Blog


How to Use a Microfilm Reader or a Microfiche Reader
 Not sure how to use microfilm or microfiche readers? Watch these quick video tutorials before your next trip to the library!
Not sure how to use microfilm or microfiche readers? Watch these quick video tutorials before your next trip to the library!
Recently I heard from a Genealogy Gems Premium member who is digging in deep to her family history. But she confessed that she left the Oklahoma Historical Center in Oklahoma City “in tears because I really didn’t know what I was doing” with the microfiche machine and with microfilms.
I totally understand. Microfilm and fiche readers are not my favorite part of genealogy research, either. But despite the wealth of digitized records that continue to appear online, microfilm is going to be around for a while! FamilySearch and other publishers of microfilmed data (like state archives) do not have copyright permissions to digitize all their microfilmed materials. Even if they can get it, it’s going to take a long time to make that happen.
Meanwhile, we will continue to need microfilm and microfiche readers!
- Microfilm is a long reel of film (up to 125 feet, I’ve heard) that are essentially page-by-page photos of a document collection, book, newspaper, etc.
- Microfiche is a single sheet of film (about 4″ x 6″) that contains the same, only shrunk down so small you need a magnified reader to make sense of it.
These were standard technologies for duplicating records in the pre-digital era. The Family History Library in Salt Lake City alone has over 2.4 million rolls of microfilm. Yes, that’s million! (And yes, they will lend them out to a Family History Center or FamilySearch Library near you.)
To access these fantastic films and fiches, you will need to use microfilm readers and microfiche readers. It’s easy to walk into the library and think everyone knows how to use them but you. But that’s not true. In fact, every single genealogist has had to face their first encounter with a reader. Don’t be shy about asking politely for a tutorial (and help when you do it wrong and something gets stuck). And don’t be shy about watching these tutorials on YouTube before you go to the library again:
How to Use a Microfilm Reader:
How to Use a Microfiche Reader:
As you can see, YouTube is a fantastic place to pick up essential genealogy skills! Click here to check out our more great ideas for using YouTube for family history.
More Beginning Genealogy Tips from Genealogy Gems
4 Beginning Genealogy Answers to Get You Started
6 Sources That May Name Your Ancestors’ Parents
Try These Two Powerful Tools for Finding Genealogy Records Online: Google and FamilySearch Wiki
Use Facebook for Family History: Gather Memories
Here’s an innovative way to use Facebook for family history. It comes from my downloadable video class, Pain-Free Family History Writing Projects.
Are you using Facebook to gather family history from your relatives? You can! It’s a version of “crowd-sourcing,” or using the internet to ask lots of people at a time for help. Here are two specific examples:
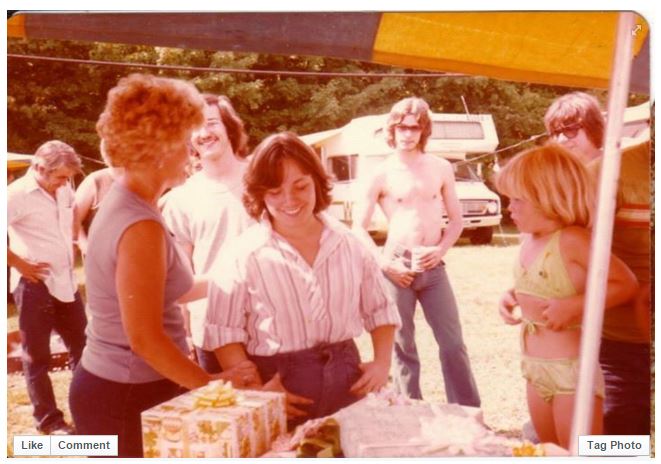 I posted this first photo in my husband’s family reunion Facebook page, after being given a ton of photos from past reunions. I couldn’t identify anyone in the picture and I couldn’t tell what was happening, but it looked like something special. After I posted it, one person commented, “Boy that’s an old photo of me”–which identified someone in the picture! Then an aunt commented that this was a bridal shower held during the annual family reunion. Yay! The mystery photo was captioned.
