Blog


How to Find and Browse Unindexed Records at Ancestry – The Better Browsing Checklist
Browse-only collections at Ancestry and other genealogy websites are sometimes viewed as inaccessible, but they are actually a hidden treasure. Learn how to access these browse-only collections at Ancestry and expand your family history research.

In the past we’ve written about how to access browse-only content at FamilySearch.org. Many readers said it opened a whole new world of genealogy records to them that they didn’t know they were missing.
The good news is that FamilySearch is not alone in offering browse-only content. Ancestry.com also has browse-only collections of digitized records. (Not an Ancestry.com subscriber yet? Click here to learn more. This is an affiliate link and we are compensated if you make a purchase, which supports this free blog. Thank you!)
Knowing how to search and browse records effectively is critical because you shouldn’t just rely on hints. Ancestry, for example, only provides hints from about the top 10% of their most popular databases. That means if you only spend time on reviewing hints, you’re missing a massive amount of genealogical information available in all of the other records.
Typically you’ll be using the search feature to find those other records. However not all records are searchable. That’s because after the long process of acquiring the rights to digitize and publish a genealogy record collection, it takes even longer to get them indexed for a variety of reasons. Thankfully, Ancestry doesn’t always make us wait to gain access to them until the indexing is complete.
The digital images are published without an index. This means they are not searchable by names and other keywords. Therefore, it can take some time to locate a record within one of these collections. But I think you’ll agree it’s more convenient to look through them from the comfort of your own home rather than renting microfilm or traveling to a far off location!
Here’s your checklist for better browsing.
HOW TO FIND BROWSE-ONLY RECORDS AT ANCESTRY
While Ancestry.com doesn’t make it quite as easy as FamilySearch to find browse-only or partially-indexed databases, it’s still very much worth the effort.
1. Head to the Card Catalog
From the main menu on the Ancestry website, select Search > Card Catalog.
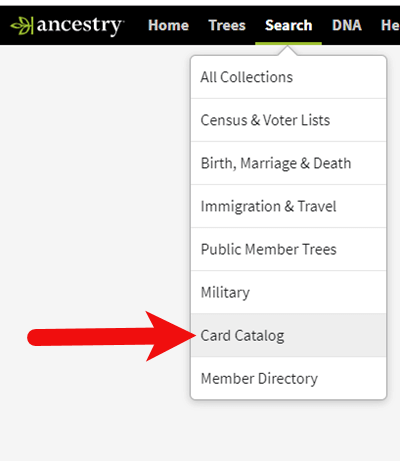
2. Search and Filter
In the upper left corner you can search the catalog by title and / or keyword. However, if you know the type of record you are looking for, such as military records, the best place to start is filtering by that category. If the list is long, you can then search within that category by keywords.
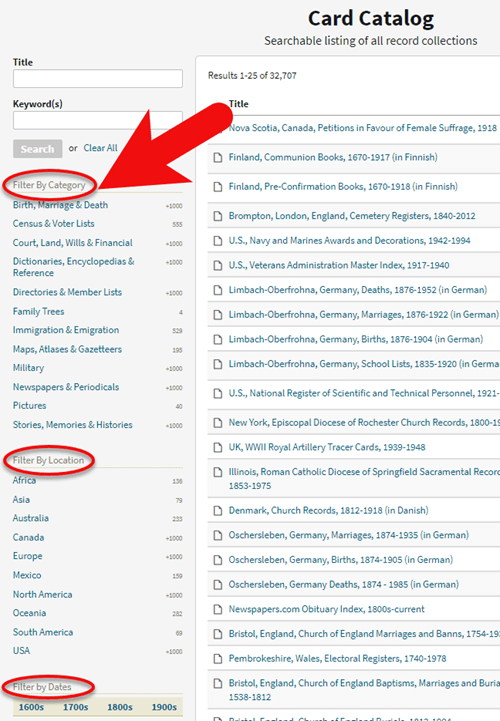
3. Determining if the Records are Searchable
If you don’t see a search box on the left side, then you can assume that this collection has not yet been indexed and therefore isn’t searchable by keywords and other data. Instead you will see typically see the source information box at the top.
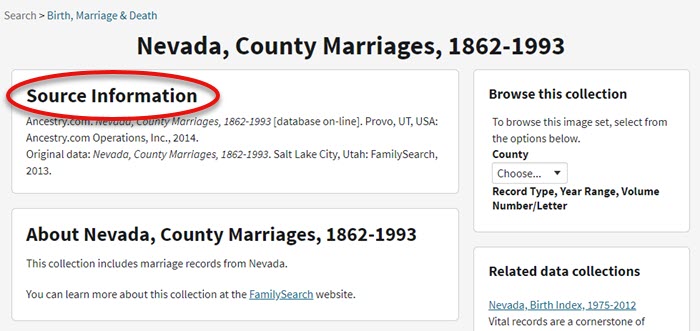
HOW TO FILTER BROWSE-ONLY GENEALOGY RECORDS
1. Browse This Collection Box
On the right side of the screen you will see a Browse this Collection box. The filtering options presented will depend on the way the collection is organized.
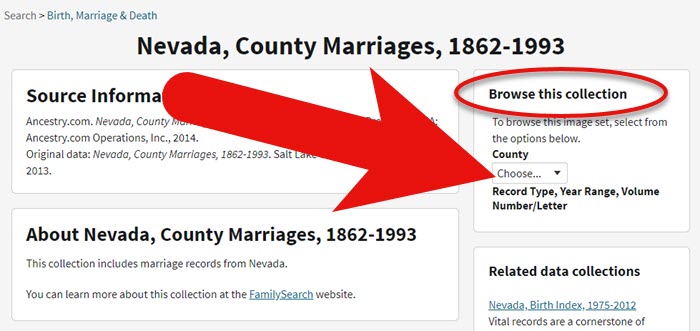
In the case of the Nevada County Marriage database, a drop down menu allows you to filter by county.
2. Make a Selection
As you can see in my example, once I selected a county I can also filter down by record books. So even though you can’t search names, you can often zero in on the portion of the collection most relevant to your search.

