Blog


New Free Historical Records Recently Added to FamilySearch
FamilySearch.org added new, free, historical records this week from Benin, Brazil, England, France, Ireland, the Netherlands, Puerto Rico, South Africa and the United States including 2 million North Carolina birth, marriage, and death records (1800 to 2000).
Search these new genealogical records and images by clicking on the collection links below.

Brazil
Brazil, Rio de Janeiro, Civil Registration, 1829-2012
Indexed Records: 739,447
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
England

England and Wales, National Index of Wills and Administrations, 1858-1957
Indexed Records: 49,830
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
England, Essex Parish Registers, 1538-1997
Indexed Records: 159,775
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
France
France, Haute-Garonne, Toulouse, Church Records, 1539-1793
Indexed Records: 4,686
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Ireland
Ireland Civil Registration, 1845-1913
Indexed Records: 2,673
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Ireland, Thom’s Irish Who’s Who, 1923
Indexed Records: 2,356
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
Netherlands

Netherlands, Archival Indexes, Vital Records
Indexed Records: 113,686
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Netherlands, Archival Indexes, Vital Records
Indexed Records: 3,097
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico, Catholic Church Records, 1645-1969
Indexed Records: 45,832
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
South Africa
South Africa, Transvaal, Civil Death, 1869-1954
Indexed Records: 97,711
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
United States
Alabama
Alabama, Jefferson County Circuit Court Papers, 1870-1916
Indexed Records: 41,089
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Alaska

Alaska Naturalization Records, 1884-1991
Indexed Records: 4,822
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
Arkansas
Arkansas, Sevier County, Record of Voters, 1868-1966
Indexed Records: 212,716
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
California
California, County Marriages, 1850-1952
Indexed Records: 48,368
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Florida

Florida, County Voter Registration Records, 1867-1905
Indexed Records: 25,453
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
Georgia
Georgia Probate Records, 1742-1990
Indexed Records: 7
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
Hawaii
Hawaii, Death Records and Death Registers, 1841-1925
Indexed Records: 33,593
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
New Jersey
New Jersey, Church Records, 1675-1970
Indexed Records: 0
Digital Images: 413,237
Added images to an existing collection
North Carolina

North Carolina, Department of Archives and History, Index to Vital Records, 1800-2000
Indexed Records: 2,509,434
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
North Carolina, Voter Registration Records, 1868-1898
Indexed Records: 15,059
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, Register of Military Volunteers, 1861-1865
Indexed Records: 12,386
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
Pennsylvania, Wayne County, Court of Common Pleas, Naturalization Records, 1799-1906
Indexed Records: 13,963
Digital Images: 0
New indexed records collection
United States
United States, Recruits for the Polish Army in France, 1917-1919
Indexed Records: 4,321
Digital Images: 0
Added indexed records to an existing collection
About FamilySearch
FamilySearch International is the largest genealogy organization in the world. FamilySearch is a nonprofit, volunteer-driven organization sponsored by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Millions of people use FamilySearch records, resources, and services to learn more about their family history. To help in this great pursuit, FamilySearch and its predecessors have been actively gathering, preserving, and sharing genealogical records worldwide for over 100 years. Patrons may access FamilySearch services and resources free online at FamilySearch.org or through over 5,000 family history centers in 129 countries, including the main Family History Library in Salt Lake City, Utah.
What Did You Find in the New Online Records?
We’ve got our fingers crossed that you are able to unearth some new genealogy gems from these new updates. If you do, please leave a comment and let us know, and then share this post with your friends.

New and Updated Genealogy Records Come in All Shapes and Sizes
New records at genealogy websites can come in all shapes and sizes. They may include new or updated indexes, digitized records, or improvements to the search function. It all adds up to new opportunities for you to find more information on your family history. Here’s the latest from some of the most popular genealogy records sites.

