by Diahan Southard | Apr 5, 2019 | 01 What's New, Adoption, DNA |
Combining DNA test types can give you a better picture of your overall genealogical relationship to someone else. DNA expert Diahan Southard shares an example from her family about how she used different DNA tests to solve an adoption mystery.
Combine your autosomal test results with the results of your mitochondrial DNA or YDNA test to make some amazing connections today!
My family recently visited the Jelly Belly Factory in northern California. Of course, at the end of the tour, they funneled us into their gift shop where we felt compelled to buy jelly beans and other sundry treats.
My favorite part of the big box we bought were the recipes on the side. We could turn the already delicious variety of flavors into even more pallet-pleasing options by eating specific combinations of jelly beans at the same time. Like 2 green apply jelly beans + 1 cinnamon jelly bean = apple pie. Who knew!
Naturally, this got me thinking about DNA.
Combining DNA Test Types
Specifically, I was thinking about the power of combining multiple test types to get a better picture of our overall genealogical relationship to someone else.
If you recall, there are three kinds of DNA tests available for genealogists:
- Autosomal DNA
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
- Y chromosome DNA (YDNA)
Much of the focus these days is on how to use the autosomal DNA in our family history research. This may be because the autosomal DNA covers both sides of your family tree, so it is seen as a catchall for our family history. While it is a very powerful tool for our research, it can also be a bit overwhelming to try to determine how you are related to someone else.
Let’s look at an example from my own family history.
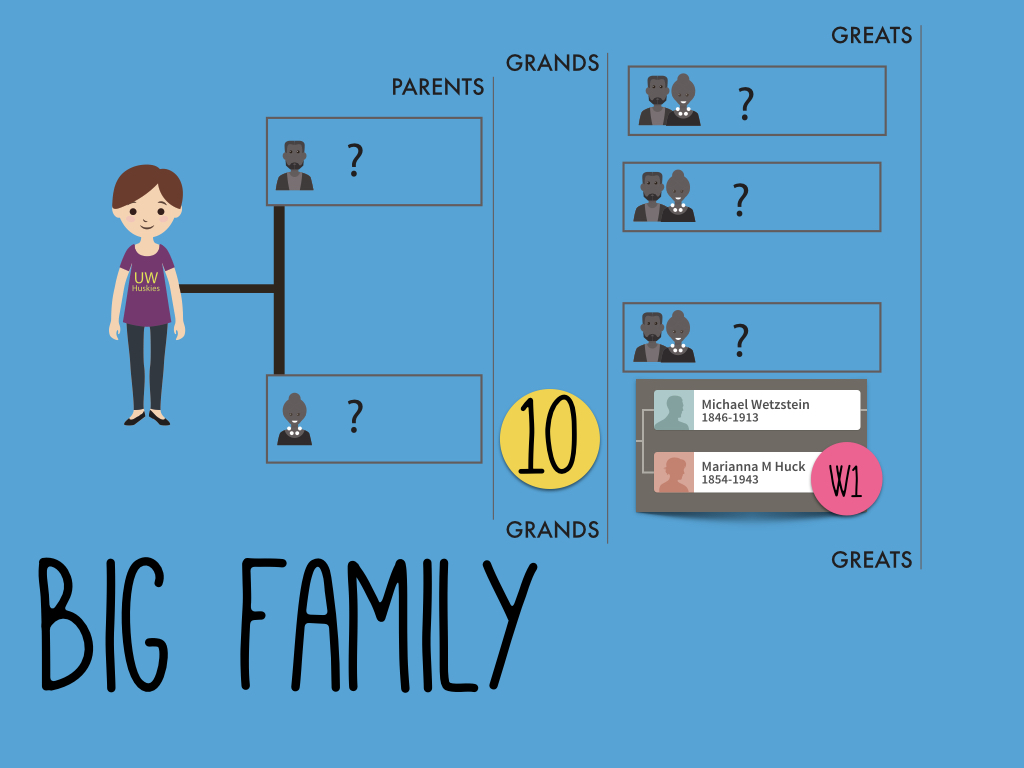
My mom took an autosomal DNA test at 23andMe and matched with Tom. Their predicted genealogical relationship, based on how much DNA they shared, was second cousins.