Browse this Collection box
HOW TO BROWSE RECORDS AT ANCESTRY.COM
Once you have selected the available filters, you’ll find yourself in the digitized records. They are displayed in a filmstrip layout which will come in quite handy for navigation through the pages.
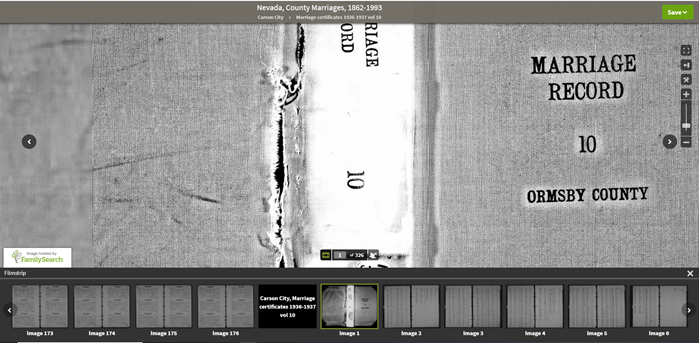
Navigation is crucial since we can’s search by names and keywords. Let’s take a closer look at the ways you can navigate:
Browsing a digitized genealogy record collection at Ancestry.com
Finding the Filmstrip
if you don’t see the filmstrip view, click the filmstrip icon:

Finding and Using the Original Index
WATCH THE BONUS VIDEO below to see the next section in action. Click on the sound button to the right of the play button to turn on the sound.
Many records that were originally bound in books like this collection include index pages. In this book the index appears at the beginning. If you look closely at the filmstrip images it’s easy to spot where the index lists are and where the records begin.

