by Diahan Southard | Apr 5, 2019 | 01 What's New, Adoption, DNA |
Combining DNA test types can give you a better picture of your overall genealogical relationship to someone else. DNA expert Diahan Southard shares an example from her family about how she used different DNA tests to solve an adoption mystery.
Combine your autosomal test results with the results of your mitochondrial DNA or YDNA test to make some amazing connections today!
My family recently visited the Jelly Belly Factory in northern California. Of course, at the end of the tour, they funneled us into their gift shop where we felt compelled to buy jelly beans and other sundry treats.
My favorite part of the big box we bought were the recipes on the side. We could turn the already delicious variety of flavors into even more pallet-pleasing options by eating specific combinations of jelly beans at the same time. Like 2 green apply jelly beans + 1 cinnamon jelly bean = apple pie. Who knew!
Naturally, this got me thinking about DNA.
Combining DNA Test Types
Specifically, I was thinking about the power of combining multiple test types to get a better picture of our overall genealogical relationship to someone else.
If you recall, there are three kinds of DNA tests available for genealogists:
- Autosomal DNA
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
- Y chromosome DNA (YDNA)
Much of the focus these days is on how to use the autosomal DNA in our family history research. This may be because the autosomal DNA covers both sides of your family tree, so it is seen as a catchall for our family history. While it is a very powerful tool for our research, it can also be a bit overwhelming to try to determine how you are related to someone else.
Let’s look at an example from my own family history.
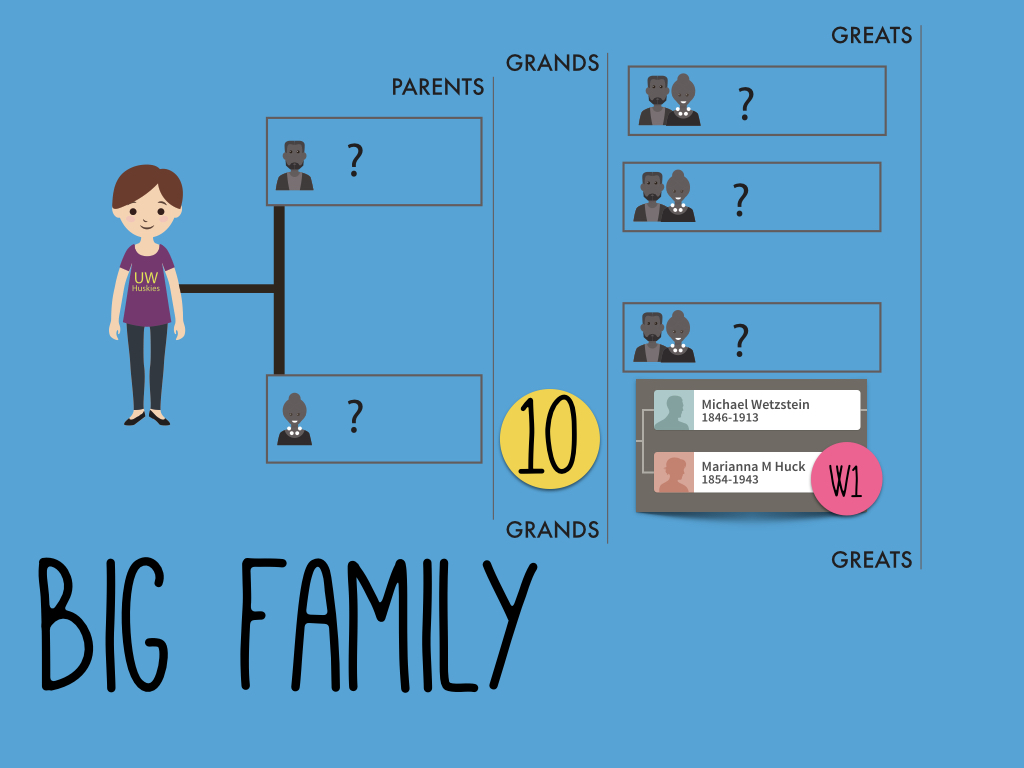
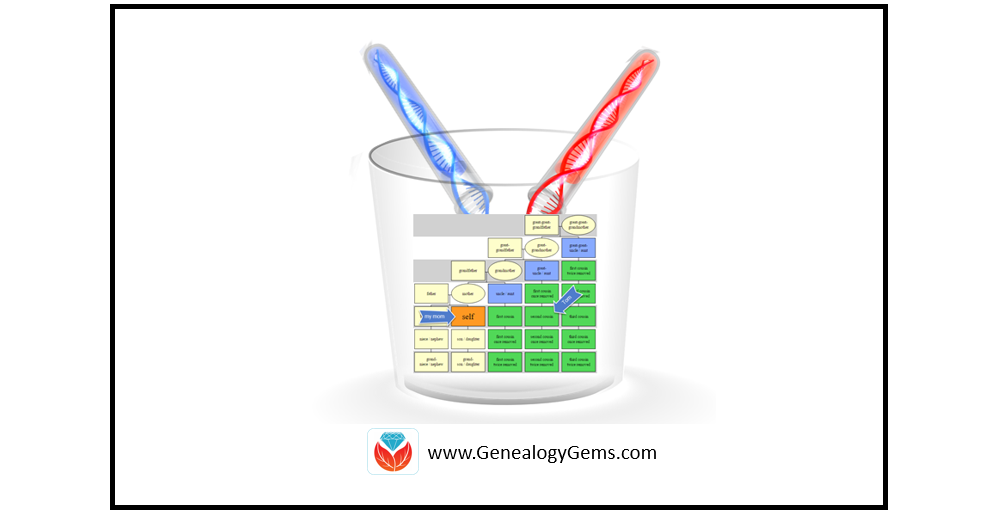
My mom took an autosomal DNA test at 23andMe and matched with Tom. Their predicted genealogical relationship, based on how much DNA they shared, was second cousins.
To begin to understand how they are related, we need to understand which ancestor could be shared by people who are genetic second cousins. To figure it out, you can count backward like this: people who share parents are siblings, sharing grandparents makes you first cousins, and sharing great-grandparents makes you second cousins.
So, if my mom and Tom are true second cousins (meaning there aren’t any of those once-removed situations going on, but that’s a subject for another time), then we should be able to find their common ancestor among their great-grandparents.
