell.
And speaking of telling your story, Sunny Morton’s new book can help you do just that. It includes:
- fill-in pages with thought-provoking prompts to capture key moments that define your life
- Advice and exercises to reconstruct memories from long ago
- Interactive pages for family and friends to share their own stories
- Special forms for spotlighting important people, places and times.
Get Story of My Life by Sunny Jane Morton.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

by Lisa Cooke | Feb 15, 2017 | 01 What's New, African-American |
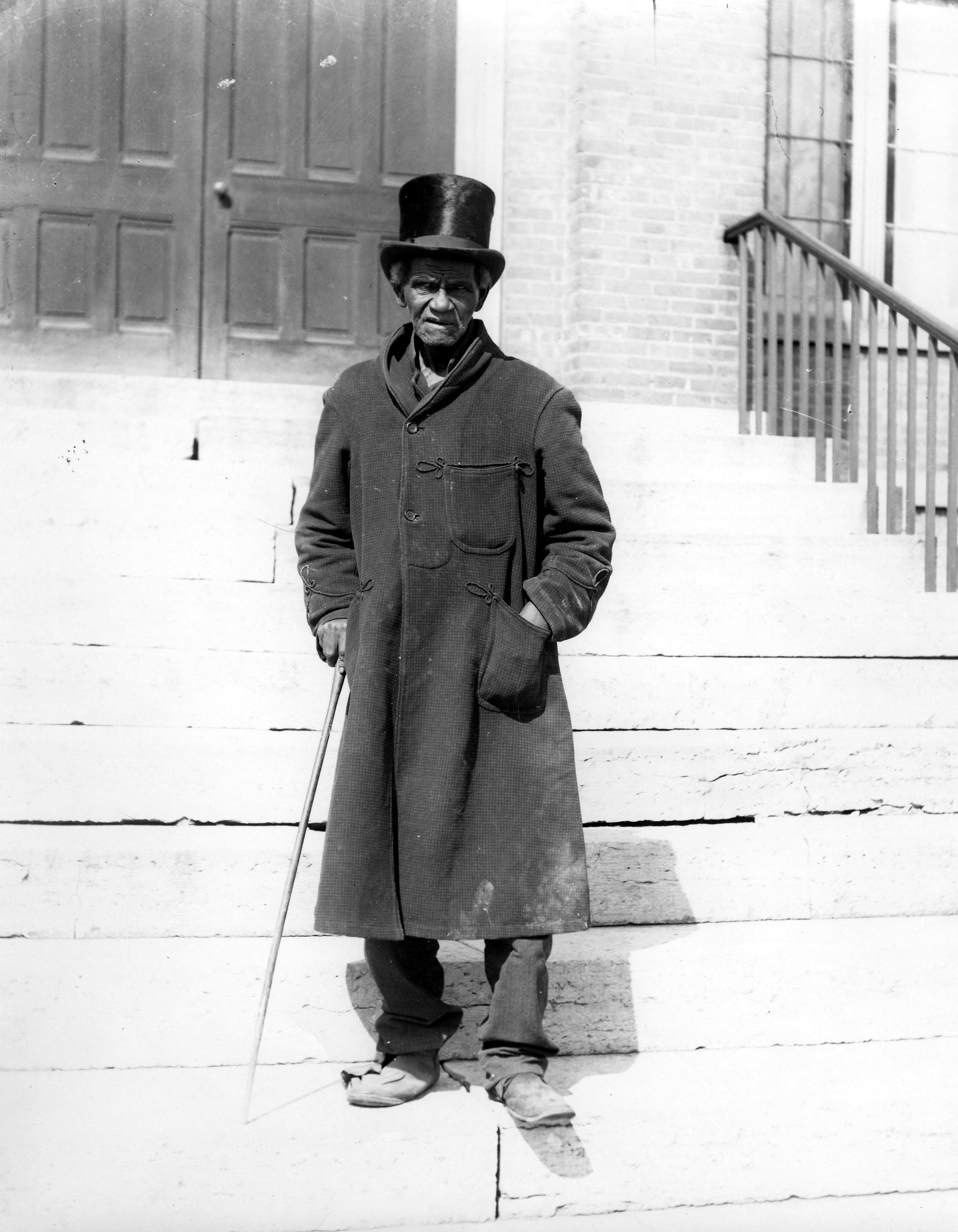

Not all people of color were enslaved prior to the emancipation. In fact, many were freed long before that. Researching free people of color can be quite complex. Tracing my own family line (who were free people of color) continues to be a real learning process for me. However, don’t let the challenges deter you from exploring this rich part of your heritage. In this “Getting Started” post, we discuss the manumission process, “negro registers,” and more for tracing your free people of color.