So even though Ancestry hasn’t had the chance to index the records yet, they are indexed in the book. This will make the job of browsing for the records you need even easier.
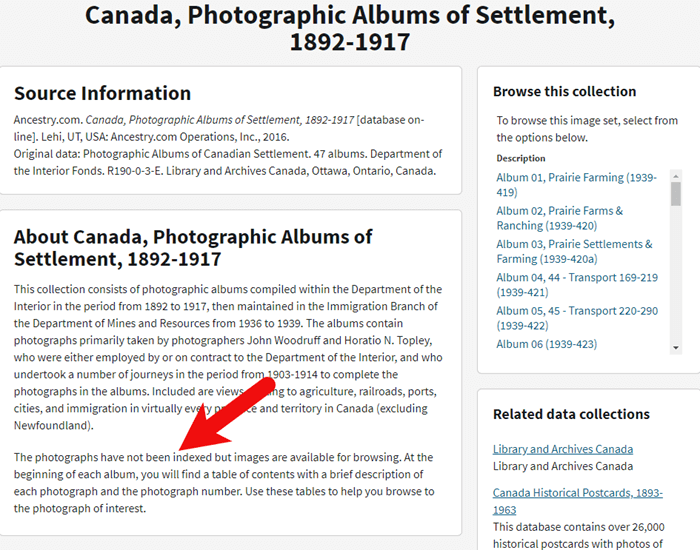
The “About” box on the card catalog entry often includes important information about whether or not the collection has an index. One example of this is the Canada, Photographic Albums of Settlement, 1892-1917 record collection. It is a browse-only series of digitized photo albums by Canada’s Department of the Interior between 1892 and 1917. The collection description includes very useful instructions such as: “At the beginning of each album, you will find a table of contents with a brief description of each photograph and the photograph number. Use these tables to help you browse to the photograph of interest.” As you can see, taking a few extra moments to read about the collection can make browsing it much easier.
Save Time When Browsing Between Volumes
Remember that Browse this Collection box on the right hand side of the card catalog entry page? (See the Browse this Collection box image 6 images above.) This handy menu is also embedded in the record viewer. If you need to switch to a different book, album or other portion of the collection, you don’t have to hit the back button and start over. Instead, at the top of the viewing page, click the volume or collection you are currently viewing (this appears as a sub-title under the main title of the collection.) A browse structure menu will appear showing you all the other options within the collection. Just click the one you want and you will be instantly switched over. Think of it as pulling a different volume of a series of books off the shelf!
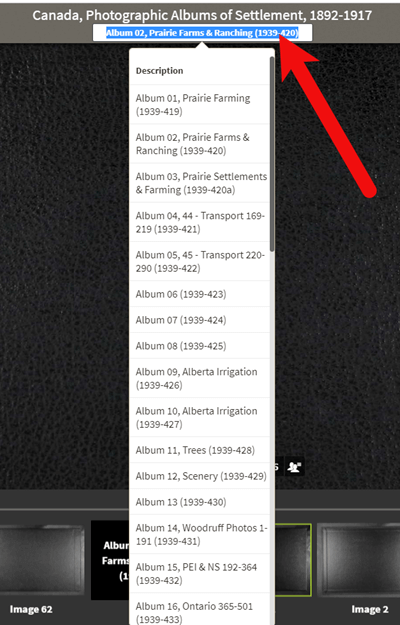
Switching volumes within the collection within the viewer.
Browsing Indexed Records
There will be times when even though a record collection is indexed, you may still want to browse it. Browsing isn’t just for unindexed records. Many genealogy gems can be found by browsing a database that you’ve already searched. You may spot neighbors of interest, other surnames from your family tree, and more. So even when you are working with a record collection that has a search box, look for the browsing option in the right column.
HOW TO FIND THE NEWEST RECORDS AT ANCESTRY.COM
The records most likely to not yet be indexed, and therefore browse-only, are the newest records added to Ancestry. If you’re looking to bust through a brick wall, here’s a great way to find the newest records that just might do it.
1. Go to the Card Catalog
From the main menu on the Ancestry website, select Search > Card Catalog.
2. Sort the Records
In the right hand corner you’ll find a Sort By menu. Select Date Added.
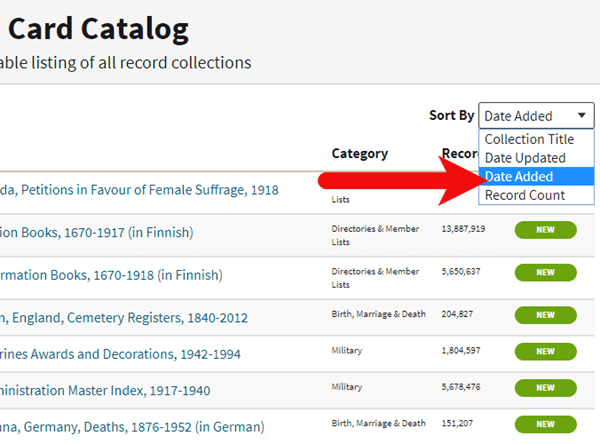
Select Date Added from the Sort by menu.
3. Newest Record View
The Card Catalog will now be presented in the order in which the records were added. The newest records will appear at the top of the list.
4. Filter the List
Use the filters along the left side of the page to filter the collections by record type, location, and date. Then use the search boxes to target keywords. This will give you results that include your keyword starting with the newest collections.
BONUS PDF AND MORE RESOURCES
Making a small investment of time in getting to know the search and browsing functions of a website can pay off big.
BONUS PDF: Click to download a handy ad-free PDF version of this article for easy reference: How to Find and Browse Unindexed Records at Ancestry
Here are three more articles and podcast episodes here at Genealogy Gems that can help you maximize your genealogy research efforts:
- Searching Browse-Only Records at FamilySearch.org
- 4 Tips for Getting the Most from Ancestry.com
- Using Ancestry Library Edition and Other Genealogy Databases at Your Public Library (in Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast episode 125 (Premium Membership required to listen)
WHAT DID YOU UNCOVER USING THESE BROWSING STRATEGIES?
Please leave a comment below and share the genealogy gems that you uncover using these techniques. And of course if you have any questions, leave those as comments as well and I’ll reply.

