Blog


Two Mysterious Deaths in the Family! Time to Use Google for Genealogy
The mysterious deaths of a father and son present a perfect opportunity for using Google for genealogy.
Recently I heard from Lydia, who has just started listening to my podcasts. She asked a great question that Google can help answer:
“I have two relatives, great-grandfather and great-great-grandfather, who died under conditions where an inquest was conducted. I wrote to the county clerk’s office in Joplin, MO. They were only able to send me the “bill” for both inquests, stating they had no other information. What I want to know, what they didn’t answer, was are they the ones to ask for the inquest report? If it still exists who would have it?”
She shared their names (both Esterline) and details about their deaths and I just couldn’t help myself: I had to Google them myself. There’s nothing like a couple of mysterious deaths–two generations in a row!–to pique my curiosity.
Here’s the path I took and take-home tips to offer anyone looking for genealogical records:
1) A Google search for: coroner’s inquest 1928  Missouri delivered the Coroner’s Inquest database at the Missouri Digital Heritage archive. From there, you discover that you can request copies of records by emailing the citation for the record you want to the Missouri State Archives at archref@sos.mo.gov. According to the instructions, “The record will be located, the number of pages counted, and you will be notified by email of the cost of the copies. Upon receipt of a check, the copies will be made and mailed to you. There may also be additional notations in the record about other locations where the files can be accessed.” Interestingly, when I searched for her two relatives, I didn’t find them, but there was a file for a woman with the same surname: Esterline. It’s worth seeing if she’s related somehow.
Missouri delivered the Coroner’s Inquest database at the Missouri Digital Heritage archive. From there, you discover that you can request copies of records by emailing the citation for the record you want to the Missouri State Archives at archref@sos.mo.gov. According to the instructions, “The record will be located, the number of pages counted, and you will be notified by email of the cost of the copies. Upon receipt of a check, the copies will be made and mailed to you. There may also be additional notations in the record about other locations where the files can be accessed.” Interestingly, when I searched for her two relatives, I didn’t find them, but there was a file for a woman with the same surname: Esterline. It’s worth seeing if she’s related somehow.
2) I was suspicious about no other Esterlines coming up in the database, so I tried a search in the Archives on Joplin and Jasper to see if other cases from that town or county come up in the results, and they don’t. Further digging reveals: “The Coroner’s Inquest Database project is ongoing; additional counties will be added to the database as completed.” However, it would be very worthwhile to contact them by email and inquire as to where this county is in the queue and where the physical files are now. Another result in that same Google search reveals which counties the Archive currently does have: includes Andrew, Cape Girardeau, Clinton, Cole, Greene, Pemiscot, Perry, St. Charles, St. Francois, St. Louis, and Stoddard (coverage varies by county).
3) After searching a single database on a website like Missouri Digital Heritage, I always look for a global search page, where I can search all databases on the site at once. Missouri Digital Heritage has one here. A search on Esterline brings up not only death certificates (which you probably already have) but city directory entries, newspapers and more.
4) I always recommend that genealogists get to know their record sources. Again, through my Google search I discovered The Laws of Missouri Relating to Inquests and Coroners (1945). This may provide some further insight. And the FamilySearch Wiki is always invaluable. Here’s the page on Missouri Vital Records and it states that “original records are available on microfilm at the Missouri State Archives.”
5) I pretty much always do a quick search specifically at Google Books since they have over 25 million books. I searched Ben Esterline and the first result was a listing in the Annual Report of the Bureau of the Mines (1932) (the year he died!): “FATAL ACCIDENTS— LEAD AND ZINC MINES Ben Esterline, prospector.” The book is not fully digitized in Google Books, but click “Libraries that have it” and you’ll be taken to the card catalog listing in WorldCat which will show you where you can obtain it.
