by | Feb 18, 2014 | Beginner, FamilySearch, History, Immigration

Women’s suffragists demonstrate in February 1913. Photographer unknown. Library of Congress, Prints & Photographs Division.
We’re nearing the completion of the enormous Community Indexing Project of U.S. Immigration and Naturalization Records. Already finding naturalization records is a lot easier: we can search newly-created indexes to millions of naturalization records at FamilySearch.org. But often we don’t find the women we’re looking for.
Let’s look at why. But I’ll warn you, the reasons aren’t pretty. In the past, women had very few legal rights. None could vote. Married women had even fewer rights. Typically their legal identity disappeared when they married, enveloped by their husband’s. Married women did not handle legal matters in their own name, own property or keep their own money. Sometimes they did not even have legal liability for their actions. This was known as the legal principle of coverture.
In 1855, a law was enacted establishing that women who weren’t ineligible for other reasons (like race) were automatically made citizens when their husbands were naturalized. There was no extra paperwork or court costs. Their husbands’ papers (in combination with their marriage records) served as proof of the women’s citizenship, even though before 1906, you will not usually find the women’s names even listed on their husbands’ applications.
This represented a step forward for most married women, but not all. If a husband didn’t naturalize, the wife couldn’t naturalize without him. On the flip side, if a U.S.-born woman married a foreigner, she often lost her U.S. citizenship, whether or not she left the country. This problem wasn’t fully resolved until many years later; learn more about the laws and resulting paperwork in this article by the National Archives.
Naturalization laws were not applied evenly, and some women got their citizenship anyway. Eventually, as women won voting rights in various states in the early 1900s, men who applied to naturalize were sometimes denied because their wives, who would be granted citizenship and therefore voting privileges, didn’t speak English or meet other requirements. Men complained that their wives’ nationalities were getting in the way, a problem women had lived with for years!
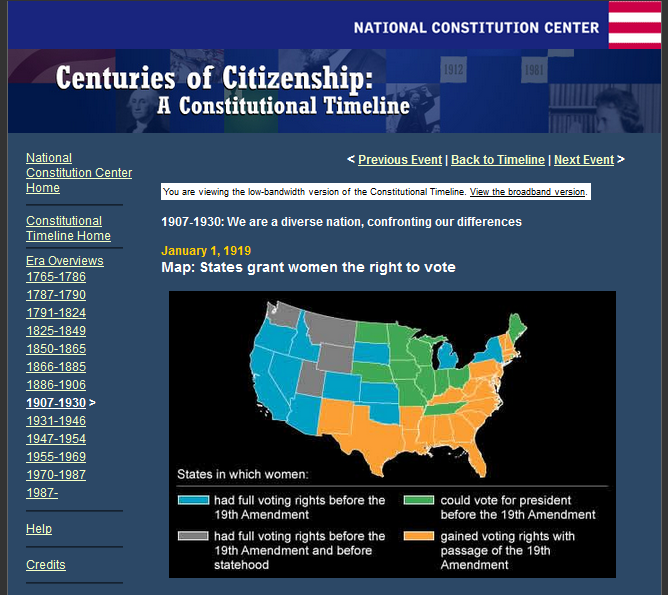
Check out this interactive timeline on women’s right to vote in the U.S.
In 1922, women gained the right to naturalize independent of marital status. If their husbands were already citizens, they didn’t have to file declarations of intentions (the first step in the paperwork process), just a petition (the second step in the process). Otherwise, they had to fill out both sets of papers. Eventually even this link to their husbands’ citizenship disappeared, and they just filled out their own entirely separate paperwork.

My Great Grandmother’s Petition for Naturalization
What about unmarried women and widows? They could apply for naturalization, but in especially before the 1900s, they sometimes didn’t if they had no property. They could not vote and the law didn’t always treat them equally. They saw little benefit in investing the funds and time in applying for citizenship.
It’s fascinating how much we can learn as family historians about the status of women by the way they were handled in the records we research. The history of women in naturalization records reminds us to look past the paperwork to the reasons and intentions behind it. Unless we really understand the history of the laws and the culture at that time, we can’t be sure that we have exhausted all of the options.
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 17, 2014 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, Beginner, FamilySearch, Records & databases
Are you tracing the family history of someone who lived in the U.S. during the 20th century? Check out a wonderful free database in the United States called the Social  Security Death Index, or the SSDI. Keep reading for 5 FREE online sources for the SSDI, 7 tips for searching the SSDI and what you can do with SSDI info.
Security Death Index, or the SSDI. Keep reading for 5 FREE online sources for the SSDI, 7 tips for searching the SSDI and what you can do with SSDI info.
In 1935 the Social Security Act was signed into law by President Franklin Roosevelt, and consequently more than thirty million Americans were registered by 1937. Today, the Death Master File from the Social Security Administration contains over 89 million records of deaths that have been reported to the Social Security Administration and they are publicly available online.
Most of the information included in the index dates from 1962, although some data is from as early as 1937. This is because the Social Security Administration began to use a computer database for processing requests for benefits in 1962. Many of the earlier records back to 1937 have not been added.