Genealogy Gems Podcast Episode 235
Federal court records are wonderful because they are so packed with genealogical information. But knowing which records are available and where to find them can sound daunting, and that stops many genealogists from ever tapping into them. In this episode our aim is to fix all that. Professional forensic genealogist Michael Strauss is here to pull back the curtain and introduce you to these valuable records.
You know Michael from our Military Minutes segments here on Genealogy Gems. He also recently introduced us to descendancy research on Genealogy Gems Premium Podcast episode 174. The response to that episode was terrific. Many of you wrote in to say that it opened up a new avenue of research for you. This episode promises to do the same.
Podcast host: Lisa Louise Cooke
November 2019
Download the episode mp3
GEM: Federal Court Records with Michael Strauss
Where are Federal Records Found?
Federal Court Records are initially held in the custody of the national federal courthouses where the events occurred.
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) was founded in 1934.
National Archives, Washington DC (Archives1)
700 Pennsylvania Avenue, NW
Washington, DC 20408-0001
Toll-free: 1-866-272-6272
Email: archives1reference@nara.gov
Regional Archives – about a dozen across the country – hold record geographically by area. View the locations here at the National Archives website.
Are all the records catalogued on the National Archives website?
- Master federal indexes are not yet online. Indexes are found at the location/level where these record files were created.
- Each of the federal courts are found in record groups (RG).
- Get the finding aid for the record group online at the National Archives website. That will point in the right direction as to where to get the indices.
- Resource: Finding Aids at the National Archives
Types of Federal Courts:
The Federal Court System of the United States was established under the Judiciary Act of 1789 (1 Stat. 76) on September 24, 1789. Click here to read more about the role and structure of the federal courts at the United States Courts website.
District Courts:
Trial Courts of the United States. Their jurisdiction include:
- Admiralty
- Equity
- Bankruptcy
- and Naturalization
These courts began at different times dependent on the geographic area and when the states were created.
Circuit Courts:
Originally established in 1789 as three courts and later expanded to nine courts by 1866. Circuit Courts have jurisdiction over all matters (especially criminal) covered by Federal Law. Abolished in 1911 and taken over by District Courts.
Circuit Courts of Appeals:
Established under the Federal Court System by an Act of Congress on March 3, 1891 (26 Stat. 826), by acquiring the appellate jurisdiction of the U.S. Circuit Courts and later the U.S. District Courts. They have different geographic jurisdictions than the regular federal courts.
Supreme Court:
It is recognized as the highest court in the United States operating as an appeals court. Although a criminal case may have first been heard at the local level, it may have escalated to a federal court. Therefore, there could be federal records on that case.
Application for the Genealogist:
Michael has found that some of the richest records in the federal court system have come from the criminal court records. Our ancestors did get into trouble upon occasion. Michael’s grandfather was arrested in the 1940s and he was able to obtain those records.
Searching for Federal Records
Is it worthwhile to head to the National Archives and generally search to see if an ancestor has records? Or is it best to identify a case first, perhaps through a newspaper article, and then go to the National Archives location that would have the records for those identified cases?
No one is wasting their time going and searching the records. It’s a great way to get familiar with them. However, identifying a case through other records first can lead you quickly to the federal records. (Michael first found his grandfather’s case in a newspaper article.)
Types of Federal Court Records:
Dockets: Lists of cases heard by the court. Sometime referred to as court calendars.
Minutes:
Brief daily accounts of all actions taken by the court.
Orders:
The specific judgments or orders of the court. An example would be an order granting citizenship.
Briefs:
Legal document arguing why one Party should prevail on a case.
Mandates:
When a Defendant obligates themselves to engage in activities in exchange for suspension of sentence. Frequently seen in Criminal Court.
Case Files:
All the loose documents relating to the case bundled together.
How to Find Records at the Archives:
- Review the finding aid
- Request the Index and find the name and corresponding file information
- Request the record
An appointment is not required. They will pull the records as you request them. Record groups are pulled at different times. For the most part you will have the opportunity to view the original documents.
Record Groups:
The National Archives is set up by record groups, such as:
Records of the U.S. District Court – RG 21
Records of the U.S. Supreme Court – RG 267
Records of the U.S. Court of Appeals – RG 276
Records of the U.S. Court of Claims – RG 123 (Claims against the US. Individual citizens could actually file claims against the US)
Request the individual record groups separately.
Bankruptcy:
Bankruptcy Acts were passed by Congress usually after business disturbances or financial recessions.
Bankruptcy Act of 1800
This act followed the business disturbances of 1797.
The first national bankruptcy act was approved on April 4, 1800 (2 Stat, 19.) It provided for an effective period beginning June 2, 1800 and continuing for 5 years.
It applied only to merchants or other related parties. The act provided for compulsory or involuntary bankruptcy, but not for voluntary bankruptcy. Because of its limited applicability the act was repealed on December 19, 1803, just months before its expiration date.
Bankruptcy Act of 1841
This act followed the business panic of 1837.
The second national bankruptcy act was passed on August 19, 1841 and was to take effect on February 1, 1842.
The law allowed voluntary bankruptcy to all debtors, but limited involuntary bankruptcy to merchants, bankers, factors (an agent or commissioned merchant), brokers, and traders.
It eliminated the requirement of the consent of the creditor for a discharge. The bankrupt filer, however, could obtain his discharge through a jury trial if the jury found that he had surrendered all his property and had fully complied with the orders of the court.
Bankruptcy Act of 1867
This act followed the post-Civil War recession of 1866-1867.
On March 2, 1867, Congress approved the Nation’s third bankruptcy act to assist the judges in the administration of the law, the act provided for the appointment by the court of registers in bankruptcy.
The registers were authorized to make adjudications of bankruptcy, to hold and preside at meetings of creditors, to take proofs of debts, to make computations of dividends, and otherwise to dispatch the administrative business of the court in bankruptcy matters when there was no opposing interest.
In cases where opposition to an adjudication or a discharge arose, the controversy was to be submitted to the court.
Bankruptcy Act of 1898
This act followed the business panic of 1893 and the depression that followed. We are currently under the umbrella of this fourth act.
In 1889 The National Convention of Representatives of Commercial Bodies was formed to lobby for bankruptcy legislation. The president of the Convention, Jay L. Torrey, drafted a new Bankruptcy Bill otherwise known as the “Torrey Bill.”
In 1898 Congress passed a bankruptcy bill based on the previous Torrey bill. This Act also called the “Nelson Act” was passed July 1, 1898, (Ch. 541, 30 Stat. 544.) It was the first United States Act of Congress involving Bankruptcy that gave companies an option of being protected from creditors. Previous attempts at bankruptcy law had lasted at most a few years. Its popular name is a homage to the role of Senator Knute Nelson of Minnesota.
Bankruptcy files are in the custody of the National Archives and now stored offsite at the National Archives branch in Kansas City, MO. Researchers should contact the Archives directly to conduct searches. Some indexes are still maintained at the regional archives.
Bankruptcy Records Examples
1) Two pages from the Bankruptcy File of Percival L. Strauss of Bethel Twp. Berks Co. PA. 1 Page is the petition and the second page is a page from “Schedule A” which lists the debt owed by the bankrupt.