Each of us has eight great-grandparents. Because we can’t usually narrow down shared DNA to a single person, but rather to an ancestral couple, we are really just looking at four possible ancestral couple connections between my mom and Tom.
My mom doesn’t have any known ancestors, as she was adopted, so we can only evaluate Tom’s line. Tom was kind enough to share his pedigree chart with us, and he had all four of his couples listed. But how do we know which one is the shared couple with my mom?
Narrowing Down the Results
Now, for those of you without an adoption, you will have some other clues to help you figure out which of the four (or eight, if you are looking at a third cousin, or 16 if you are looking at a fourth cousin) ancestral couples is shared between you and your match. Start by looking for shared surnames.
If that comes up short, evaluate each couple by location. If you see an ancestral couple who is in a similar location to your line, then that couple becomes your most likely connecting point.
What then? Do genealogy! Find out everything you can about that couple and their descendants to see if you can connect that line to your own.
However, in my mom’s case, we didn’t have any surnames or locations to narrow down which ancestral couple was the connection point between our line and Tom’s. But even if we had locations, that may not have helped as Tom is very homogenous. All of his ancestors were from the same place!
But, we did have one very important clue: the mitochondrial DNA. Remember mtDNA traces a direct maternal line. So my mom’s mtDNA is the same as her mom’s, which is the same as her mom’s etc.
At 23andMe they don’t test the full mitochondrial DNA sequence (FMS) like they do at Family Tree DNA. For family history purposes, you really want the FMS to help you narrow down your maternal line connection to others. But 23andMe does provide your haplogroup, otherwise known as your deep ancestral group. These groups are named with a letter/number combination. My mom is W1 and we noticed that Tom is also W1.
This meant that my mom and Tom share a direct maternal line – or put another way, Tom’s mother’s mother’s mother was the same as my mom’s mother’s mother’s mother. That means there is only one couple out of the four possible couples that could connect my mom to Tom: his direct maternal line ancestor Marianna Huck, and her husband Michael Wetzstien.
Now you can only perform this wondrous feat if you and your match have both tested at 23andMe, or have both taken the mtDNA test at Family Tree DNA.
Just as a Popcorn Jelly Belly plus two Blueberry Jelly Bellies makes a blueberry muffin, combining your autosomal DNA test results with your mtDNA test results (or YDNA for that matter) can yield some interesting connections that just might break down that family history brick wall.