 I’m telling you, Google is the most powerful, flexible, furthest-reaching free genealogy search engine out there—and it’s right at our fingertips! But you do need to learn how to use it effectively, or you could find yourself wading through 87,400 results for an ancestor like “Ben Esterline.” Instead, learn the strategies I teach in The Google’s Genealogist Toolbox. This second edition–new in 2015–is fully updated and loaded with techniques and examples on search strategies and tools that help you use Google for genealogy (and everything else in your life!). Click here to order your copy and you’ll start Google searching much smarter, much sooner.
I’m telling you, Google is the most powerful, flexible, furthest-reaching free genealogy search engine out there—and it’s right at our fingertips! But you do need to learn how to use it effectively, or you could find yourself wading through 87,400 results for an ancestor like “Ben Esterline.” Instead, learn the strategies I teach in The Google’s Genealogist Toolbox. This second edition–new in 2015–is fully updated and loaded with techniques and examples on search strategies and tools that help you use Google for genealogy (and everything else in your life!). Click here to order your copy and you’ll start Google searching much smarter, much sooner.
More Gems on Google for Genealogy
7 Free Search Strategies Every Genealogist Should Use
How to Make Google Cache Pay Off in Your Genealogy Research
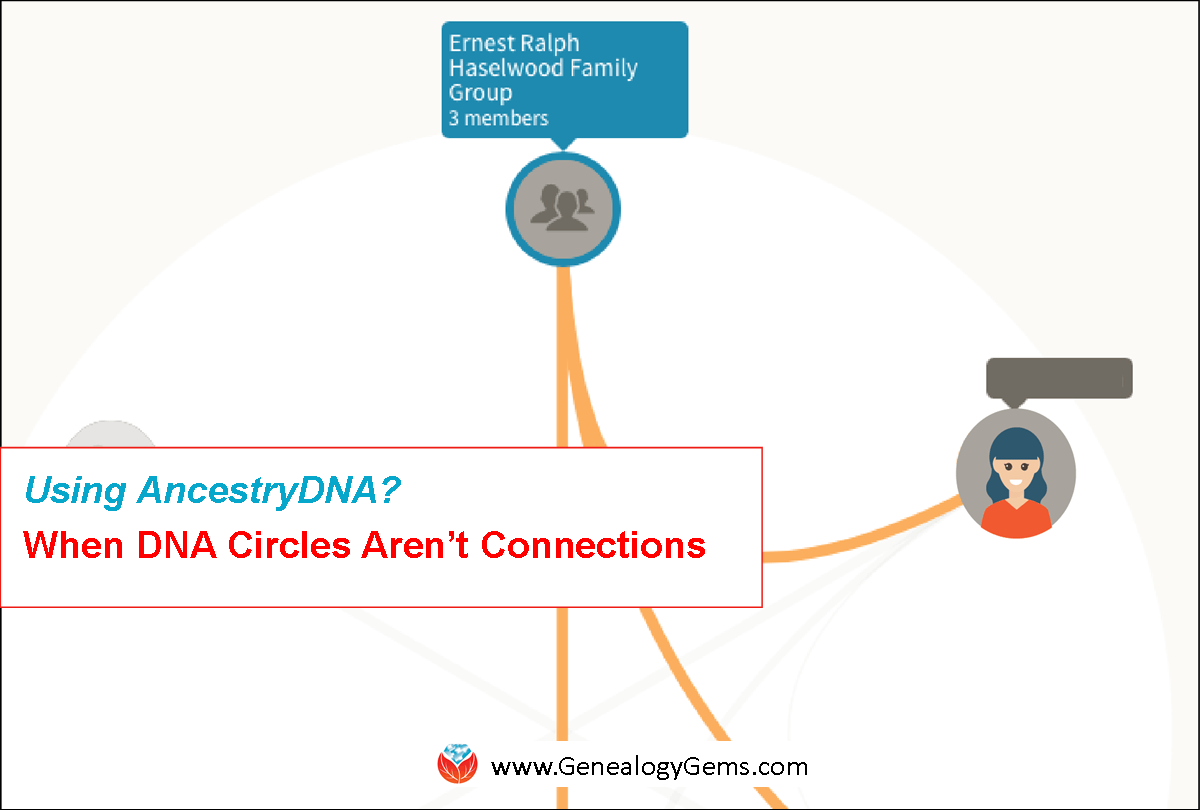
DNA Circles – Here’s when they DON’T mean connections on AncestryDNA
DNA Circles at AncestryDNA can get problematic when participants’ trees are unverified. This is why.