To begin to understand how they are related, we need to understand which ancestor could be shared by people who are genetic second cousins. To figure it out, you can count backward like this: people who share parents are siblings, sharing grandparents makes you first cousins, and sharing great-grandparents makes you second cousins.
So, if my mom and Tom are true second cousins (meaning there aren’t any of those once-removed situations going on, but that’s a subject for another time), then we should be able to find their common ancestor among their great-grandparents.
Each of us has eight great-grandparents. Because we can’t usually narrow down shared DNA to a single person, but rather to an ancestral couple, we are really just looking at four possible ancestral couple connections between my mom and Tom.
My mom doesn’t have any known ancestors, as she was adopted, so we can only evaluate Tom’s line. Tom was kind enough to share his pedigree chart with us, and he had all four of his couples listed. But how do we know which one is the shared couple with my mom?
Narrowing Down the Results
Now, for those of you without an adoption, you will have some other clues to help you figure out which of the four (or eight, if you are looking at a third cousin, or 16 if you are looking at a fourth cousin) ancestral couples is shared between you and your match. Start by looking for shared surnames.
If that comes up short, evaluate each couple by location. If you see an ancestral couple who is in a similar location to your line, then that couple becomes your most likely connecting point.
What then? Do genealogy! Find out everything you can about that couple and their descendants to see if you can connect that line to your own.
However, in my mom’s case, we didn’t have any surnames or locations to narrow down which ancestral couple was the connection point between our line and Tom’s. But even if we had locations, that may not have helped as Tom is very homogenous. All of his ancestors were from the same place!
But, we did have one very important clue: the mitochondrial DNA. Remember mtDNA traces a direct maternal line. So my mom’s mtDNA is the same as her mom’s, which is the same as her mom’s etc.
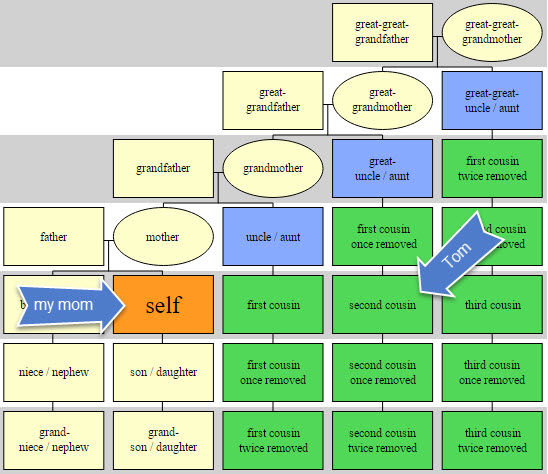
At 23andMe they don’t test the full mitochondrial DNA sequence (FMS) like they do at Family Tree DNA. For family history purposes, you really want the FMS to help you narrow down your maternal line connection to others. But 23andMe does provide your haplogroup, otherwise known as your deep ancestral group. These groups are named with a letter/number combination. My mom is W1 and we noticed that Tom is also W1.
This meant that my mom and Tom share a direct maternal line – or put another way, Tom’s mother’s mother’s mother was the same as my mom’s mother’s mother’s mother. That means there is only one couple out of the four possible couples that could connect my mom to Tom: his direct maternal line ancestor Marianna Huck, and her husband Michael Wetzstien.
Now you can only perform this wondrous feat if you and your match have both tested at 23andMe, or have both taken the mtDNA test at Family Tree DNA.
Just as a Popcorn Jelly Belly plus two Blueberry Jelly Bellies makes a blueberry muffin, combining your autosomal DNA test results with your mtDNA test results (or YDNA for that matter) can yield some interesting connections that just might break down that family history brick wall.
Get your mtDNA and YDNA tested at Family Tree DNA
If you are considering testing your YDNA and/or your mtDNA, then Family Tree DNA is the place for you!