New at MyHeritage
Here’s the latest on new records from MyHeritage:
1801 Norway Census Index
“The 1801 census was carried out on Sunday, February 1, 1801, and is based on complete lists of individuals.
The census contains the names of farms (in rural areas), the full names of inhabitants, the familial ties between household members, their age, marital status, and occupation.
For married and previously married people, it was recorded how many times they had been married or widowed.
The age listed was the age on the next birthday.
The names of smallholdings are typically not included. People were registered in the regions where they belonged. Those who were absent, e.g. sailors, should be listed in their hometowns.
The department of statistics of the Exchequer in Copenhagen prepared the census and processed its results. In the rural districts, the census was carried out by parsons with the assistance of precentors and school teachers. In the towns the efforts were supervised by the Town Administration and carried out by the Subdivision Heads of each conscription district. The town lists are arranged by building numbers. This collection is provided through cooperation with the National Archives of Norway.”

1865 Norway Census Index
“This collection of over 1.68 million records is the first national census to list a place of birth for all persons recorded. This census contains the person’s name, residence, status in the family, occupation, sex, marital status, age, place of birth, religion if not a member of the state church, and other miscellaneous information.
Censuses have been taken by the Norwegian government and by ecclesiastical officials for population studies and taxation purposes.
Census and census-like records are found from the 1500s to 2000. After 1900, a national census was taken every 10 years until 2000. Access to the national census records is restricted for a period of 100 years after the date of enumeration.
Generally, you will find more detailed family information in more recent censuses.
Some known deficiencies in the 1865 original census material include records from Gol parish in Buskerud county, Holtålen Parish in Sør-Trøndelag county, Bjerke parish in the Nannestad dioceses in Akershus county, and at least 106 special lists in Kristiania (Old name for Oslo). This collection is provided through cooperation with the National Archives of Norway.”
United Kingdom, War Memorials, 1914–1949 Index
“This free collection of 1.1 million records provides details on soldiers from the United Kingdom that died during the wars in the early to mid 20th century.
During the first World War, alone, there was an average of over 450 British casualties per day. Information listed on these records may include: name, date of death or burial, burial place, and age at death. These records might also include rank, service and unit of the military as well as any honors earned during service.
The records primarily consist of soldiers from the First and Second World Wars with a few records from different wars. The number of British casualties was smaller in wars following World War II, and the number of records from other conflicts is consequently low.
This collection content is copyright of the Imperial War Museums and the index is provided by MyHeritage free of charge as a beneficial service to the genealogy community.”
Estonia, Gravestones, 1812–2019 Index
“This collection includes information from Estonia cemeteries and consists of records from 1812-2019. These include the name of the deceased, birth date when available, death date when available, date of burial when available, and the name of the cemetery.
Cemeteries can help you trace the burial and or death place of an Estonian relative. Cemetery records may also help identify ancestors when access to church records and census records is limited, or the death was not recorded in other records.”
North Carolina, Mecklenburg County Birth Index, 1913–2019 Index
“This collection is an index of birth records from Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. The records may contain the first name, middle name, last name, gender, and date of birth of the individual. Mecklenburg County is the largest county in North Carolina by population, and its county seat is Charlotte.”
North Carolina, Mecklenburg County Marriage Index, 1884–2019 Index
“This free collection is an index of marriage records from Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. The records may contain the following searchable information: first name, middle name, and last name of the bride and groom, and the marriage date of the couple. Records may also contain the marriage license number and the date of the application.
Mecklenburg County is the largest county in North Carolina by population, and its county seat is Charlotte.
Most records in this collection are from the 20th century or later, with just three percent from before the year 1900. However, there is a select amount of records dated from before 1884, with approximately one percent of the collection falling under this category.”
North Carolina, Mecklenburg County Death Index, 1916–2019 Index