Get your mtDNA and YDNA tested at Family Tree DNA
If you are considering testing your YDNA and/or your mtDNA, then Family Tree DNA is the place for you!
Even if you aren’t trying to solve an adoption mystery, you can utilize these additional tests to break down other brick walls in your genealogical research and learn more about your heritage. You can take their Family Finder autosomal test, YDNA, or Mitochondrial (mtDNA) full sequence test. Click here to shop now!
About the Author: Diahan Southard has worked with the Sorenson Molecular Genealogy Foundation, and has been in the genetic genealogy industry since it has been an industry. She holds a degree in Microbiology and her creative side helps her break the science up into delicious bite-sized pieces for you. She’s the author of a full series of DNA guides for genealogists.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
This article was originally published on April 17, 2017 and updated on April 5, 2019.
by Lacey Cooke | Sep 18, 2018 | 01 What's New, DNA, MyHeritage |
Since 2016, MyHeritage DNA has offered the ability to transfer your DNA data from other DNA companies for free, and now they’ve expanded that offering to include Living DNA and 23andMe v5. With this news comes additional changes to their free upload offerings, so get your data transferred now to take advantage of all their tools.
Our friends at MyHeritage.com, one of the Genealogy Giants and a sponsor of the free Genealogy Gems Podcast, recently made the announcements we are sharing below.
MyHeritage DNA news you can use
1. Transfer your DNA results from Living DNA and 23andMe v5.
“We’re happy to announce another industry first from MyHeritage! We now support the upload of 23andMe v5 and Living DNA data files, in addition to supporting data uploads from all major DNA testing services, including Ancestry, 23andMe (prior to V5) and Family Tree DNA (Family Finder).
Since 2016, MyHeritage has allowed users who have already tested their DNA to upload their DNA data from Ancestry, 23andMe and Family Tree DNA. They receive DNA Matches and ethnicity estimates on MyHeritage for free. Our free upload service is a unique benefit not offered by any of these other companies. However, previously MyHeritage did not support the upload of tests based on the chip called GSA (Global Screening Array), now being used by 23andMe (v5), and by Living DNA. Recent improvements to our DNA algorithms now allow us to support DNA data processed on GSA chips, and so we now support uploads of 23andMe v5 and Living DNA data files.
Uploading your DNA data to MyHeritage is fast and simple. For users that upload now, we offer full access to DNA Matching, Ethnicity Estimates, our industry-leading chromosome browser, and more, for FREE.”
Click below to upload your DNA now for FREE!
The announcement continues:
“If you manage additional DNA kits for some of your relatives, and you have their permission, upload their DNA data too, and MyHeritage will let you associate the data with the respective individuals on your family tree. DNA data uploaded to MyHeritage is completely private and secure. Only you can see the DNA data you upload.”
2. Upcoming Changes to Tools Access
The announcement goes on to discuss a few changes you can expect with their free upload service:
“As of December 1, 2018, our policy regarding DNA uploads will change: DNA Matching will remain free for uploaded DNA data, but unlocking additional DNA features (for example, ethnicity estimate, chromosome browser, and some others) will require an extra payment for DNA files uploaded after this date. We will announce the full details of the new policy once it is finalized, closer to December 1st. All DNA data that was uploaded to MyHeritage in the past, and all DNA data that is uploaded now and prior to December 1, 2018, will continue to enjoy full access to all DNA features for free. These uploads will be grandfathered in and will remain free.
So, don’t delay, and upload your DNA data to MyHeritage now, while all the DNA features are free (and they will remain free for you). If you have tested with 23andMe (any versions including v5) or Living DNA, you’re in luck, and you can now upload this data to MyHeritage too. You can also upload DNA data from Ancestry and Family Tree DNA’s Family Finder test. Instructions for exporting your data and uploading it to MyHeritage are provided on our upload page.”
Lacey has been working with Genealogy Gems since the company’s inception in 2007. Now, as the full-time manager of Genealogy Gems, she creates the free weekly newsletter, writes blogs, coordinates live events, and collaborates on new product development. No stranger to working with dead people, Lacey holds a degree in Forensic Anthropology, and is passionate about criminal justice and investigative techniques. She is the proud dog mom of Renly the corgi.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Sunny | Mar 17, 2018 | 01 What's New, DNA, Health History |
The FDA has approved the first direct-to-consumer DNA test for cancer risk. Offered by 23andMe, results include genetic health risk reports on BRCA1- and BRCA2-related genetic risk for breast, ovarian and prostate cancer.