Even if you aren’t trying to solve an adoption mystery, you can utilize these additional tests to break down other brick walls in your genealogical research and learn more about your heritage. You can take their Family Finder autosomal test, YDNA, or Mitochondrial (mtDNA) full sequence test. Click here to shop now!
About the Author: Diahan Southard has worked with the Sorenson Molecular Genealogy Foundation, and has been in the genetic genealogy industry since it has been an industry. She holds a degree in Microbiology and her creative side helps her break the science up into delicious bite-sized pieces for you. She’s the author of a full series of DNA guides for genealogists.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
This article was originally published on April 17, 2017 and updated on April 5, 2019.
by Lisa Cooke | Apr 24, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA |
The Family Tree DNA ethnicity report has been updated, and this means more details about ethnic and geographic origins for both autosomal and mtDNA DNA testers.
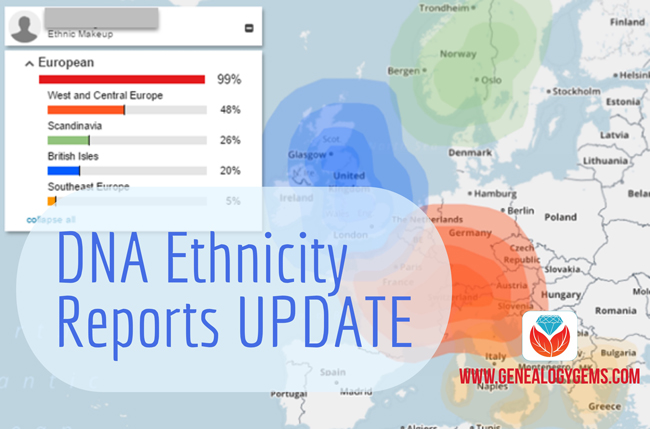
Family Tree DNA recently announced a round of updates to myOrigins, its mapping tool for ethnic and geographic ancestry. New are more detailed breakdowns of their population clusters and in-depth descriptions of them. (Visit Family Tree DNA’s website here.)

It is so exciting to see new or updated reports from our genetic genealogy testing companies! It is a good reminder of two things: First, that the results we currently have, especially in the arena of our ethnicity results, will continually be improving. Second, that once you test with any company, these improvements are added to your account and your results are updated automatically.
Family Tree DNA is the only company offering a complete look at your mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), the one that traces your direct maternal line. They recently updated the deep ancestral assignments for these mtDNA tests. The updates were based on scientific advances in the world of mtDNA and can sometimes give you a more specific idea of where your ancestral line came from.
In addition to the mtDNA updates, FTDNA has also updated their MyOrigins results as part of your autosomal DNA test. Previously your MyOrigins results broke up the world into 18 different pieces and you were told your affiliation with each. Now with 6 new populations added, there are a total of 24. The changes include splitting three categories into smaller parts, like they are now reporting Finland separate from Siberia, as well as adding three new categories in South America, West Middle East, and Oceania.
Your MyOrigins results will now also include trace amounts, which are those percentages that are very low and therefore do not carry a high confidence. But many genetic genealogists wanted to see any area that may have been detected, and so FTDNA responded.
How to Review Your Family Tree DNA Ethnicity Report
1. Log in to your Family Tree DNA account. From your dashboard, select myOrigins.
2. On the myOrigins page, click View all to see your full ethnic percentages, as defined by Family Tree DNA. You can also click View myOrigins map to see your results mapped out. (The map looks like the one at the beginning of this post.)
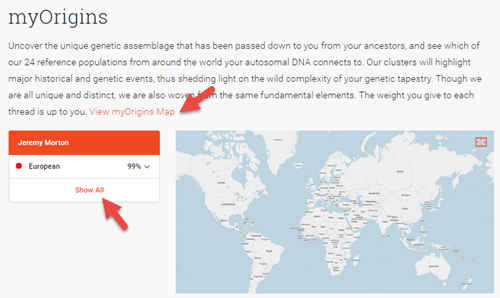
3. When you click to view all your ethnicity results, you’ll see a more detailed breakdown of your population groups. Click View all population descriptions to read more about each one.