“This free collection is an index of death records from Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. The records may contain the following searchable information: first name, middle name, last name, gender, and death date of the individual. Records may also contain the certificate number for the death. Mecklenburg County is the largest county in North Carolina by population, and its county seat is Charlotte.
In some cases, the gender is given as unknown along with a missing given name. This usually means the record is for a still-born baby. All records in this collection are from the 20th century or later. However, there is a select amount of records dated before 1916, with the earliest from 1908.”
Pennsylvania, Lawrence County Index of Obituaries, 1871–2016 Index
“This collection includes an index of obituaries and death records from Lawrence County Pennsylvania for the years 1871-2016. A record may include the first and last name of the deceased, death date, date of death announcement, name of spouse, name of parent(s), and the name of the newspaper that published the information.
Obituaries can be a good source of information about a person and may also include information about the deceased’s family members. Often an obituary will include information such as the birth date, marriage date, children, occupation, education, and the location of living family members at the time the obituary was written.”
Pennsylvania, Lawrence County Index of Marriage Announcement, 1858–2006 Index
“This collection includes marriage announcements from Lawrence County, Pennsylvania for the years 1858-2006. Records may include the first and last name of the bride and groom, the names of parent(s), the title of the newspaper that published the announcement, the page on which the announcement is located, the date of the marriage announcement, and the year of the marriage.
Marriage records are a valuable source of information. Marriage records found in newspapers are not limited to a specific form, like most government marriage records, therefore newspapers may contain details about a marriage not found elsewhere, such as names of siblings or other relatives.
Newspapers can report marriages of people who no longer live in the area but who still have friends or family there.”
Chile, Electoral Rolls, 2013 Index
“This collection of over 12 million records contains information about Chilean voters during the November 17, 2013 elections. Records include the names of voters and the location of the vote. The collection also includes records about canceled voters, mostly because of the death of the voter, and disqualified voters.
Search these collections at MyHeritage here.
All of the above newly updated collections are now available through MyHeritage SuperSearch™. Searching these records is free, but a Data or Complete subscription is required to view the records, save them to your family tree, and access Record Matches. Our Record Matching technology will get to work and notify you automatically if any of these records mention a member of your family tree. You’ll then have the ability to review the record and decide if you’d like to add the new information to your family tree.”
New Newspaper Content at GenealogyBank
GenealogyBank is one of the leading providers of digitized newspapers, and they’ve recently added new content for 152 newspaper titles from across 35 states including:
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Texas
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
Here’s a short video about another historic newspaper resource (click for sound):
More New Newspaper Content at the British Newspaper Archive
One of my favorite websites, the British Newspaper Archive celebrated its 8th birthday this week (the Archive was launched on 29th November 2011) and also reached the milestone of 35 million searchable pages. Here’s ta brief overview of the 128,362 new pages recently added.
New title added:
- Sporting Gazette
Updated:
- Elgin Courant, and Morayshire Advertiser (Scotland, 1863-1905)
- The Reading Evening Post
- Wells Journal and the Bristol Times and Mirror (West country area)
Search or start a free trial here.
New at Ancestry
Here’s the latest from Ancestry:
Finland, Pre-Confirmation Books, 1670-1918
Pre-Confirmation Books
“Pre-Confirmation books, otherwise known as Childrens’ Books, were used to record the names of children who had not yet been confirmed into the Lutheran church. These records are extremely valuable as they record family groups and provide dates of birth and sometimes a place of birth as well. Death dates may also occasionally be included. Once the child became eligible for Communion, they were then recorded in the Communion books.
Pre-Confirmation books were organised by villages and then by farm and household.
This Collection
Users may find the following details for individuals found in the communion books (where available):
- Name
- Gender
- Relation to Head
- Birth Date
- Birth Place
- Burial Date
- Death Date
- Residence”
UPDATED: U.S., Social Security Death Index, 1935-2014
On November 14, 2019 changes were made to improve the performance of this collection, so if you’ve ever searched it and not found what you were looking for, it might be worth another try. Note: no new records were added.
Washington, Marriage Records, 1854-2013
On May 20 Ancestry added 1,388,625 new records to this collection.