I posted this first photo in my husband’s family reunion Facebook page, after being given a ton of photos from past reunions. I couldn’t identify anyone in the picture and I couldn’t tell what was happening, but it looked like something special. After I posted it, one person commented, “Boy that’s an old photo of me”–which identified someone in the picture! Then an aunt commented that this was a bridal shower held during the annual family reunion. Yay! The mystery photo was captioned.
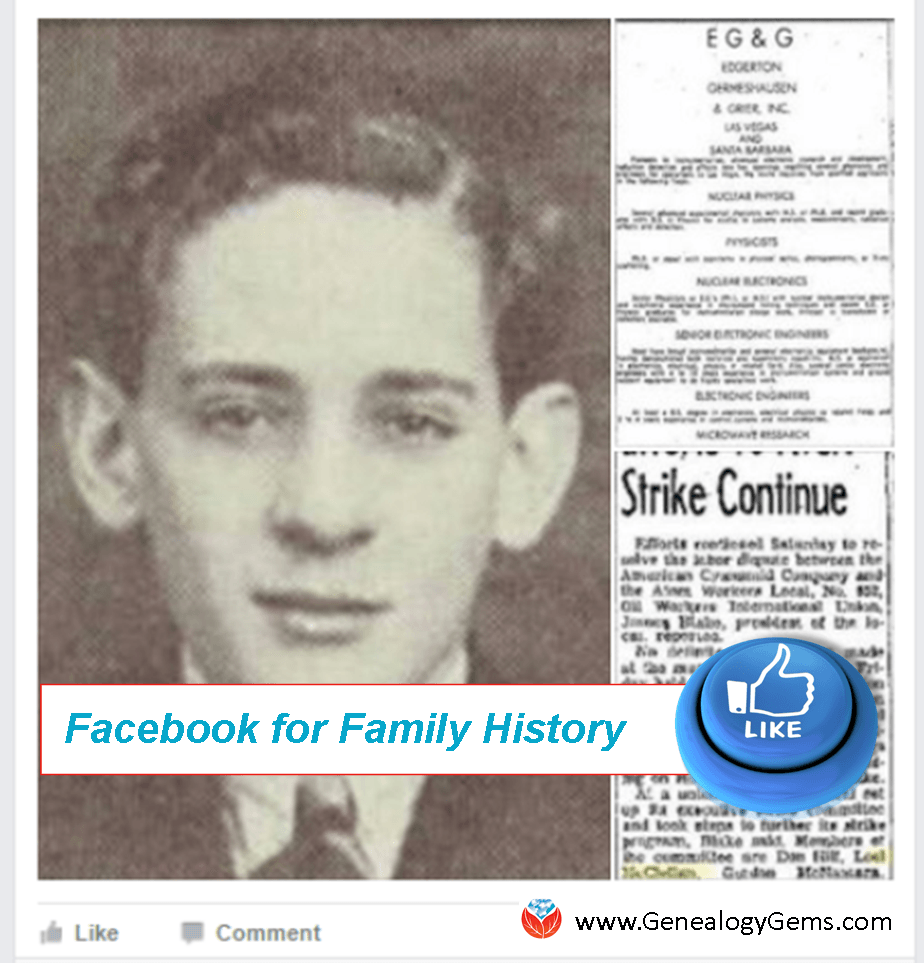
 In this second example, I asked for more than just a photo caption. I posted a yearbook photo of my grandfather and two newspaper articles about him in our family Facebook group. In the accompanying post I asked, “Does anyone know anything about his time in the military? All I know is his entry/release dates, that he was in the Navy and a radar tech.” I tagged several close relatives so they would see it. (This was in our closed Facebook group. You can tag people by typing the @ sign and then their names in the post or in a comment below it.)
