by Lisa Cooke | Oct 23, 2017 | 01 What's New, DNA, Trees |
If you’re doing DNA tests for family history, you may see lots of predicted cousin matches: 2nd, 3rd, 4th, etc…..But what does that predicted genetic relationship actually mean? Learn about centimorgans, the powerful genetic genealogy unit of measure, and how it helps your research.

How DNA Tests Measure Genetic Relationships
 When we are looking at genetic relationships, there are also many ways we can measure them. But ultimately, we want the testing company to tell us how likely it is that a particular individual shares a single, recent common ancestor with us. One factor in this calculation is to take into account the total amount of DNA we share with that match.
When we are looking at genetic relationships, there are also many ways we can measure them. But ultimately, we want the testing company to tell us how likely it is that a particular individual shares a single, recent common ancestor with us. One factor in this calculation is to take into account the total amount of DNA we share with that match.
Currently, all the testing companies are reporting this sum in centimorgans (cMs). Every company reports to you the total number of shared cMs, as outlined below.
 AncestryDNA: Click on the match to access the personal profile page for that match. In the second section, under Predicted Relationship, you will see the confidence level. To the right of the confidence level, you will see a grey circle with a little “i” in it. Clicking there will show you the total amount of shared cMs as well as how many pieces of DNA you share.
AncestryDNA: Click on the match to access the personal profile page for that match. In the second section, under Predicted Relationship, you will see the confidence level. To the right of the confidence level, you will see a grey circle with a little “i” in it. Clicking there will show you the total amount of shared cMs as well as how many pieces of DNA you share.- Family Tree DNA: On the main match page for your Family Finder results, you will see the total amount of shared cMs in the third column.
- 23andMe: You can see the percentage of shared DNA from the main DNA Relatives home page. To convert the percentage into centimorgans, just multiply your percentage by 68 (that will at least get you close). You can also see total shared cMs in the chromosome browser tool (go to Tools > DNA Relatives > DNA).
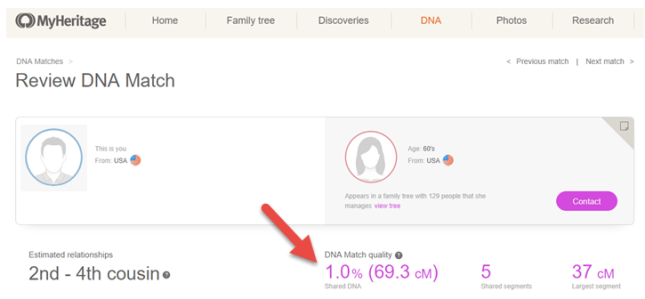
- MyHeritageDNA: The total amount of shared DNA is shown on the main match page under the title Match Quality. MyHeritage also has a new DNA Match Review page. Click here to read more about that.
Centimorgan: A Genetic “Crystal Ball”
 It is very tempting to think of a cM just like you would think of an inch or a centimeter, and for all practical purposes, that is okay. But it is actually much more complicated than that.
It is very tempting to think of a cM just like you would think of an inch or a centimeter, and for all practical purposes, that is okay. But it is actually much more complicated than that.
A cM is actually more like a crystal ball: it helps us predict how likely a piece of DNA looks exactly as it did a generation ago. This, in turn, helps us calculate how far back we should be looking for the common ancestor between two people.
But for our practical purposes, you can use the total amount of shared DNA, in combination with this chart compiled by Blaine Bettinger and the Shared cM Project, to better assess your genealogical relationship with your match based on your genetics.
To use the chart, take the total amount of shared DNA you have with a match, and look up that number in the chart to get an idea of what kind of genealogical relationship might best fit the genetics that you see. For example, if I share 69 cM with my match, we might be third cousins. But we might also be second cousins once or twice removed.
How do you figure out which one? Simply put: do genealogy research! It’s time to use traditional records and research skills to better understand the genetic clues in your family history mysteries.

My series of DNA quick reference guides can help you get the most out of your DNA tests for family history. I definitely recommend the value-priced bundle of all 10 guides. But I especially recommend the guides listed below if you’re to the point where you’re trying to understand what genetic relationships mean:
Thanks for sharing this post with someone who would enjoy reading it! You’re a gem!
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

by Lisa Cooke | Aug 27, 2015 | 01 What's New, Ancestry, DNA, images, Trees
A new tool at Ancestry DNA is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open!
is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open!