Marriage Records
“This database contains both images of and indexes extracted from various records of marriages in Washington.
Marriage records can offer a wide range of details. While the indexes in this database may provide the basic facts surrounding a wedding—bride, groom, date, and place—images of marriage certificates may also include additional information such as
- addresses
- ages
- race
- birthplaces
- occupations
- marital status (single, divorced)
- whether a first marriage
- fathers’ names and birthplaces
- mothers’ names, maiden names, and birthplaces
This database does not contain an image for every document included in the index.”
U.S. WWII Draft Cards Young Men, 1940-1947
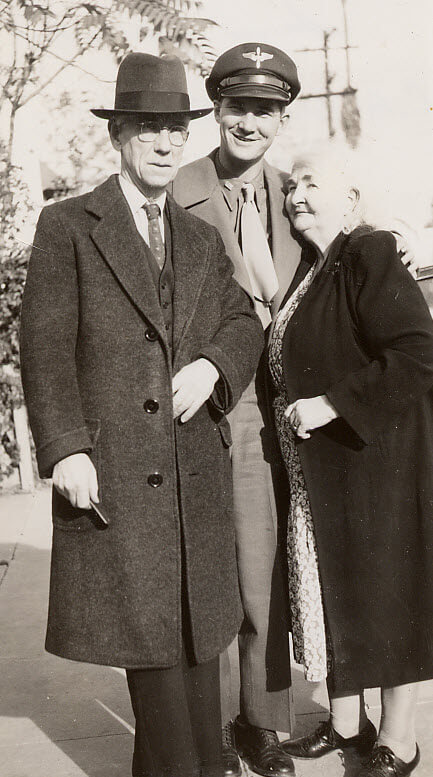

Military Records
On Nov 7 Ancestry added 4,651,830 new records from the following states to the U.S. WWII Draft Cards Young Men, 1940-1947 collection:
- New Jersey
- New York
- North Dakota
- Vermont
- Illinois
- Kentucky
- New Hampshire
Search the updated collection here.
What Did You Find in the New Online Records?
We’ve got our fingers crossed that you are able to unearth some new genealogy gems from these new updates. If you do, please leave a comment and let us know, and then share this post with your friends.

5 Steps to Digitizing Your Old Negatives
Do you have old family photo negatives in your closet? You may be wondering, “can I still get my old negatives printed into photos? What should I do with these old negatives?” To answer questions like these, we’ll need to think through your goals, budget and resources. Follow these 5 steps to digitizing old negatives and soon you may be looking at your family history in a new way!

Don’t Let Your Old Negatives Languish Like I Did
Having just gone through the process of getting my old family negatives digitized, I’m excited to share with you what I learned along the way.
In my case, I inherited photos and negatives from my paternal grandmother. I’m embarrassed to say how long they’ve been languishing in the guest room closet.
After having amazing success getting my maternal grandmother’s old home movies digitized (you can read more about that and listen to the podcast episode here), I became determined to finally address these items. It was time to see just what these negatives were and get them digitized and preserved. I couldn’t be happier that I did!
Here’s just one example of the negatives. This one is actually two photos in a medium size format. Though I’ve never seen these images before, I was pretty sure that the bottom picture was my dad and his little sister in the 1950s.
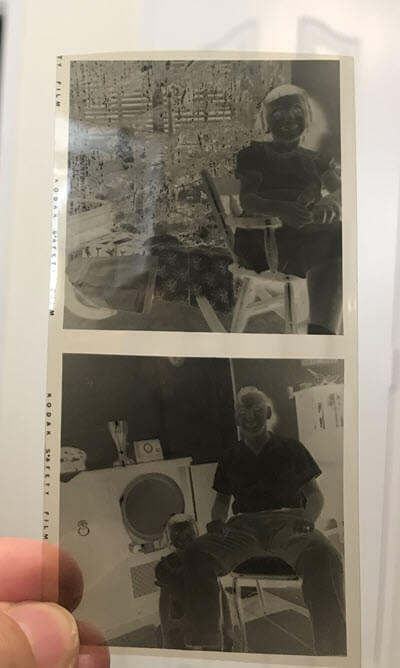

