Find Undiscovered Treasures at Ancestry.com: Expert Tips
Ancestry.com is packed with all kinds of mostly-undiscovered genealogical treasures, and some of them you’ll never find from a search box.
Here, expert Nancy Hendrickson shares some favorite treasures, tips for finding those treasures, and helpful reminders for improving your genealogy research.

(We provide links for your convenience to the various online resources and some may be affiliate links for which we receive compensation at no additional expense to you. Thank you for your support.)
Ancestry.com is a “genealogy giant:” one of the four biggest global records resources. Whether you subscribe or have free access through your local library or Family History Center, you should not miss exploring this website for your family history.
Ancestry is also a financial investment. If you’ve been using the site for quite a while, you may be wondering if you are really getting all you can out of it’s vast genealogical record collections and many research tools.
Nancy Hendrickson, the author of The Unofficial Guide to Ancestry.com and the Unofficial Ancestry.com Workbook: A How-To Manual for Tracing Your Family Tree on the #1 Genealogy Website knows the website inside and out. Today she’s sharing four great tips for taking your research to the next level. In addition, we’ve added in some examples and additional things to consider. So let’s get started using Ancestry more effectively.
4 Tips for Using Ancestry.com More Effectively
1. Verify what you learn.
Any single record can be wrong, incomplete, or misread by you or by the person how indexed it. Double check the assertions made in the record by looking for that same information in additional sources. Be careful to make sure your sources weren’t getting their information from the same person or place. Otherwise, they’ll naturally say the same thing!
Nobody wants to discover conflicting information, of course. But you do want to know if something is inaccurate before it leads you down a wrong research path.
The best thing about verifying facts in additional sources is that sometimes you find NEW or BETTER information such as:
- parents’ names,
- a middle name that proves key to someone’s identity,
- or a burial place.
For example, let’s say you find an ancestor’s death date in the Social Security Death Index. While it’s a great source, don’t stop there!
Like any record, the SSDI is sometimes wrong and the information it contains is definitely limited. Use the Ancestry.com Card Catalog to see what records about death may be on the site for that time and place. You’ll find the Card Catalog under Search in the main menu.
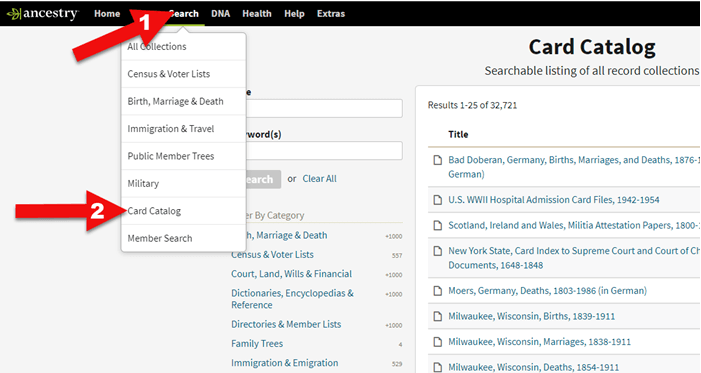
Ancestry Card Catalog
Use the filters on the left side to drill down to death records for the location you want. Remember that records collections have been created on a specific geographical level: try local, regional (such as state or province) as well as national levels.
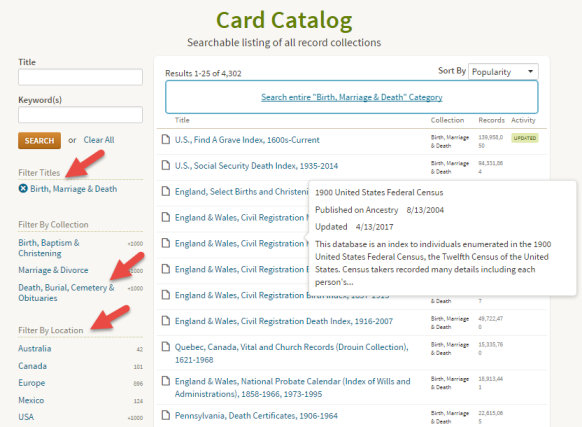
Using the Card Catalog search filters
2. Don’t just repeat what other people’s trees say.
Seeing the same information over and over can provide a false sense of accuracy. Remember, just because seven different online trees name the same parents for one of your ancestors doesn’t mean those are the correct parents. Those Ancestry users may all be misquoting the same wrong source without actually verifying the information!