In this second example, I asked for more than just a photo caption. I posted a yearbook photo of my grandfather and two newspaper articles about him in our family Facebook group. In the accompanying post I asked, “Does anyone know anything about his time in the military? All I know is his entry/release dates, that he was in the Navy and a radar tech.” I tagged several close relatives so they would see it. (This was in our closed Facebook group. You can tag people by typing the @ sign and then their names in the post or in a comment below it.)
The response was fantastic. My aunt said grandpa served on a ship in the Atlantic and mentioned a rank she thinks he achieved. My uncle said he had some related papers and would send them to me (yay!). Even better, some younger family members commented how much a sibling or son looked like grandpa at that age. A cousin snagged what I’d posted for her daughter’s family history project. So even those younger relatives who couldn’t tell me about grandpa could benefit from the online conversation.
BONUS TIP: I get the best response when I post an image or video along with my questions. Pictures and videos will catch people’s interest, jog their memories and sometimes prompt additional comments. This is a good way to remind people of your interest in the family stories and to share what you already have.
This story collecting tip came from my video class: Pain-Free Family History Writing Projects.

We Dig These Gems! New Genealogy Records Online
 Every week, we post about exciting new genealogy records online. Scan this week’s list for anything you should search (or share with a friend): a colonial North American digital archive; Revolutionary War-era residents of Alabama; U.S. military burials; Freedmen’s Bureau records; California naturalizations and British WWI databases.
Every week, we post about exciting new genealogy records online. Scan this week’s list for anything you should search (or share with a friend): a colonial North American digital archive; Revolutionary War-era residents of Alabama; U.S. military burials; Freedmen’s Bureau records; California naturalizations and British WWI databases.
AFRICAN-AMERICAN RECORDS. Over 130,000 indexed images were added to the United States Freedmen’s Bureau Hospital and Medical Records 1865-1872 collection, searchable for free on FamilySearch. The index includes “patient registers, registers of sick and wounded, prescription books, and other medical records from freedmen hospitals and dispensaries….Records include letters and endorsements sent and received, account books, applications for rations, applications for relief, court records, labor contracts, registers of bounty claimants, registers of complaints, registers of contracts, registers of disbursements, registers of freedmen issued rations, registers of patients, reports, rosters of officers and employees, special and general orders and circulars received, special orders and circulars issued, records relating to claims, court trials, property restoration, and homesteads.”
ALABAMA REVOLUTIONARY WAR. A new database of indexed images at Ancestry “contains biographies, news clippings, and cards in paragraph form detailing persons who were residents in Alabama during the Revolutionary War in America.”
BRITISH WWI RECORDS. Findmypast has released new databases relating to World War I service: Surrey, Military Tribunals, 1915-1918 (military exemptions for the county of Surrey); and two British Army memorial rolls for employees of Lloyds of London and the London Stock Exchange who died in service.
CALIFORNIA NATURALIZATIONS. A database with indexed images of over a century’s worth of California naturalization records (1887-1991) has been updated at Ancestry.com.
COLONIAL NORTH AMERICA. A new digital archive has been launched: The Colonial North American Project at Harvard University. Its goal is to post digitized versions of “all known archival and manuscript materials in the Harvard Library that relate to 17th and 18th century North America.” According to the site, its “documents reveal a great deal about topics such as social life, education, trade, finance, politics, revolution, war, women, Native American life, slavery, science, medicine, and religion. In addition to reflecting the origins of the United States, the digitized materials also document aspects of life and work in Great Britain, France, Canada, the Caribbean, and Mexico.” (Click here to read our blog post about the project’s announcement in 2013.)
U.S. MILITARY BURIALS. BillionGraves.com recently added over 8 million U.S. military veterans’ burial records to the Special Collections that can be accessed by BG+ subscribers. These records include burial and cemetery records from the Veterans Affairs office, as well as military headstones from civilian headstones around the world.
 Thanks for sharing these new genealogy records online with friends and fellow genealogists and through your genealogical society social media channels. It’s fun to spread good news!
Thanks for sharing these new genealogy records online with friends and fellow genealogists and through your genealogical society social media channels. It’s fun to spread good news!