After professional scanning, I can fully enjoy this image:
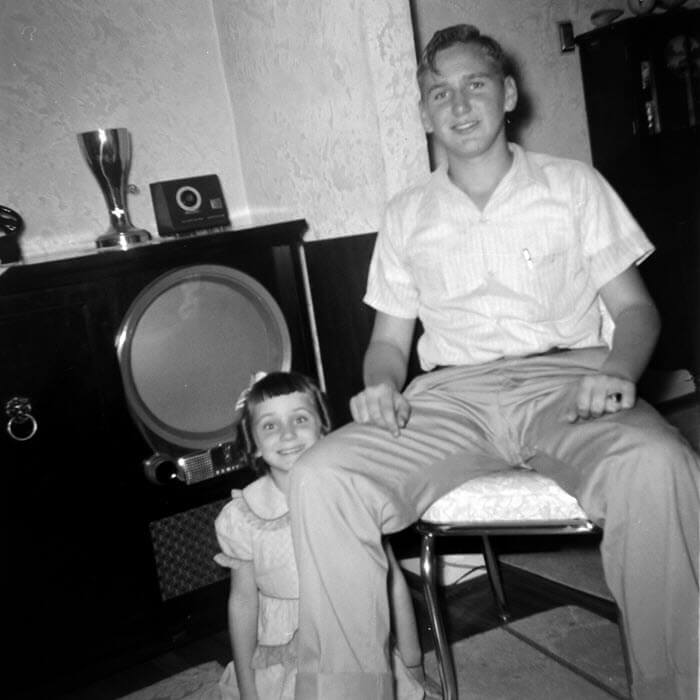