The SSDI does not have a death record for everyone; and occasionally you may find an error here and there if something was reported inaccurately, but overall it’s a terrific resource! It’s especially great for many people who were missed in the 1890 census or whose birth predated vital records registration in their home state. Remember they just needed to live past 1937 and to have worked to have been included. So they could have been born sometime in the later 1800s.
5 FREE Online Sources for the SSDI
Several genealogy websites provide free access to the SSDI, including (click to go right to the SSDI at these sites):
On the Search page, enter your relative’s name and other details you’re asked for. Hopefully you will get back results that includes your relative!
7 Tips for Searching the SSDI
If your relative doesn’t show up in the SSDI, even though you know they worked after 1937 and you know they have passed away, try these search tips:
1. Does the website you are using to search the SSDI have the most current version available? Look in the database description on the site to see how recently it was updated. Try searching at other sites.
2. Make sure that you tried alternate spellings for their name. You never know how it might have been typed into the SSDI database.
3. Many SSDI indexes allow you to use wildcards in your search. So for example you could type in “Pat*” which would pull up any name that has the first three letters as PAT such as Patrick, Patricia, etc.
4. Try using less information in your search. Maybe one of the details you’ve been including is different in the SSDI database. For example it may ask for state and you enter California because that’s where grandpa died, when they were looking for Oklahoma because that’s where he first applied for his social security card. By leaving off the state you’ll get more results. Or leave off the birth year because even though you know it’s correct, it may have been recorded incorrectly in the SSDI and therefore it’s preventing your ancestor from appearing in the search results.
5. Leave out the middle name because middle names are not usually included in the database. However, if you don’t have luck with their given name, try searching the middle name as their given name. In the case of my grandfather his given name was Robert but he went by the initial J.B. But in the SSDI his name is spelled out as JAY BEE!
6. Remember that married women will most likely be listed under their married surname, not their maiden name. But if you strike out with the married name, go ahead and give the maiden a try. She may have applied for her card when single, and never bothered to update the Administration’s records. Or if she was married more than once, check all her married names for the same reason.
7. Don’t include the zip code if there is a search field for it because zip codes did not appear in earlier records.
While most folks will appear in the SSDI, there are those who just won’t. But knowing where information is not located can be as important down the road in your research as knowing where it IS located, so I recommend making a note in your database that you did search the SSDI with no result. This will save you from duplicating the effort down the road because you forgot that you looked there.
What You Can Do with SSDI Information
Now, here comes the most exciting part of the SSDI: what you can do with that information. First, it usually includes a death date (at least the month and year) and sometimes a state and last known residence. Use this information to look for death records, obituaries, cemetery and funeral records. And use that Social Security Number to order a copy of your relative’s application for that number: the SS-5. Click here to read more about the SS-5 and how to order it.
Up next, read:
Get Started: How to Find Your Family History for Free
7 Great Ways to Use Your iPad for Family History
How to Find Your Family Tree Online
Best Genealogy Software
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 16, 2014 | 01 What's New, Adoption, Beginner, History
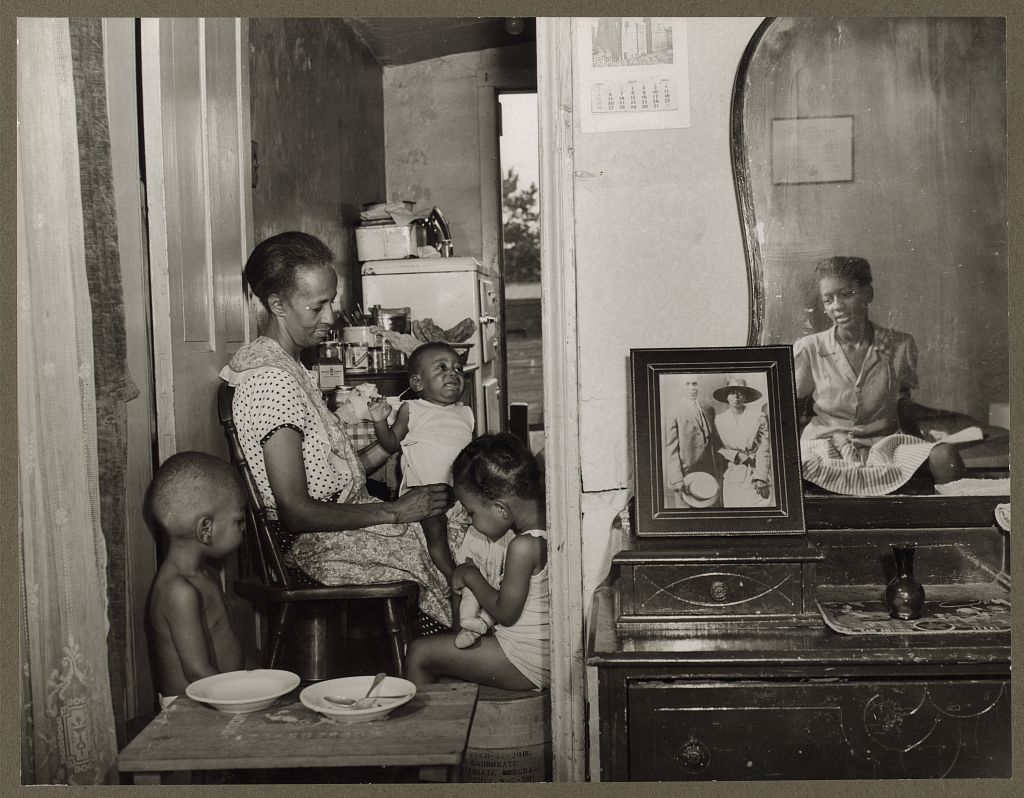

Mrs. Ella Watson, a government charwoman, with three grandchildren and her adopted daughter [reflected in the mirror]. Image from The Gordon Parks Archives in the Library of Congress.