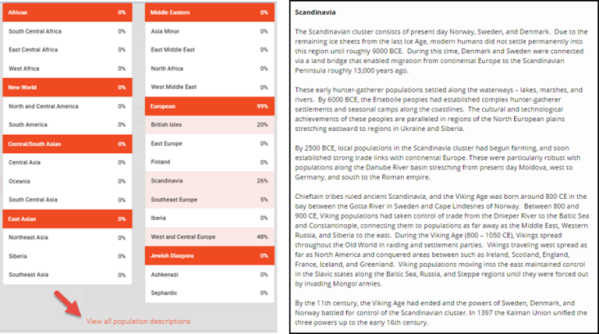
The Impact of Updated Family Tree DNA Ethnicity Reports
On the whole, are these updated results going to significantly impact your family history research if you have tested at Family Tree DNA? Likely not. The greater impact is just in the idea that these things can be improved, updated, and changed, which means our experience will continue to improve, and more people are likely to test. More people in the database means more possible cousins. More possible cousins means more genealogy breakthroughs, and a more complete picture of our heritage, and that is what we are really all after.
Learn More About DNA Testing for Genealogy
Click here to see individual guides for topics I talked about above, such as testing at Family Tree DNA, testing your autosomal or mitochondrial DNA and getting started (in which I explain ethnicity results). Or click here for the ultimate Genetic Genealogy Jumbo Pack: ALL 10 of my guides PLUS my video class, “Getting Started with Genetic Genealogy.”

by Lisa Cooke | Feb 20, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA, Kids |
DNA testing for kids is a great way to spark their interest in their heritage, while teaching science, math, geography, and more. Consider these reasons and start with the budget-friendly option of an autosomal test.

According to a 2010 study out of Emory University, if we want to encourage kids toward an activity that will positively impact them, we should steer them toward family history. The researchers reported, “Children who know stories about relatives who came before them show higher levels of emotional well-being.”
Now, I know I don’t need to convince you of this. You are already sold on genealogy. But let’s explore how DNA testing might be able to help you share your love of family history with your children and grandchildren.
Why Try DNA Testing for Kids
Since you know this is me, the genetic genealogist talking, you can probably guess what I’ll suggest for getting kids interested in family history. DNA testing is a great way to personally and physically involve them. There is the tangible process of taking the sample at home, and the marvel at how such a simple act can produce the amazing display of our ethnicity results. Since each of us is unique, it will be fun for them to compare with you and other relatives to see who-got-what-from-who. This will naturally lead to questions about which ancestor provided that bit of Italian or Irish, and wham! You’ll be right there to tell them about how their 5th great-grandfather crossed the ocean with only the clothes on his back, determined to make a new start in a new land.

If there are parts of the ethnicity report you can’t explain, use that as a hook to encourage them to start digging and to find out why you have that smattering of eastern European or Southeast Asian. Taking them for a tour of the DNA match page, you can show them how they share 50% of their DNA with their sister (whether they like it or not!) and how they share 25% with their grandparent!
DNA test results give kids a totally unique look at their personal identity with technology that is cutting edge. Looking at their DNA test results can turn into a math lesson, a science lesson, a geography lesson, a lesson on heredity or biology, or a discussion on identity. DNA is the perfect introduction to the wonders that genealogy can hold, especially for children.
A Warning and Caution
As with all DNA testing pursuits, this one should not be taken lightly, even with all of its benefits.
An important word to parents: Be sure to keep unintentional consequences in the forefront of your mind. This includes the possibility of revealing family secrets. Talk with your spouse and make sure you are both on the same page. In the end, this is your decision.
An important word to grandparents and other relatives: DNA testing is a parent’s decision. Even though you’re passionate about preserving the family’s history and the benefits of including children are numerous, you must obtain parental consent if you are not the parent.
More About Autosomal DNA Testing for Kids
 Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
Click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos (available to Gems fans for a special price) or start your kids’ or grandkids’ DNA journey with two of my genetic genealogy quick guides. The first is a great overview and the second talks about autosomal testing which is a good test for genetic genealogy beginners.