Petition by Debtor: Percival L. Strauss

Schedule A – No. 3: Creditors Whose Claims are Unsecured (Percival L. Strauss)
2) Tintype of Percival L. Strauss-circa 1872 within a few years of filing Bankruptcy.

Percival L. Strauss. (Courtesy of Michael’s cousin Harry B. Strauss of Myerstown, PA)
Biographical information:
Percival Long Strauss (Son of Benjamin Strauss & Rebecca Long)
Born: December 16, 1830-Upper Bern Township, Berks Co. PA
Died: Mohnton, Berks Co. PA
Married: April 9, 1855-Bethel Township, Berks Co. PA to Malinda Smith (12 Children)
May 18, 1867 (Page 3, Column 6), in the Berks & Schuylkill Journal newspaper the entry reads: “P.L. Strauss of Bethel Twp. Berks County, PA Class #13 License paid $10.00 to conduct store (merchant).”
This is the business he had at the time of his bankruptcy filing on May 27, 1867 in Philadelphia, PA in the Eastern District of Pennsylvania.
Types of Information Found in Bankruptcy Records:
- Lists of creditors (name, address)
- Amount of money owed (the debt)
- Specific information about the items for which the debt was incurred
- Total dollar amounts
Follow the Federal Record Trail:
Information found could lead you to additional records. For example, if your ancestor filed for bankruptcy due to debts associated with his business, you could go back to the local level to look for records such as a business license, newspaper articles, etc.
Lisa suggests searching Google Books for digitized items such as county histories, almanacs, catalogs, merchant association books, etc. Here’s an example of a bankruptcy notice found in Google Books (which is free) for Michael’s ancestor Percival L. Strauss
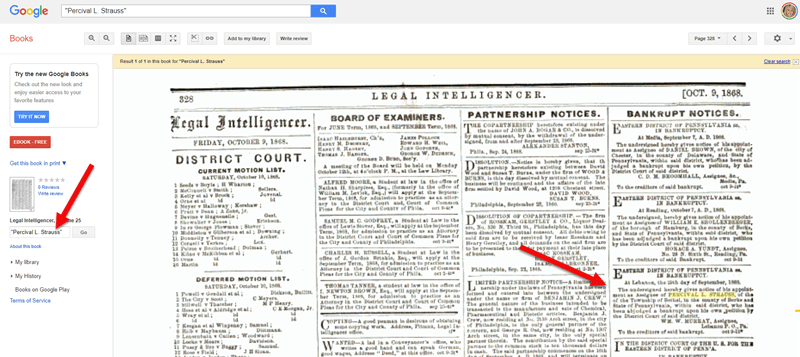
Searching for Percival L. Strauss bankruptcy notice in Google Books

Bankruptcy notice (Oct. 9, 1868) found in Google Books
The National Archives has been consolidating all of the bankruptcy records. It is going to be the Kansas City, MO branch of the National Archives, which currently has the Patent files.
Examples of bankruptcy cases:
- Bankruptcy Act of 1841 – Edgar Allen Poe filed bankruptcy in 1841.
- Bankruptcy Act of 1898 Act – Dean Martin in New York
Amendments to the most recent bankruptcy act include:
1933: The “1898 Bankruptcy Act”
Amended to include railroad reorganization, corporate reorganization, and individual debtor arrangements.
1938: The “Chandler Act”
Amended the earlier 1898 Bankruptcy Act, creating a menu of options for both business and non-business debtors. Named for Walter Chandler.
1978: The 1898 Bankruptcy Act
Replaced by The Bankruptcy Reform Act. This Act is still used today.
Writs of Habeas Corpus:
Habeas corpus is a court order from a judge instructing a person who is detaining another to bring the detainee before the court for a specific purpose.
It was often used during the Civil War for soldiers under the age of 18 years and in reference to runaway slaves.
Writs can be found in most case files. They usually involves a petition, transcript, order, and the writ when ordered by the Judge. Contact the National Archives regarding RG19 for records pertaining to this set of documents and indexes.
Fugitive Slave Act:
The Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 was passed by the United States Congress on September 18, 1850 as part of the Compromise of 1850. It was one of the controversial acts passed down by law. Runaway slaves could be returned with the help of the Federal Government.
Records can include:
- Petitions
- Affidavits
- Testimonies
- Documentation of ownership
Records are typically found in the court of original petition and the court with jurisdiction over the area where the slave escaped. Search under the slave holder’s name.
The Confiscation Act of 1862:
Passed by an act of Congress on July 17, 1862, the full title is “An Act to Suppress Insurrection, to Punish Treason and Rebellion, to Seize and Confiscate the Property of Rebels, and for Other Purposes.”
This Act gave the power to take the land and businesses of persons who served the Confederacy. Records include case files include; petitions, orders of the court, proofs of public notice, and notices of seizure
Example: General Robert E. Lee. The act covered land under Union Control. Lee lived in Northern Virginia, and his home was confiscated. The file has a complete inventory of his house. The location is now the Arlington National Cemetery.
Federal Criminal Records
Criminal records could include cases covering:
- Treason
- Assault and Battery on the high seas
- Conspiracy to over through our government
- Smuggling
- Forgery
- Counterfeiting
- Carrying on a business without a license
- Not paying taxes
Naturalization Records:
Records were created:
- at the federal level
- at the local level – local court at the county level
1790: The first national act created a two-step process:
- Declare your intention to become a citizen
- File your petition for citizenship
Your ancestors may not have finished the process, and they may have filed both at local and federal levels.