DNA testing company 23andMe recently announced an important new addition to the personal health reports that come with its Health + Ancestry test (which retails for $199, compared to its Ancestry-only test): cancer risk.
DNA test for cancer risk
Effective immediately for existing and new testers, 23andMe “will report on three variants in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes associated with a significantly higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer in women, and breast cancer in men,” states a company press release.
Anne Wojcicki, 23andMe CEO and co-founder, calls the 23andMe reports “potentially life-saving information,” especially for those with Ashkenazi Jewish ancestors, who are at greatest risk for having one of the reported variants. According to the press release, about 1 in 40 people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent has one of these variants: “Women with one of these variants have a 45-85% chance of developing breast cancer by age 70.”
The company emphasizes that this information doesn’t replace regular cancer screenings or other recommended health care. Most cancers aren’t hereditary to begin with, and genetic screenings don’t capture all the possible genetic variants related to cancer risk.
Customers who purchase the 23andMe Health + Ancestry test must select whether they want to receive this health report as part of their results. This is consistent with all their genetic health risk reports, which include Celiac disease, Parkinson’s disease, late-onset Alzheimer’s and several others (click here to read more about 23andMe’s health reports). Customers also receive an “education module” to help them fully understand what they can learn from this report and how to use the results.
The press release points out that currently, those recommended to be evaluated for genetic risk of cancer are primarily those with a known “personal and/or family history of certain cancers.” But recent medical findings show that 50% of families with BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutations had no known family history. 23andMe reports similar results in their test population: “Of those BRCA carriers who gave family medical history, about half reported no history of cancer in first-degree relatives. 23andMe has also observed that many of its customers for whom Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry was detected did not self-report any Jewish ancestry.” The concern: lack of awareness of genetic risk could prevent critical screenings and monitoring.
Health and wellness reports are, for many genealogists, one more compelling reason to participate in DNA testing. Family history, after all, encompasses family health history, too!
More on DNA tests for health information
Your DNA Guide Diahan Southard keeps Genealogy Gems readers up-to-date with the broader conversation about DNA testing and your family history—including health reports. Keep reading and learn!
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Diahan Southard | Apr 11, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA, Health History
If you have ever wondered if you or your loved ones are at higher risk for diseases such as Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, read on to learn about big changes that are happening. Health history is just one of the ways in which genealogy research can benefit your family.

According to a recent FDA press release, “The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today allowed marketing of 23andMe Personal Genome Service Genetic Health Risk (GHR) tests for 10 diseases or conditions. These are the first direct-to-consumer (DTC) tests authorized by the FDA that provide information on an individual’s genetic predisposition to certain medical diseases or conditions, which may help to make decisions about lifestyle choices or to inform discussions with a health care professional.”
The release goes on to say:
Consumers can now have direct access to certain genetic risk information,” said Jeffrey Shuren, M.D., director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “But it is important that people understand that genetic risk is just one piece of the bigger puzzle, it does not mean they will or won’t ultimately develop a disease.”
The GHR tests are intended to provide genetic risk information to consumers, but the tests cannot determine a person’s overall risk of developing a disease or condition. In addition to the presence of certain genetic variants, there are many factors that contribute to the development of a health condition, including environmental and lifestyle factors.
The 23andMe GHR tests work by isolating DNA from a saliva sample, which is then tested for more than 500,000 genetic variants. The presence or absence of some of these variants is associated with an increased risk for developing any one of the following 10 diseases or conditions:
- Parkinson’s disease, a nervous system disorder impacting movement
- Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills
- Celiac disease, a disorder resulting in the inability to digest gluten
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a disorder that raises the risk of lung and liver disease
- Early-onset primary dystonia, a movement disorder involving involuntary muscle contractions and other uncontrolled movements
- Factor XI deficiency, a blood clotting disorder
- Gaucher disease type 1, an organ and tissue disorder
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency, also known as G6PD, a red blood cell condition
- Hereditary hemochromatosis, an iron overload disorder
- Hereditary thrombophilia, a blood clot disorder
You can read the complete article called FDA allows marketing of first direct-to-consumer tests that provide genetic risk information for certain conditions here.
 FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide
FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide
I look to Your DNA Guide, Diahan Southard for all things genetic genealogy, and here’s what she had to say about the recent news:
23andMe is certainly the outlier among our genetic genealogy companies. It is different because its purpose is not necessarily to help you find your ancestors or determine your ethnic composition, though it can do both, but their goal is to empower your personal health.