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 13, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA |
The genetic genealogy community has a crush. A big one. Everyone is talking about it. “It has such great features,” says one. “It has a chromosome browser!” exclaims another. “It’s FREE!” they all shout. What’s all the hype about? GEDmatch.
GEDmatch is a mostly free online tool where anyone with autosomal DNA test results from 23andMe, FTDNA, and AncestryDNA can meet and share information. All you need to do is download your data from your testing company and upload it into your newly created GEDmatch account.
GEDmatch Set-up
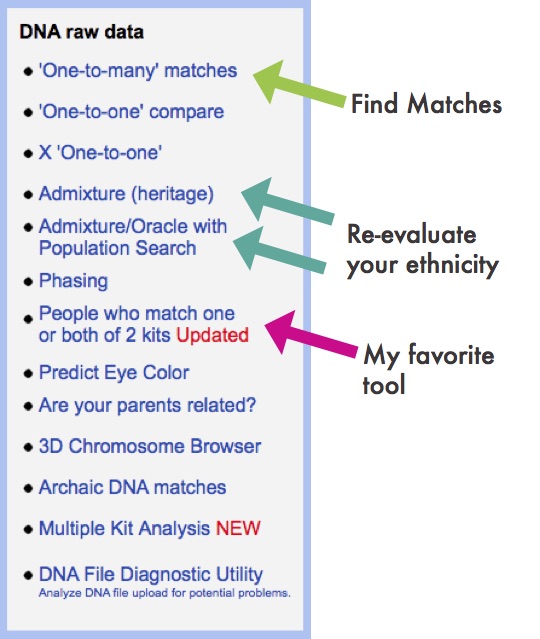 GEDmatch is set up just like your testing company and provides two kinds of reports: ethnicity results and a match list. Remember, ethnicity results, meaning those pie charts that report you are 15% Italian and 32% Irish, are based on two factors: a reference population and fancy math. GEDmatch has gathered data from multiple academic sources to provide you with several different iterations of ethnicity reports. This is like getting a second (and third and fourth, etc) opinion on a science that is still emerging. It is a fun exercise, but will likely not impact your genealogy research very much.
GEDmatch is set up just like your testing company and provides two kinds of reports: ethnicity results and a match list. Remember, ethnicity results, meaning those pie charts that report you are 15% Italian and 32% Irish, are based on two factors: a reference population and fancy math. GEDmatch has gathered data from multiple academic sources to provide you with several different iterations of ethnicity reports. This is like getting a second (and third and fourth, etc) opinion on a science that is still emerging. It is a fun exercise, but will likely not impact your genealogy research very much.
The more important match list does allow you to see genetic cousins who have tested at other companies. Of course, only those who have downloaded their results and entered them into GEDmatch will show up on your list. This means GEDmatch has the potential to expand your pool of genetic cousins, increasing your chances of finding someone to help you track down that missing ancestor.
Many also flock to GEDmatch because they were tested at AncestryDNA and so do not have access to a chromosome browser. A chromosome browser allows you to visualize the physical locations that you share with someone else (see below). Some find this a helpful tool when analyzing their DNA matches, though in my opinion, it is not essential.
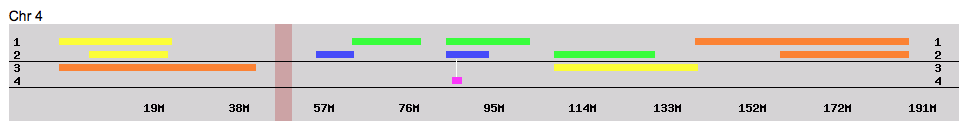 GEDmatch also has some great genealogy features that let you analyze your pedigree against someone else’s, as well as the ability to search all the pedigree charts in their system so you can look specifically for a descendant of a particular relative. However, even with all of these great features, GEDmatch is still yet another website you have to navigate. With that, there will be a learning curve and certainly some frustration.
GEDmatch also has some great genealogy features that let you analyze your pedigree against someone else’s, as well as the ability to search all the pedigree charts in their system so you can look specifically for a descendant of a particular relative. However, even with all of these great features, GEDmatch is still yet another website you have to navigate. With that, there will be a learning curve and certainly some frustration.