Who are Free People of Color?
[Note: Throughout our post, we will be using terminology that was used at the time the records were created.] A ‘free negro’ or ‘free black’ was a fairly recent status in the U.S. which differentiated between an African-American person who was free and those who were enslaved prior to emancipation. If a person was referred to as a ‘free negro’ or ‘free black’, that meant the person was not living in slavery. It is a fascinating and little know fact that, as Ancestry Wiki states, “one in ten African-Americans was already free when the first shots were fired on Fort Sumter.”
Step 1 for Tracing Free People of Color: Censuses
Sometimes, the story of your ancestors being free people of color was passed on through oral traditions. In my own family, our “line of color” was not talked about. Instead, my first clue was when I found my ancestor in the 1840 population census listed as free. I also found that one woman (presumably his wife) was marked in the column for “free white persons,” but John and the children were marked as “free colored persons” in this census. This was the first step to identifying my ancestor as a free person of color.
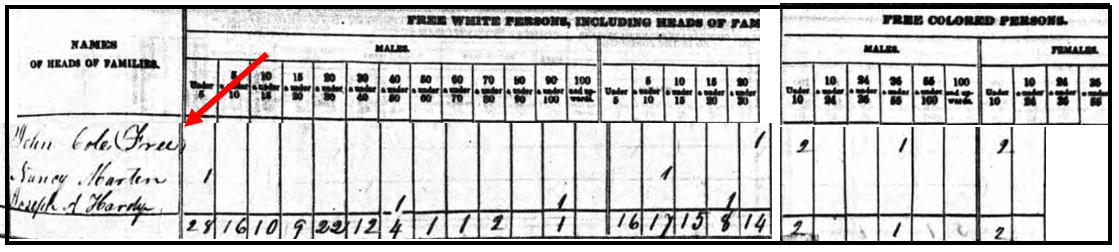
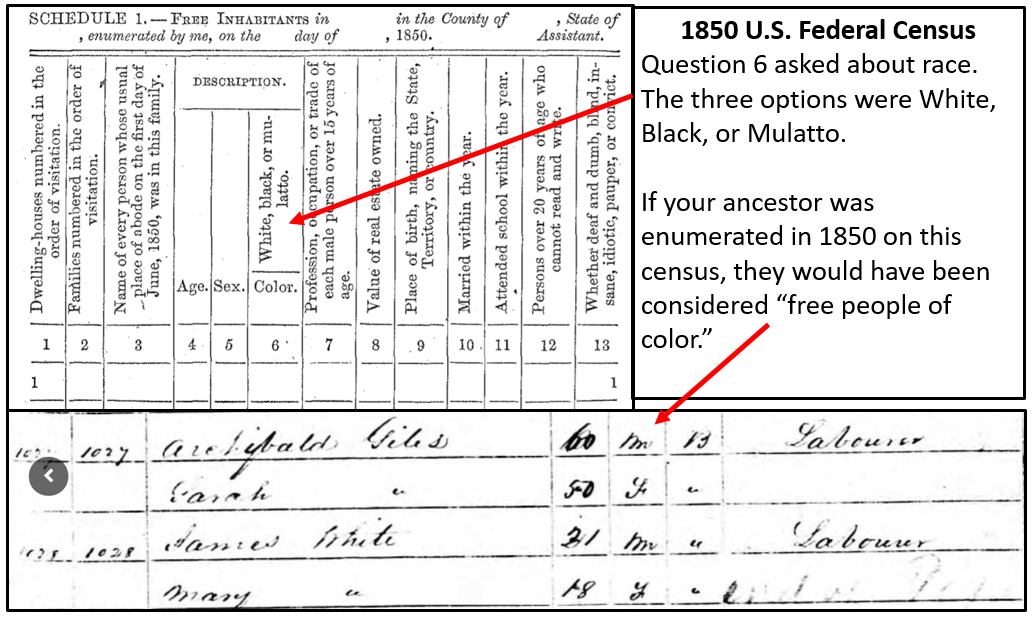
Let’s see another example. The 1850 and 1860 U.S. Federal Censuses included two population schedules. One enumerated free inhabitants, and the additional schedule, referred to as a Slave Schedule, was for making an enumeration of those persons who were enslaved. [We will discuss this further, below.]