I have been up since 5:30 with plenty of goals and ambitions for today. But I got distracted. Distracted by a new tool at AncestryDNA that is blowing my genealogy mysteries wide open.
The new tool AncestryDNA Common Matches tool is hiding between the “Pedigrees and Surnames” filter and the “Map and Locations” filter on your matches’ main match page. The Common Matches tool pulls out the shared 4th cousin or higher matches between two people.
Let’s take a look at how this might work for you.
 Let’s say you have a second cousin, Denise, that you have already identified in the Ancestry database and you know your common ancestral couple is Joseph and Louise Mitchell. You want to gather others who share DNA with both you and Denise. Those individuals then have a high likelihood of being related to Joseph and Louise in some way.
Let’s say you have a second cousin, Denise, that you have already identified in the Ancestry database and you know your common ancestral couple is Joseph and Louise Mitchell. You want to gather others who share DNA with both you and Denise. Those individuals then have a high likelihood of being related to Joseph and Louise in some way.
So we click on the “Shared Matches” button on Denise’s page and find that Mike, Spencer, and Wendy all have DNA in common with you and Denise. After reviewing pedigree charts, you are able to determine that Mike is related through Louise’s sister and Wendy is related through Joseph’s brother. Note that Wendy’s actual relationship to you is not 4th cousin, as it is shown, but she is actually your 3rd cousin once removed. Remember that the relationship given is not always the exact relationship of two people who have been tested.
 But what about Spencer? Spencer, unfortunately has not yet linked his family tree to his Ancestry account or answered any of your queries about his family tree. I am sure he has just been busy. Or he doesn’t know his family tree. Or his computer was captured by aliens or smashed by his two-year-old grandson just as he was about to click “send” and reveal how the two of you were connected. Whatever the case may be, up until this point you haven’t heard a peep from Spencer and therefore had absolutely no way to figure out how Spencer was related to you.
But what about Spencer? Spencer, unfortunately has not yet linked his family tree to his Ancestry account or answered any of your queries about his family tree. I am sure he has just been busy. Or he doesn’t know his family tree. Or his computer was captured by aliens or smashed by his two-year-old grandson just as he was about to click “send” and reveal how the two of you were connected. Whatever the case may be, up until this point you haven’t heard a peep from Spencer and therefore had absolutely no way to figure out how Spencer was related to you.
But now you know that he is somehow associated with the Joseph and Louise Mitchell family because he came up as In Common With (ICW) you and Denise.
We can take this one step further and ask Ancestry to show us who has DNA ICW you and Spencer. You can see here that while Mike still remains, Wendy has dropped off the list. Now there are two possible explanations for this: The first is that Spencer is related through Louise’s parents, John and Sarah, and that is why he is not sharing DNA with Wendy.
The other, less likely, possibility is that Spencer is related through Joseph’s parents Louis and Mary, but doesn’t share enough DNA with Wendy to be detected on this test.
While this information is helpful, it still hasn’t completely solved the case. The first thing you should do with your new-found knowledge is start sending more pointed questions to your matches. Here is an example message you might send to Spencer:
“Dear Spencer,
I was just playing around with the new AncestryDNA Common Matches tool and I see that you are related to a few of my other matches that connect through Joseph and Louise Mitchell. Louise’s parents, John and Sarah Marsh, were both born in Mississippi in the 1840’s and Joseph’s parents Joseph and Mary Mitchell, were born in Tennessee in 1856 and 1863 respectively.
Do any of these names or places sound familiar to you?
I am looking forward to working with you on this connection.
Your DNA Cousin, Diahan”
Assuming this garners a response, you can then work together to find your connection. If his budget is not allowing for a new computer at this time and you never hear from Spencer, the key to figuring out how he is related to you may be in the new match, Beth, who is ICW you and Spencer. If you can figure out how Beth is related to you, you will know Spencer is related in a similar way.
 If you’ve decided you would like to get in the DNA game, start with Ancestry DNA: Genetic Testing – DNA Test
If you’ve decided you would like to get in the DNA game, start with Ancestry DNA: Genetic Testing – DNA Test , and then head over to AncestryDNA and start growing your genetic family tree!
, and then head over to AncestryDNA and start growing your genetic family tree!
For a little more guidance, I suggest you purchase my laminated quick guides, “Understanding AncestryDNA and “Understanding Family Tree DNA.” These are also available as a part of a complete bundle of DNA guides specifically designed to help you navigate your results at the leading genetic genealogy testing companies. Click here to see all our DNA quick guides.

 When we are looking at genetic relationships, there are also many ways we can measure them. But ultimately, we want the testing company to tell us how likely it is that a particular individual shares a single, recent common ancestor with us. One factor in this calculation is to take into account the total amount of DNA we share with that match.
When we are looking at genetic relationships, there are also many ways we can measure them. But ultimately, we want the testing company to tell us how likely it is that a particular individual shares a single, recent common ancestor with us. One factor in this calculation is to take into account the total amount of DNA we share with that match. AncestryDNA: Click on the match to access the personal profile page for that match. In the second section, under Predicted Relationship, you will see the confidence level. To the right of the confidence level, you will see a grey circle with a little “i” in it. Clicking there will show you the total amount of shared cMs as well as how many pieces of DNA you share.
AncestryDNA: Click on the match to access the personal profile page for that match. In the second section, under Predicted Relationship, you will see the confidence level. To the right of the confidence level, you will see a grey circle with a little “i” in it. Clicking there will show you the total amount of shared cMs as well as how many pieces of DNA you share. It is very tempting to think of a cM just like you would think of an inch or a centimeter, and for all practical purposes, that is okay. But it is actually much more complicated than that.
It is very tempting to think of a cM just like you would think of an inch or a centimeter, and for all practical purposes, that is okay. But it is actually much more complicated than that.