GEDMatch or Not?
So, is it worth it? If you are fairly comfortable with the website where you were tested, and you are feeling both curious and patient, I say go for it!
It’s too much to tell you right this minute how to download your data from your testing site and upload it to GEDmatch, but you’re in luck! I’ve put step-by-step instructions for getting started in a free tutorial on my website at www.yourDNAguide.com/transferring.

After you’ve done the upload, you may need a little bit more help to navigate the GEDmatch site because there are so many great tools on it. I recently published a GEDmatch Quick Guide, where I have condensed into four pages the most essential features of GEDmatch to get you started and help you make use of this tool for genetic genealogy. Using my guide is an inexpensive and easy way to get a lot more out of a free online resource. I will also be adding more GEDmatch tutorials to my online tutorial series later this fall. Genealogy Gems fans get a nice discount on these! (Click here for that discount).
By the way, have you tried GEDmatch? I would love to hear about your experiences. You can email me at guide@yourDNAguide.com.
DNA QUICK GUIDE BUNDLES

Advanced DNA Quick Guide Bundle by Diahan Southard which includes:
- GEDmatch: A Next Step for your Autosomal DNA Test
- Organizing Your DNA Matches: A Companion Guide
- Next Steps: Working with Your Autosomal DNA Matches

SUPER DNA Quick Guide Bundle by Diahan Southard with ALL 10 Guides
- Getting Started: Genetics for the Genealogist
- Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist
- Mitochondrial DNA for the Genealogist
- Y Chromosome DNA for the Genealogist
and Testing Companies:
- Understanding Ancestry: A Companion Guide to Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist
- Understanding Family Tree DNA: A Companion Guide to Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist
- Understanding 23 and Me: A Companion Guide to Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist
and Advanced Tools
- Next Steps: Working With Your Autosomal DNA Matches
- Organzing Your DNA Matches
- GEDmatch: A Next Step for Your Autosomal DNA Test
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 20, 2016 | 01 What's New, DNA, Societies |

The Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) accepts limited DNA evidence to prove descent from a Revolutionary War veteran. In my opinion, the DAR DNA policy is a little too limited. Here’s why–and what you can do.
Membership to the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) has been a holy grail for U.S. genealogists for 125 years. With its requirement of proof of a “lineal bloodline descendant from an ancestor who aided in achieving American independence” in three categories: birth, marriage, and death, as well as proof of Revolutionary War Service, membership is exclusive to those with an iron-clad paper trail.
That is, until 2014, when the DAR added DNA evidence to its list of acceptable documents proving a relationship to a Revolutionary War ancestor.
What does the DAR DNA Policy Accept?
The DAR only accepts one of the three forms of DNA testing which is the Y chromosome test, or YDNA. The YDNA traces only a direct paternal line, making it a great choice when trying to link living males with their Revolutionary counterparts. This YDNA is basically passed unchanged from generation to generation, making the modern day holder of the YDNA the proud owner of possibly exactly the same YDNA that fought the Redcoats. That’s pretty cool, don’t you think?
The DAR recently announced that to further help those wanting to use their YDNA as part of their application, they have formed a project at Family Tree DNA, the company that provides the YDNA testing. Projects are absolutely the best way to get the most out of your YDNA testing. There are surname projects, location projects, haplogroup (deep ancestral group) projects, and even special interest group projects, such as this one for the DAR.
While the results of the testing are only available to members of the group, the statistics page gives us an idea of the scope of this project. They currently have 1,242 total members and what looks to be about 430 YDNA tests completed (though it is admittedly difficult to tell based on the chart online.) This means if you think your paternal line may be a candidate for the DAR, you can have a representative of your line tested and compared to the group. If you find a match, you will have relative certainty that you do connect to that Patriot, and can then be more confident in your traditional research in pursuit of the necessary paper connections.
In April the DAR opened up project membership to include mtDNA and autosomal DNA. They will not be using these two kinds of DNA in their applications (yet), but hopefully this project will pave the way for the addition of those tests in the future (though, for several reasons, inclusion of these tests in the application process will be more difficult.)