Petition for Naturaliztion
Resource: The Family History: Genealogy Made Easy Podcast
Episodes focusing on the Naturalization process include:
Episode 29: Immigration and Naturalization Records for Family History, Part 1
This episode begins a 3-part series on U.S. immigration and naturalization records. Learn about passenger arrival lists in the U.S., little-known certificates of arrival and naturalization records: how to find them and what’s in them.
Episode 30: Immigration and Naturalization Records for Family History, Part 2
In this episode we focus on passenger departure records created in European ports. He also talks more in-depth about U.S. naturalization records.
Episode 31: Immigration and Naturalization Records for Family History, Part 3
In-depth discussion of passenger list annotations and the immigrant’s experience at Ellis Island. Unlock the meaning of those mysterious scribbles on 20th-century passenger manifests!
Learn More with Michael Strauss:
Visit Michael’s Website: Genealogy Research Network
Register for Michael Strauss’ week-long Salt Lake Institute of Genealogy (SLIG) 2020 course called Court #2 A Guide to Treasures Found in Federal Records.
Hear More from Michael Strauss: Genealogy Gems Premium Membership
Gain access to the complete Premium podcast archive of over 150 episodes and more than 50 video webinars, including Lisa Louise Cooke’s newest video The Big Picture in Little Details.
More Reading:
Black, Henry Campbell. Black’s Law Dictionary. Sixth Edition. St. Paul: West Publishing, 1990.
Burton, William C. Burton’s Legal Thesaurus. New York: Macmillan Library Reference, 1998.
Chapin, Bradley. Criminal Justice in Colonial America, 1606–1660. Athens: University of Georgia Press, 1983
Eichholz, Alice ed., Red Book: American State, County, and Town Sources, 3rd Ed Provo: Ancestry, 2004.
Evans, Barbara Jean. The New A to Zax: A Comprehensive Genealogical Dictionary for Genealogists and Historians. Second Edition. Champaign: B.J. Evans, 1990
Neagles, James C. and Lila Lee Neagles. Locating Your Immigrant Ancestor: A Guide to Naturalization Records. Logan: Everton Publishers, 1986.
Rapaport, Diane. New England Court Records: A Research Guide for Genealogists and Historians. Burlington: Quill Pen Press, 2006
Rose, Christine. Courthouse Research for Family Historians. San Jose: CR Publications, 2004.
Schaefer, Christina. Guide to Naturalization Records of the United States. Baltimore: Genealogical Publishing Company, 1997.
Szucs, Loretto Dennis, and Sandra Luebking. The Archives: A Guide to the National Archives Field Branches. Salt Lake City: Ancestry Publishing, 1988.
Thank you to Michael Strauss for contributing to these notes and sharing his expertise!
This free podcast is sponsored by:
MyHeritage.com is the place to make connections with relatives overseas, particularly with those who may still live in your ancestral homeland. Visit www.MyHeritage.com
Learn German Handwriting
Katherine Schober of SK Translations, professional German script expert, translator, and author has created Reading the Old German Handwriting Online Course – so you can be reading those old German letters in just a matter of months. Complete with videos, flash cards, games, and more, this do-it-yourself course has students raving. Learn more here.
Read our latest articles at Genealogy Gems:
Dakota (AKA Kota Bear) makes Her Debut on this Episode