Adding people to a family tree without verifying the connection is a fairly common genealogical practice. This happens a lot when people “graft” information from another online tree.
In addition to the problems this can create in your tree, it can create problems when you start looking at genetic connections. We have received a few inquiries about this topic here at Genealogy Gems, and I chatted with a fellow genealogist about this at a recent conference.
The practice of copying online trees factors most heavily in the DNA Circles and New Ancestor Discoveries (NAD) at AncestryDNA. You will remember from our previous conversations that these tools are like parties that your DNA has secured your tickets to attend. Each of these parties is “hosted” by one of your ancestors, in the case of the DNA circle, and a presumed ancestor, in the case of a NAD. Sometimes we catch ourselves declaring that our membership in the DNA circle “proves” our connection to the party host.
But we must be careful. Because it does not.
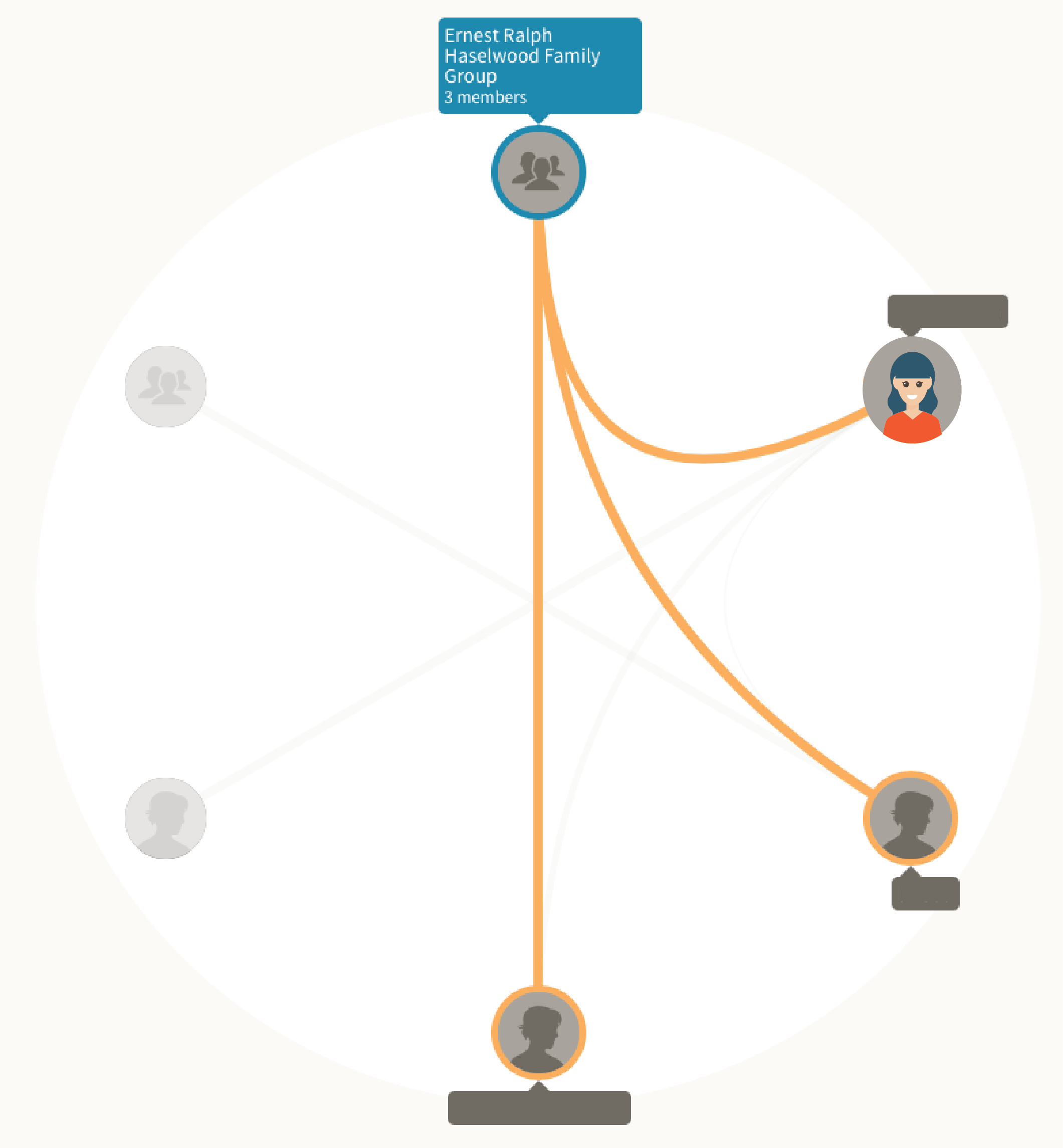 “Proves” is too strong of a word. All your membership in the DNA circle can really tell you is that you have a genetic connection to those marked with the orange line. Those with the grey connecting lines have a DNA connection to some of the circle members, but not to you. Placing the name of an ancestor on the cover of this gathering does not guarantee that the named person is your common ancestor. It is just a suggestion; a hint.
“Proves” is too strong of a word. All your membership in the DNA circle can really tell you is that you have a genetic connection to those marked with the orange line. Those with the grey connecting lines have a DNA connection to some of the circle members, but not to you. Placing the name of an ancestor on the cover of this gathering does not guarantee that the named person is your common ancestor. It is just a suggestion; a hint.