Though, in all honesty, they have made the YDNA process difficult enough. Let’s say that you are actually able to trace down multiple generations to find a direct male descendant of your Revolutionary guy to be tested, an individual who is, the DAR mandates, “sharing your maiden name or your mother’s maiden name,” and you convince that unassuming relative to give up his saliva, you still are only half way there. The DAR guidelines also state that you have to have a second individual who is “a descendant of the same Revolutionary War ancestor through a different unbroken male lineage that has been previously proven on a DAR application…” (I added the emphasis here.)
A Practical Example of the DAR DNA Policy
OK, so let’s say you are a genealogical whiz and, let’s face it, you were lucky, and you find two such candidates and have them tested.
Well, the DAR tells us that those two men must match EXACTLY on the 37 YDNA markers tested. Now there is no telling when that YDNA might experience a mutation. So to me it seems a little unfair to require perfection. So it is possible, that even after all the work of finding the right guys to be tested, the test itself may work against you, as even one difference is enough to keep this YDNA off of your application, at least for now.
So while I applaud the DAR for using YDNA testing at all, and for spearheading a special interest project at Family Tree DNA, the reality is that the limitations of direct paternal line genealogy and the requirements of testing make it unlikely that very many will be able to take advantage of the YDNA in their DAR applications.
However, there are a few things you can take away from this article now:
- First, collect those DNA samples whenever you can, especially for key relatives, like your paternal line and the oldest living generation (whose DNA is less likely to have experienced any mutation.)
- Second, keep your research paper trail strong. Nothing in the near future of the genetic genealogy industry tells us that distant relative connections (like to your Revolutionary War ancestor) will be provable by DNA alone.
- And third, definitely look at crowd-sourced studies for your particular DNA. Those surname, location, haplogroup, and special interest group projects I mentioned from FTDNA are just some of the ones that might help your research—or that you could use to help someone else’s. I’ve talked about these studies before: click here to read about them.
My Complete DNA for Genealogy Research Guide Series
I am Diahan Southard, Your DNA Guide, and the author of a series of genetic genealogy quick guides. My guide called Y Chromosome DNA for the Genealogist is the perfect tool to help guide you through the testing and analysis process. Click here to learn more about this guide and here for all of my guides, or click here to learn more about my series of how-to videos, also available to Gems fans for a special price.
Thanks for sharing this post with your genealogy friends who do DNA research (especially those who may have Revolutionary War ancestors!)















 GEDmatch is set up just like your testing company and provides two kinds of reports: ethnicity results and a match list. Remember, ethnicity results, meaning those pie charts that report you are 15% Italian and 32% Irish, are based on two factors: a reference population and fancy math. GEDmatch has gathered data from multiple academic sources to provide you with several different iterations of ethnicity reports. This is like getting a second (and third and fourth, etc) opinion on a science that is still emerging. It is a fun exercise, but will likely not impact your genealogy research very much.
GEDmatch is set up just like your testing company and provides two kinds of reports: ethnicity results and a match list. Remember, ethnicity results, meaning those pie charts that report you are 15% Italian and 32% Irish, are based on two factors: a reference population and fancy math. GEDmatch has gathered data from multiple academic sources to provide you with several different iterations of ethnicity reports. This is like getting a second (and third and fourth, etc) opinion on a science that is still emerging. It is a fun exercise, but will likely not impact your genealogy research very much. GEDmatch also has some great genealogy features that let you analyze your pedigree against someone else’s, as well as the ability to search all the pedigree charts in their system so you can look specifically for a descendant of a particular relative. However, even with all of these great features, GEDmatch is still yet another website you have to navigate. With that, there will be a learning curve and certainly some frustration.
GEDmatch also has some great genealogy features that let you analyze your pedigree against someone else’s, as well as the ability to search all the pedigree charts in their system so you can look specifically for a descendant of a particular relative. However, even with all of these great features, GEDmatch is still yet another website you have to navigate. With that, there will be a learning curve and certainly some frustration.