Getting these photos digitized has given me the opportunity to collect so many more family stories, like the one my Dad told me about the photo above when I emailed it to him:
“That was our FIRST TV, my mom had to have the large cabinet, I’m sure you understand that. Black and white only of course. I was about 12 years old, so that’s about 1951. First TV I ever saw was when my dad took me to his friend’s house and we watched wrestling. We got one not long after that. The first kids program I recall was Howdy Doody.”
Are you ready to finally digitize your old negatives? Here are my 5 Steps to Digitizing Your Old Negatives:
1. Consider Your Budget Before Digitizing Old Negatives
If you’re on a limited budget, you might be tempted to just do the scanning yourself with a home desktop scanner. While that may sound like a cost-effective option, it may turn out to be problematic in the long run. Here are several reasons why:
Home film scanners are an investment.
If you have an older scanner, it may not be suited to digitizing negatives. This means you’ll need to invest in a new flatbed scanner. While these days scanners like mine (the Epson Perfection V600) can scan film as well as documents, you still may not get the clarity and quality a professional service can deliver.
Scan quality can vary.
Scanning on your own puts your images at risk for being unclear. It can also be difficult to get them to a high enough resolution that they can be enlarged beyond their original size.
Negatives should be scanned between 1500-4000 dpi, with 4000 being optimum. Professional services like the one I used can reach these numbers, but it’s very important to ask exactly what the output will be when ordering. I get all my negatives digitized by Larsen Digital where I can select the desired scan size and I know I’ll consistently get the highest quality scan possible. Visit Larsen Digital here where you’ll also find their latest discounts exclusive to Genealogy Gems readers. For a limited time negatives are discounted with the coupon code: GenGem.
Digitizing negatives can be deceivingly time consuming.
Time spent carefully scanning is time not spent doing other things you love. And digitizing your negatives can only go as fast as your scanner can scan. Confirm the scanning time of any scanner you’re considering using and evaluate the quantity of negatives you have.
In my case, I have a fair number of negatives of various ages and sizes. Once they are digitized I don’t anticipate that I’ll have a need to scan more negatives in the future. Therefore buying a new scanner and dedicating desk space to it was not appealing.
Since my negatives were old family photos, I wanted to ensure that they were done right, so I opted for professional digitizing. In the end the financial investment was about the same. However professional scanning won hands down when it came to the quality of the scans and the time and space I saved. I would rather spend time researching my ancestors than scanning their negatives!
Keep reading because our next steps will help you keep your costs down while still getting your negatives professionally digitized.
2. Make Three Piles to Separate Your Negatives
Since we want to get our negatives digitized in the most cost-effective way it’s important to take a moment to identify which negatives are worth digitizing. We’re going to sort our negatives into three piles:
Pile #1: Digitize
These are the negatives you are going to send to the professional scanning service.
Pile #2: Archive
These are the negatives you want to keep, but don’t plan to digitize.
Pile #3: Throw / Give Away
These are the negatives not worth keeping. (Yes, there are some you don’t need to keep!) It certainly couldn’t hurt to send out an email blast to your family members to see if anyone is interested in keeping them. If not, toss!
As you can see, not all negatives are alike. So let’s head to step three and let’s start sorting in a discerning way.
3. Determine if You Already Have Photographic Prints of Your Negatives
Since digitizing photographs is generally less expensive than digitizing negatives, you will want to check to see if you already have a photo printed from the negative. This means it’s time to take a closer look at your negatives.
Here are just a few easy and low-cost options for viewing your negatives:
Do it the old-fashioned way.
Hold the negative up to a lamp.
Use your phone or tablet.
Here are two simple options:
1) Turn on your phone’s flashlight feature and then turn your phone around to face you and hold the negative in front of it.
2) Use a free app to turn your phone’s screen into a light box.
I downloaded the free Screen Light to my iPhone which is also available on Android. Open the app and adjust the setting to maximum “White” and “Light.” You can then hold your negative in front of it or even lay it on the screen.
I reviewed my pile which included negatives from my own family as well as the ones my grandmother gave me. I knew I had prints of all the color negative strips of the family I raised. In fact, in many cases I had double prints! (Remember the days of the double print developing?)
In the case of the negatives I inherited from my grandmother, I wasn’t so sure that I had photos of everything. The photos were probably printed when the negatives were developed, but I didn’t necessarily inherit all of the photos.
I carefully combed through my collection, making sure that I didn’t lose the context of the order in which they came to me. I knew there was a good chance that they may have been at least somewhat in chronological order. That can be valuable information when it comes time for labeling the digitized files.
Consider purchasing some acid-free negative sleeves or envelopes like these so that you not only have a place to safely store them but you can also make notes about important details you notice and whether or not you have prints, etc. (Disclosure: We include affiliate links in our posts for the products we suggest. The compensation we receive if you make a purchase helps support articles like this one and the free Genealogy Gems Podcast. Thank you!)
In the end you will have a pile of negatives that you do have prints of, and a pile that you do not.
4. Select the Best Negatives and Photos to be Scanned
Now that you have reviewed your negatives, let’s make decisions about which negatives and photos will be scanned.
If you do have a photograph of the negative:
Determine if the photo is in better condition than the negative for digitizing. Again, photos are usually less expensive to digitize than negatives.
Typically, the negative will be in better condition, however over the years they may have been smudged or scratched, so a careful review is worth the effort.
If the photo happens to be in better condition than the negative, your next decision will be what to do with the negative that you will not be digitizing.
If the negative is in good condition and is an image of particular importance to you, put it in the Archive pile.
If the negative is not in good condition, and therefore not likely to ever need to be reprinted from the negative again, drop it in the Throw /Give Away pile. I know it’s hard to do, but the storage space you save can be used for other more important things.
If the photo has some flaws and the negative is in better condition, put the negative in the Digitize pile. You may still want to keep the photo for an album or display, but your digitized image will be created from the better quality negative.
If the printed photo is the item in better shape, but it still has some flaws, don’t fret. These days you can dramatically and easily improve the digitized scan of the photo with the free Adobe Fix app on your phone or tablet. Click the play button on the video player below to watch my short demonstration video:
Learn more about photo restoration on mobile devices in my book Mobile Genealogy available in the Genealogy Gems store.
5. Send Your Old Negatives in for Professional Scanning
Now that you have organized a pile of negatives ready for digitization, it’s time to send them out to a professional scanning company.
I sent mine to Larsen Digital. I’ve met them in person and have been impressed with the quality of their work, and the incredibly wide variety of digitization work they can do.
Visit the Larsen Digital website here. This page has special discounts specifically for Genealogy Gems readers. Click on Negatives and you’ll find many options. I was thrilled to see that they could accommodate the variety of negatives I have like:
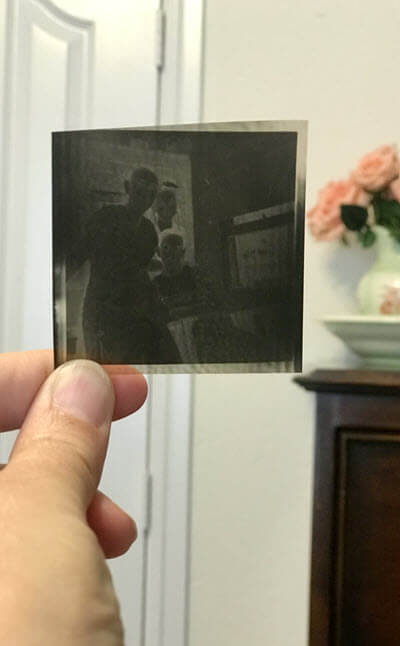