Formal, legal adoption wasn’t common in the U.S. until the late 1800s. (State adoption laws didn’t even exist until after Massachusetts passed the first one in 1851.) Before that, if mom and dad couldn’t take care of a child, a relative, neighbor or friend took that child in, or the child was sent to a county orphanage or poor home. In even earlier days, orphaned or poverty-stricken children were also sold by their towns into indentures.
The Adoption History Project at the University of Oregon has a great timeline of adoption history in the U.S. Check it out to see what was going on when your family member was adopted.
To learn more about adoption and genealogy research, check out these links:
FamilySearch Wiki U.S. Adoption Research
All About Adoption Research by Maureen Taylor
RootsWeb’s Guide to Tracing Family Trees: Adoption
by Lisa Cooke | Feb 11, 2014 | 01 What's New, Family History Library, Family History Podcast
Listen to the Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast by Lisa Louise Cooke. It’s a great series for learning the research ropes and well as refreshing your skills.
Originally Published 2009
Republished February 11, 2014
[display_podcast]
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-2009. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.
Episode 18: Using Family History Centers, Part II
This episode is the second in a series about Family History Centers, the regional satellite facilities of the main Family History Library in Salt Lake City, Utah.
My very special guest is friend of the show Margery Bell, Assistant Director of the Oakland Family History Center in Oakland, California. Last week Margery Bell introduced us to the Family History Center, and walked us step by step through the process of ordering and using microfilm. She also discussed the wide range of resources beyond microfilm that you will find at both your local Family History Center and one of the 14 larger regional centers.
In our first segment in this episode she preps us for our visit and reveals the subscription websites you can use for free at Family History Centers. Then in our second segment, Margery discusses making copies in all forms, the future of digitizing microfilm, and the future of Family History Centers.
We also talk about tips for visiting the main Family History Library (see link below and link to Show Notes, above).
In next week’s show, part three of the series on Family History Centers, Margery Bell will talk about educational opportunities through the centers, she’ll give us her 7 top tips for getting the most out of your visit, and we’ll wrap up with some wonderful inspirational stories of genealogical serendipity.
Updates/Links
- Some Family History Centers are now called FamilySearch Centers. Many Centers have opened in public and private libraries in the past few years, not just in meetinghouses of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Click here to find a FamilySearch Center/Family History Center near you.
- Many records are now available online, either in indexed form or just the digitized images. Click here to visit the online catalog of the Family History Library. When you find something you’d like to order, look at the catalog entry. If it’s digitized and online, you’ll see a link.
- Many of the same principles apply to visiting the Family History Library and Family History Centers. Click here for updated information about preparing for your visit to the Family History Library (this is instead of the handout mentioned in the podcast).
- Here’s a link to the main Family History Centers page on the FamilySearch website, which has an updated list of databases available there (and a lot more information).
by | Feb 7, 2014 | 01 What's New, Collaborate, Source Citation
 I’m hearing so much these days about source citation and I love it! Everyone seems to be getting smarter and better at sourcing their research finds. And genealogy websites are making it easier and more collaborative. Here’s just one example, an announcement just made by BillionGraves:
I’m hearing so much these days about source citation and I love it! Everyone seems to be getting smarter and better at sourcing their research finds. And genealogy websites are making it easier and more collaborative. Here’s just one example, an announcement just made by BillionGraves:
“After months of work in response to hundreds of user requests, BillionGraves has added several new features designed to validate and enhance the headstone records found on BillionGraves. The Supporting Record feature now allows users to upload evidence-based documents that support the BillionGraves records that have been collected through our mobile Apps. This means that users are now able to upload headstones, birth/death, burial, marriage, cremation, and many other types of records without needing a smart phone.
Thousands of records are being uploaded every day and are breaking down genealogy brick walls and making connections that once seemed impossible. While working closely with our users and genealogists we found that there were many headstones and burials that just couldn’t be accounted for with our current systems; including unmarked graves, cremation scatterings, destroyed stones, and so on. Our Supporting Records features eliminate this problem while maintaining the validity and accuracy of the BillionGraves database.”




 Security Death Index, or the SSDI. Keep reading for 5 FREE online sources for the SSDI, 7 tips for searching the SSDI and what you can do with SSDI info.
Security Death Index, or the SSDI. Keep reading for 5 FREE online sources for the SSDI, 7 tips for searching the SSDI and what you can do with SSDI info.