Please Help Us by Taking the 1 Minute Genealogy Gems Survey
Please help us create the best podcast for you by taking this very short survey.
Join Lisa Louise Cooke in person at Genealogy Roots
If you didn’t have an opportunity to attend this event in Salt Lake City in October 2019, this is your chance!
Click here for all the details and tickets.
What: 2 days of innovative genealogy education at the Senior Expo
When: January 14 & 15, 2020. 9am – 4:30pm
Where: Dixie Convention Center in beautiful St. George, Utah
Who: All ages and skills levels
Cost: 2 day pass: $50 | Early Bird Price: $35 (Expires 12/31/19)
Watch the video recap of Day 1 of Genealogy Roots in Salt Lake City:
Watch the video recap of Day 2 of Genealogy Roots in Salt Lake City:
Get the Genealogy Gems Podcast App Here
Follow Lisa and Genealogy Gems on Social Media:
- Instagram.com/genealogygemspodcast
- Facebook.com/genealogygems
- Pinterest.com/lisalouisecooke
- YouTube.com/GenealogyGems
Sign Up for the Free Genealogy Gems Newsletter
The Genealogy Gems email newsletter is the best way to stay informed about what’s available with your Premium eLearning Membership. Click below to sign up today.
Lisa Recommends Computer Backup with:
Learn more about Backblaze computer cloud backup and get your computer backed up today at www.backblaze.com/Lisa

New Genealogy Records this Week Nov. 8, 2019
It’s another big week for genealogical records. Here’s the latest including two rare opportunities for free access to subscription military records.

Ancestry® Veteran’s Day 2019 Free Access To World’s Largest US Military Records Collection
From Ancestry: Ancestry® boasts the world’s largest US military records collection. Find inspiring stories about heroic family members who served our country.
- The free access promotion ends November 17 at 11:59 PM EST.
- Visit the collection here.
- More than 260 million US military records
- More than 60% of Ancestry U.S. subscribers who have a family tree have found at least one military record for an ancestor!
- Find draft cards, enlistment records, soldier pension indexes and more
- Our U.S. military records cover all 50 states and nearly 400 years of American history
- View the full list of collections
- Anyone can help honor our veterans: Capture WWII Veteran’s Stories
My search for Sidney Mansfield retrieved at least three records:
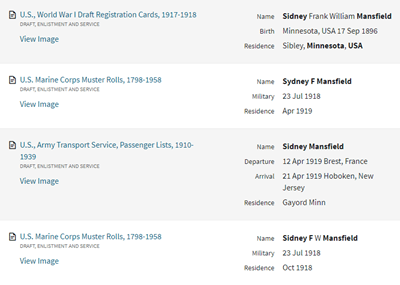
Search results for Sidney F Mansfield of Minnesota
While I had found some of these before, this records from the U.S., Army Transport Service, Passenger Lists, 1910-1939 collection was a pleasant surprise, although reading it brings to light an unpleasant time for Sidney:
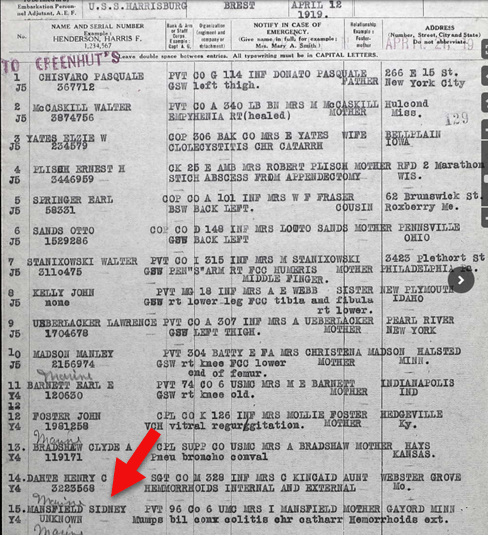
Record of Sidney F. Mansfield
Findmypast Granted Free Access to International Records Ahead of Veterans day 2019
The free access promotion ended at 12 pm GMT on Monday, November 11th
Findmypast includes more than 85 million military records covering the Armed Forces of the United States, Canada, Great Britain, Australia, New Zealand and Ireland. Researches can search for their ancestors in a variety of fascinating documents ranging from service records and pensions to medal rolls, POW records, casualty lists and more.
New Historical Records at MyHeritage
From the MyHeritage blog: “18.6 million new historical records have been added in October 2019 in seven new collections from all over the world, including:
- Australia,
- Spain,
- the former Soviet Union,
- Latvia,
- the United States,
- Germany,
- and Denmark.”
Here are the full details of these new record collections:
Australia Death Notices, 1860–2019
“This collection of over 7 million records contains death notices, funeral notices, and obituaries from Australia from a variety of sources. The dates of these notices primarily range from 1900–2019, with a few entries from the previous 50 years.”
Spain, Bilbao Diocese, Catholic Parish Records, 1501–1900
“This collection of over 4.9 million records consists of baptism, marriage, and death records for the Roman Catholic Diocese of Bilbao in Spain. The majority of the records correspond to the historical region of Biscay, Spain within the Basque Country, with a small minority of records from Cantabria.
Baptismal records contain the following searchable information: first name, primary surname and secondary surname of the child and parents, date, and location. For marriages: first name, primary surname and secondary surname of the bride and groom, date, and location. For death records: first name, primary surname and secondary surname of the deceased, date, and location. The parish is also listed in most records.”
Soviet Union, Soldier Memorials, 1915–1950
“The 4.5 million records in this collection provide details on soldiers from the Soviet Union who died or went missing during the wars in the early to mid-20th century.
Information listed on these records may include:
- name
- year of birth
- place of birth
- rank
- date of retirement
- place of retirement
These records might also include place of service, cause of death, and hospitalizations. Most of the information in this collection is in Russian. MyHeritage provides the ability to search this collection in one language and receive results in another using its unique Global Name Translation™ technology. The technology automatically translates given names and surnames into the language of the query. For example, a search for Alessandro (Alexander in Italian) will also find “Саша,” the Russian form of Sasha — a popular nickname for Alexander — with its corresponding translation into the language of your search.”
Latvia, Riga Internal Passport Holders Index, 1918–1940
“In the city of Riga during the interwar period, every person over the age of 15 was supposed to have an internal passport as proof of identity. This database of 890,811 records includes residents of Riga and may include the surname, given name, father’s name, date of birth, place of birth, and place of origin of the passport holder. This collection is completely free to search, view, and add to your family tree.
Many of the internal passport files contain all addresses the person lived at during the passport’s validity, including those outside of Riga.
Whenever the passport’s validity expired, the passport was to be returned to the government. It is not known how many actually returned their passport to the government, so this collection is not a complete representation of all people who lived in Riga during this period of time.”
United States Index of Gravestones, 1900–2018
“This collection includes 601,986 records from more than 25 cemeteries located in the United States.
The records include headstone inscriptions and burial records. In these records you may find information such as:
- deceased’s name
- date of birth
- date of death
- date of burial
- place of burial
Cemetery records are especially helpful for identifying ancestors who were not recorded in other records, such as children who died young or women.
Records from cemeteries in the following states can be found in this collection:
- California,
- Connecticut,
- Washington D.C.,
- Georgia,
- Illinois,
- Indiana,
- Massachusetts,
- Pennsylvania,
- Michigan,
- Ohio,
- Oregon,
- Rhode Island,
- and South Dakota.”
Germany, Emigrants from Southwestern Germany, 1736–1963
“This collection of 285,158 records is an index of emigrants leaving Southwestern Germany largely between 1736 and 1963. Records may contain the following searchable information: first and last name, birth date, date and county of emigration, and first and last name of a relative.
The following information may also be viewable:
- title
- alternate name
- former residence
- district
- address
- marital status
- religion
- occupation
- birth name
- destination
- additional information on the family of the individual.
Emigration from Germany occurred in a number of waves, triggered by current events such as the July Revolution of 1830, the 1848 March Revolution, the foundation of the German Reich in the 1870s, World War I, and other significant events. The majority of the records from this collection are from the mid 1750s to the early 1900s.”
Denmark, Copenhagen Burials, 1860–1912
“This collection of 255,733 records is an index to burial records from Copenhagen, Denmark.
Records typically list:
- the name of the deceased
- death date
- burial place.
In some cases, the deceased’s age, occupation, and cause of death may also be listed.
Burials usually took place with a few days of death. Burials in Denmark were recorded in the records of the parish where the burial occurred. Original burial records have been digitized and made searchable by the Copenhagen City Archives.”