Think about this for just a second. Let’s say that Joan does a bit of research and decides that her immigrant ancestor’s father is Marcus Reese, born in 1823 in Wales. She adds this to her pedigree chart. She sees on a census record that he had four children, one of whom shared the name of her ancestor, William, and adds those to her chart as well.
Months later, Charlotte is researching her Mary Reese and sees Mary listed on Joan’s pedigree chart as the child of Marcus. She knows Mary’s father was born in Wales and adds Marcus to her pedigree chart telling herself that she will go back later and double check. And so on.
After a while, we have 7 people all connected back through Marcus and his four children, and they all independently decided to get their DNA tested through Ancestry.com.
Ancestry sees their shared DNA and that they have all listed Marcus Reese as their common ancestor. So they create a DNA circle for the seven of them, with Marcus Reese at the head.
Ancestry did not look at the number of cited sources or the myriad of other genealogical possibilities about how these seven individuals could all be related to each other. It saw a genetic connection and a genealogical hypothesis, and it presented them to you in the form of a DNA circle.
The genetic evidence supports a single common ancestor for these 7 people, but it certainly does not have to be Marcus Reese. You can become more certain as you gather the traditional genealogical evidence that you would in any other case. As your documentation mounts, so will your confidence, with the DNA acting like an invitation to keep searching for further evidence of your connection.
 If you enjoyed this post, you’ll love my series of DNA for genealogy quick guides. Each laminated guide–with quick, clear text that helps you act on what you learn–is targeted to a specific DNA topic, from “Getting Started” to the three types of DNA tests you can take to understanding your results with testing companies AncestryDNA, FamilyTreeDNA and 23andMe. Why not grab the “super bundle” of all 10 guides? You can also shop for them individually here.