If your ancestor appears on the 1850 U.S. Federal Census for free inhabitants, they are considered free, even if their race was listed as “Black.” An example of a Black man enumerated on the 1850 census is shown in the image below. Archibald Giles is recorded as “Black,” but appears on this census for “free inhabitants.” Therefore, he would be considered a free person of color.
If your targeted ancestor does not appear on either the 1850 or 1860 population schedule for free inhabitants, they might have been enumerated on the slave schedules of 1850 or 1860.
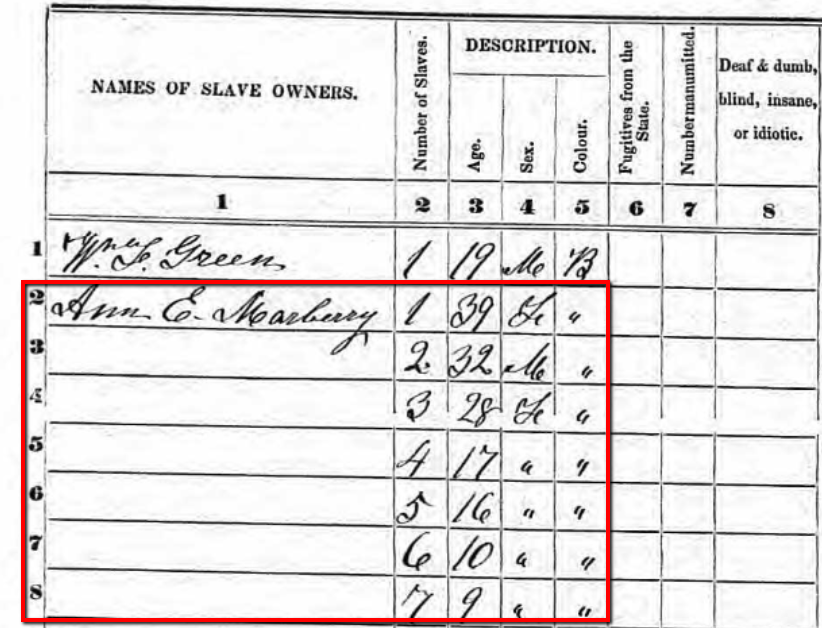
1850 Slave Schedule for Henry County, Tennessee. Snapshot via Ancestry.com.
You can check the 1850 Slave Schedule and the 1860 Slave Schedules at Ancestry.com. The 1850 census is also available at Findmypast, MyHeritage, and FamilySearch.
In this example to the left, you will see a portion of the Henry County, Tennessee Slave Schedule for 1850. Notice, only the heads of household or the “owners” were listed by name. Slaves were not named, but rather listed by age and sex under the names of their “owners.”
Step 2: The Manumission Process
Once you have identified that you have free people of color in your family tree, the next step is to determine how they became free. Many free people of color came from families that had been free for generations. This could have been due to a manumission of an ancestor or a relationship between an indentured white woman and a black slave. I make mention of this relationship between races because it is helpful to remember that the status (whether free or enslaved) of the child was based on the status of their mother. If the mother was free, then the child was free. If she was a slave, then the child was enslaved. [1]
Manumission was a formal way in which slaves were set free. There are many reasons why a slave owner may have released or freed his slaves. In some cases, slave owners would free their mistresses and children born to her. In one case, I found the following comment made by the slave owner, “I give my slaves their freedom, to which my conscience tells me they are justly entitled. It has a long time been a matter of the deepest regret to me…” And thirdly, it was possible for a slave to obtain their manumission through the act of “self-purchase.”