In November of 2013 the FDA ordered 23andMe to retract all health reporting from their website in order to better regulate the dissemination of health related information to consumers. 23andMe has slowly crawled back toward that same reporting structure, all the while jumping through the compliant hoops that the FDA has set up.
Now this week they have had a major step forward as they have been able to release the risk assessment for 10 major diseases including Parkinson’s and celiac. This is the first such test available direct to consumers, without first going to your doctor.
This is likely the first of many such developments as 23andMe works to make our own health more accessible via our genetics. If you do pursue this kind of evaluation, it is important to keep in mind the words of Jeffrey Shuren, M.D., director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, “…genetic risk is just one piece of the bigger puzzle, it does not mean they will or won’t ultimately develop a disease.”
Learn More About 23andMe
As with all genetic testing, it’s your decision in the end, so be as informed as you can. Diahan’s quick reference guide Understanding 23andMe (a Companion Guide to Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist) will help you tap into the company’s services from a genealogical perspective. Over 1 million people have had their DNA evaluated by 23andMe. This website has powerful family history tools and this guide will answer the most pressing questions like:
- How can I control how much information is being shared with others?
- How can I enter my genealogical information?
- How do I know when I have a good match?
- Is the YDNA and mtDNA information they give the same as what I see at other places?
- What is the best way to use the ethnicity results presented?
by Lisa Cooke | Oct 29, 2015 | 01 What's New, DNA
Over a million people have done DNA testing with 23andMe, many lured by that company’s health information tools. Learn to use their genetic genealogy tools to get  the most out of testing there! (and keep reading for a special limited time sale!)
the most out of testing there! (and keep reading for a special limited time sale!)
I am one of the million+ people who have tested my DNA with 23andMe. Early on in my days as a 23andMe customer, I spotted a match who listed ancestry from Washington state, where I grew up. Because I have had both of my parents tested, 23andMe told me that this match was on my dad’s side. I sent an inquiry out to the match and named a few of my paternal surnames as possible connections between us.
As it turns out, this match was my dad’s half first cousin! They are about the same age and had played together all the time as boys, but their families had lost touch over the years. What was even more exciting for me, is that using the tools at 23andMe I was able to see the actual physical locations on the DNA that I shared with this cousin.
Knowing that our common ancestor was Lucy J. Claunch, I knew that these actual physical, tangible pieces of me were once pieces of her. All at once I felt a discernible shift in myself and the way I viewed my connection to her. She was no longer a name on a genealogical record, she was my ancestor, and I wanted to know more. For me, it took the DNA connection to give me that added oomph to turn my genealogy into family history. As it happened, that DNA connection came through 23andMe.
How to Focus on Genealogy DNA testing with 23andMe
23andMe is primarily focused on empowering personal health. They recently announced the restored ability to provide limited health information to their customers. The wide variety of content on their website can easily distract you from the genetic genealogy tools they are offering. To help you focus on these tools and use them to verify and extend your family tree, I’ve just released a NEW laminated quick guide, Understanding 23andMe.
 Understanding 23andMe addresses the most pressing genetic genealogy questions for those doing DNA testing with 23andMe, like:
Understanding 23andMe addresses the most pressing genetic genealogy questions for those doing DNA testing with 23andMe, like:
- How can I control how much information is being shared with others?
- How can I enter my genealogical information?
- How do I know when I have a good match?
- Is the YDNA and mtDNA information they give the same as what I see at other places?
- What is the best way to use the ethnicity results presented?
Purchase this guide NOW in the Genealogy Gems store and you’ll SAVE BIG! It’s only $5.95 right now–regularly $8.95! You’ll also save if you buy it with a super bundle of my entire series of DNA quick guides–7 of them now to help you “do your DNA” right from start to finish!
More DNA at Genealogy Gems
A family and its female slave house servants in Brazil, c.1860. Wikimedia Commons image. Click to view full source citation.
We’re Cousins? DNA for Genealogy Reveals Surprising Relationship
DNA Confirms Presidential Love Affair 90 Years Later
Confused by Your AncestryDNA Matches? Read This Post












 FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide
FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide the most out of testing there! (and keep reading for a
the most out of testing there! (and keep reading for a  Understanding 23andMe
Understanding 23andMe