Sample: Thorvald Nikolaj Thiele Died: Sep 26 1910 Danish astronomer and director of the Copenhagen Observatory. He was also an actuary and mathematician.
Enjoy searching all of these new collections that are now available on MyHeritage SuperSearch™. Searching these records is always free, and you can also view and save records to your family tree from the Latvia, Riga Internal Passport Holders Index for free. To access Record Matches or to view or save records from the other collections, you’ll need a Data or Complete subscription.
MyHeritage’s Record Matching technology will notify you automatically if any of these records mention a member of your family tree. You’ll then be able to review the record and decide if you’d like to add the new information to your tree. Learn more about Record Matches on MyHeritage Education.
New Digitized Collections at the Library of Congress
From the Library of Congress: “Researchers and students have gained access to seven newly digitized collections of manuscript materials from the Library of Congress, including records of one of the most important women’s suffrage organizations, the papers of President Abraham Lincoln’s personal secretary and collections on the history of federal monetary policy. The availability of these collections added more than 465,000 images to the Library’s already vast online resources.”
The new collections include:
Women’s Suffrage:
The records of the National American Woman Suffrage Association:
records from one of the most important national women’s suffrage organizations in the U.S. The collection includes more than 26,000 items, most of which were digitized from 73 microfilm reels.
Civil War:
The papers of the presidential secretary and biographer John G. Nicolay (1832–1901) consist of 5,500 items scanned from original materials. Spanning the years 1811 to 1943, the collection particularly reflects Nicolay’s tenure as private secretary to President Abraham Lincoln.
From the same era, the papers of Confederate general Jubal Anderson Early were also released online.

Massachusetts Business:
Olmsted Associates Landscape Architectural Firm – The collection documents the work of the landscape architectural firm originally founded by Frederick Law Olmsted as it was continued by his sons in Massachusetts. It includes nearly 150,000 items scanned from 532 reels of microfilm.
Federal Monetary Policy:
Three newly released collections relate to federal monetary policy:
- The Nelson W. Aldrich papers (documenting the National Monetary Commission, created in 1908)
- The Charles S. Hamlin papers (document the Federal Reserve Board during the first three decades of the 20th century.)
- The Eugene Meyer papers (document the Federal Reserve Board during the first three decades of the 20th century.)
Read the entire announcement at the Library of Congress.