Medium format black and white negative
You may be a little nervous about mailing your negatives. At first, I was too, but the Larsen staff assured me that their customers safely and routinely mail their negatives. The key is to use a shipping service with tracking. I picked up a small priority box at my local post office. It gave me a little room for a little extra padding inside and I received a tracking number so that I could follow it on the journey. FedEx is another reliable way to go. Larsen was excellent about tracking the incoming and outgoing order.
When the order is complete, you will first receive a link where you can instantly download your digital files. Soon after your original negatives will arrive in the mail exactly as you sent them. Mine even came back in my grandmother’s original envelopes!

Digitized old negatives returned in their original envelope safe and sound!
The Results that Open Up a World of Family History
Needless to say, I am thrilled with the results of my digitization project! Many of the negatives are photos I have never seen before. (What in the world took me so long to get this done?!)
I just have to share a few examples with you. Here’s a photo of my great uncle proudly posing with his taxi cab in Ada, Oklahoma:
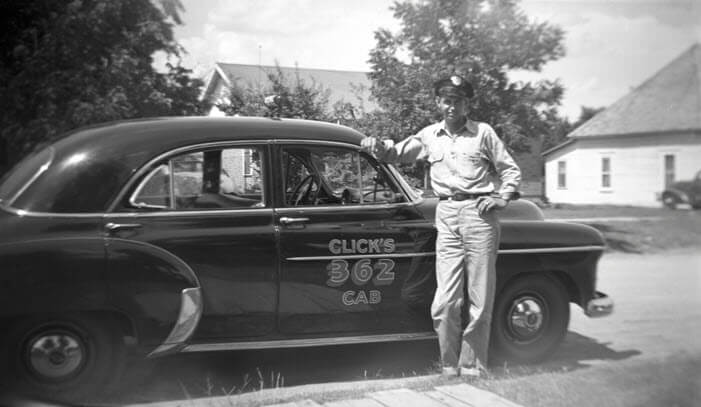

My great uncle next to his taxi cab in Oklahoma
My grandmother was an avid doll collector, so I wasn’t surprised to see my aunt in this photo with dolls. I was surprised and delighted though to spot an important artifact on the wall that held a significance to my grandparents. The framed photo of a ship commemorates one of the many ships produced at the Kaiser shipyards during World War II. Both of my grandparents worked there during the war: my grandfather helped build the ships, and my grandmother worked in in the office assisting with hiring the men and women who worked alongside him.
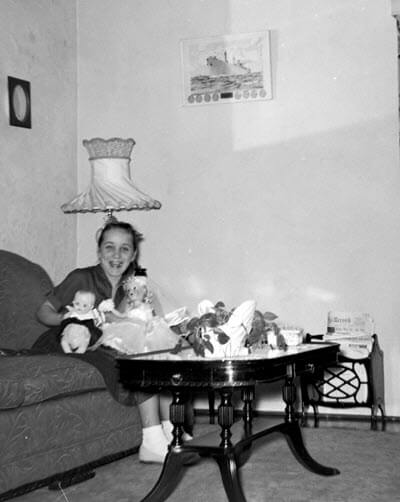
My aunt at home in the 1950s.
Although this next one has some blurring around the edges due to the person who took the photo, I treasure this rare shot of my great grandmother, my grandmother and her siblings.

The Herring Family: My great grandmother is on the far left, and my grandmother is next to and just behind her.
A New View of Your Family History
Following these 5 steps for digitizing your old negatives will not only lead to new views of your family history, but ensure that your family history photos are preserved for generations to come.
If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends. I can’t wait to hear in the Comments below the discoveries you make in your closets!