If the mother was free, then the child was free. If she was a slave, then the child was enslaved. [1]
Private manumission through probate. A private manumission decree could be made in a last will and testament. You can find these manumissions in wills, estate papers, or in probate packets. Many of these county level probate records have been microfilmed or digitized and are easily accessible online.
Sometimes, a manumission in a will would be contested. When this happened, a long paper trail of court documents may have been created. A thorough search of all of these proceedings may offer a wealth of genealogical data and clues.
Usually, manumission papers included the name of the slave owner, the name of the slave, and the reason for manumission. In the case of the slaves of John Randolph of Roanoke [Virginia,] his slaves were not named individually in his will written on 4 May 1819. Instead he stated, “I give my slaves their freedom, to which my conscience tells me they are justly entitled. It has a long time been a matter of the deepest regret to me, that the circumstances under which I inherited them, and the obstacles thrown in the way by the laws of the land, have prevented my manumitting them in my lifetime, which is my full intention to do, in case I can accomplish it.”[2]
John freed over five hundred slaves, and though each of them was not listed by name in his will, a codicil at the end of the will did name two of his slaves when he asked that Essex and his wife Hetty “be made quite comfortable.”[3]

Record of Arthur Lee purchasing his freedom.
Manumission through self purchase. Self-purchase may seem impossible; however, many slaves were not required to work on Sundays for their masters.[4] On this day, men and women could hire themselves out to do work for others. With frugality, they could save their earnings to buy their freedom or the freedom of their loved ones, though this was very, very difficult.
As you can see in this example of Arthur Lee, he was able to pay for his freedom and the freedom of his wife, though it took many years. This type of record could be found in a published book, a record listed in notarial books of the county, civil minutes books, or other courthouse holdings. It is important to speak with a knowledgeable person in your targeted area about where you should look. A knowledgeable person may be those working with the local historical or genealogical society, or a head of the local history department of the public library.
Step 3: “Negro Registers”
If you do not find the manumission in a last will and testament, perhaps due to a courthouse fire or other loss, you may have luck searching the county records where your free people of color later settled. Free people of color were often required to register, using their freedom papers, when they relocated to a new area. These types of records are called ‘negro registers’ or ‘records of free negros.’
Newly freed people carried with them their freedom papers which were given to them when they were manumitted. Once they relocated, they would register with the county clerk. They would need to show the county clerk these freedom papers and a record was made in the register. The record may include the name of members of the family, ages, and most recent place of residence.
The book titled Registers of Blacks in the Miami Valley: A Name Abstract, 1804-1857 by Stephen Haller and Robert Smith, Jr. provides the following information about registers of freed people:
“From 1804 to 1857, black people in Ohio had to register their freedom papers with the clerk of courts of common pleas in the county where they desired residency or employment. State law required this registration, and clerks of court were to keep register books containing a transcript of each freedom certificate or other written proof of freedom (see Laws of Ohio 1804, page 63-66; 1833, page 22; 1857, page 186). Few of these registers have survived to the 20th century.”[2]
Though this author says that only a few of the registers have survived, I found some microfilmed registers listing the names of free people of color who had settled in Miami County, Ohio at the local historical society archives. Again, it is important to ask those people who would be most knowledgeable, and in this case, it was the historical society.
In conclusion, we understand that tracing both our enslaved and manumitted ancestors is often a difficult task. We also know there is much more to learn and share for the best techniques to researching these lines. We encourage you to review some of the additional sources below. Please let us know what other resources have been most helpful to you in researching your free people of color in the comments section below. We want to hear from you!
Source Citations
[1] Kenyatta D. Berry, “Researching Free People of Color,” article online, PBS, Genealogy Roadshow, accessed 1 Dec 2016.
[2] Lemuel Sawyer, A Biography of John Randolph with a Selection From His Speeches, New York: 1844, page 108, online book, Google Books, accessed 20 Dec 2015.
[3] Ibid.
[4] History Detectives Season 8, Episode 10, PBS, online video, originally aired 29 Aug 2010, accessed 1 Dec 2016.
Additional Reading


 Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
