If you enjoyed this post, you’ll love my series of DNA for genealogy quick guides. Each laminated guide–with quick, clear text that helps you act on what you learn–is targeted to a specific DNA topic, from “Getting Started” to the three types of DNA tests you can take to understanding your results with testing companies AncestryDNA, FamilyTreeDNA and 23andMe. Why not grab the “super bundle” of all 10 guides? You can also shop for them individually here.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
DNA for Adoption Research: “Nice to Meet You!”
 As a daughter of an adoptee, this season I am grateful I can use DNA for adoption research. Seats at my genetic holiday table are gradually filling, even if some place cards are just penciled in.
As a daughter of an adoptee, this season I am grateful I can use DNA for adoption research. Seats at my genetic holiday table are gradually filling, even if some place cards are just penciled in.
At this time of year when many of us are spending more time with family than we otherwise might, we often reflect on the empty seats at our table. We think of those who weren’t able to travel to the family gathering, and back to those who have passed on. For some, however, a long empty seat has been filled this year, thanks to the assistance of a DNA test.
Earlier this year we related the story of Mary McPherson and her cousin Dolores Washington-Fleming who discovered a common connection through Peter Edward Williams. Mary is a descendant of his wife and Dolores through his slave.
Mary and Dolores welcomed this new connection and shared information about their common ancestor. As they reunited for the first time, perhaps they talked about what life might have been like in the 1850s in the south, and how their ancestors would’ve never guessed that the two of them would be gathered around the same table.
DNA for Adoption Research
As word spreads of the power of DNA testing to reveal the secrets of the past, many adoptees are flocking to genetic genealogy testing companies with the intention of filling the empty seats at their holiday tables. The New York Times reported a touching story of Khrys Vaughan who felt her identity crumble when she found out she was adopted. Turning to DNA testing, she was able to connect with cousins and feel a biological connection she didn’t know she had been missing. Even though she still has many open seats at her table, she felt that filling even one meant that she was no longer biologically adrift, but could now look at someone and say, “This is my family.”
A similar story broke recently out of California. Just days old, Jen Chervin was found outside a hospital in Yuba City, CA. That was 40 years ago. But this year, Jen used the power of the genetic genealogy database in combination with some serious genealogy work to find her parents. While neither is in a position to openly embrace her as a daughter at this time in their lives, Jen now has a name card to place at seats of honor around her holiday table, all thanks to a simple saliva test.
This has been a landmark year in my own family. In one seeming miracle after another, I have added the names of maternal grandparents and great grandparents to my family tree as DNA testing has helped my mom fill in some of the missing pieces in her life. We have had a true Texas welcome from some of her paternal second cousins, and an outpouring of kindness from a maternal second cousin. While our place cards for mother and father are only tentatively penciled in, I know as I look around our genetic holiday table that I am excited about the new faces I see and I can’t wait to learn more.

How to Get Started Using DNA for Adoption Research
If you want to get started filling seats at your table, there is no time like the present to give yourself (or someone else) the gift of DNA testing! (Remember, before you get started, make sure you’re emotionally ready for the unexpected. You never know what “surprises” you’re going to unwrap when you start genetic testing.)
My quick reference guides will guide you through the process and act as a reference tool along the way. It will tell you that the first rule in DNA testing is to test the oldest generation. So parents, grandparents, aunts and uncles should be first on your list. If you are that oldest generation, then pat yourself on the back and get swabbing!
The savvy shopper begins with the AncestryDNA test for all interested parties, and the YDNA 37 marker test from Family Tree DNA for all males. Then sit back and wait for the results to roll in! As they do, check back here at Genealogy Gems for tips on how to use that data to fill seats at your holiday table next year.
More Inspiring Gems About DNA for Adoption Research
 A Life-Changing Find at the National Archives
A Life-Changing Find at the National Archives- When You Are Fostered, You Don’t Know Who You Are: Scottish Siblings Reunited
- DNA Testing for Adoptees: Paul Dobbs Story
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!