You often come across likely matches in others’ trees when you review Ancestry’s automated “leaf” hints, or when you run a general search on a name. When you do, it’s simply an indication that the tree may be worth exploring. Here’s an example:
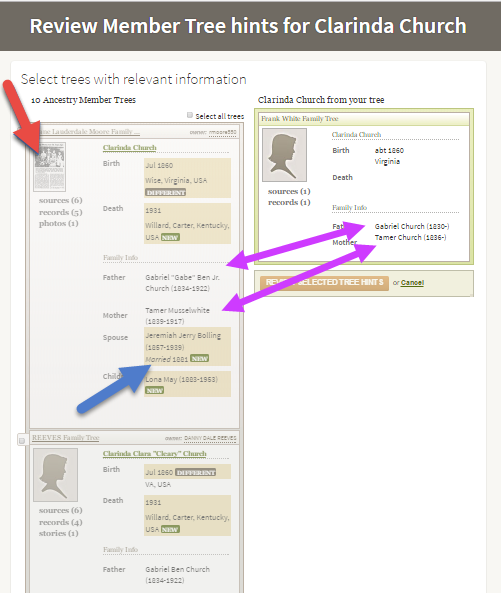
Exploring Ancestry Hints
Let’s take a closer look at this example.
The purple arrows: You can see that multiple pieces of very specific information are the same on your tree and another one.
The red arrow: You see sources attached to that person’s profile, such as the news article thumbnail image. (Note the difference with the record shown below, with just an empty profile image.) Yes, you will definitely want to review that news article!
The blue arrow: In addition to either of the above, you also see specific information that is unknown to you.
This tree profile looks promising enough you might naturally consider reviewing the tree hint and attaching it to yours. But then you wouldn’t be able to see the news article or other sources attached to that tree.
Instead, click the checkbox and then click the name of the tree to look at it and its attached sources:
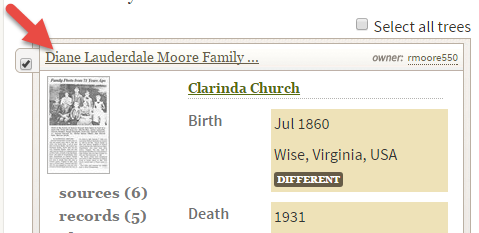
Select the tree to review it more closely.
Then you’ll be able to check out the news article along with the other sources and records attached to this person’s profile. You won’t just see what that person thinks about your common ancestor – you’ll see evidence of why she thinks it.
3. Ancestry.com has more than indexed historical documents.
Nancy reminds us that “Ancestry.com is a fantastic resource for old maps, stories, photos, published county histories, and more. For example, looking at the old maps in their collections can reveal the true nature of an ancestor’s daily life, hardships, travels, and more. And your chance of finding early American ancestors is high in county histories: there were fewer people and early settlers were talked about, even if the family wasn’t wealthy or prominent.”
Here are some of Nancy’s favorite collections at Ancestry:
U.S., Indexed County Land Ownership Maps, 1860-1918
This collection includes nearly 7 million records extracted from about 1,200 county and land ownership maps from across the country. These are indexed by property owners’ names.
According to the collection description, “They also indicate township and county boundaries and can include photos of county officers, landholders, and some buildings and homes.”
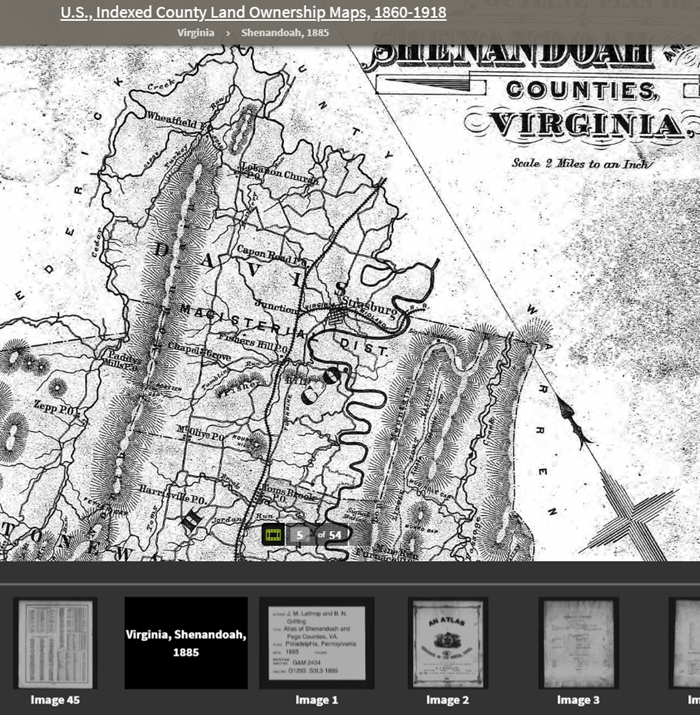
Example: Shenandoah Counties, Virginia – included in U.S., Indexed County Land Ownership Maps, 1860-1918
U.S., County and Regional Histories and Atlases, 1804-1984
This is a browse-only collection of “more than 2,200 volumes of county and regional histories from California, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin.

An Illustrated Historical Atlas of Manitowoc County, Wisconsin, 1878 in the U.S., County and Regional Histories and Atlases, 1804-1984 collection
In them you’ll find history, biographical sketches, maps, business notices, statistics and population numbers, pictures, descriptions of industry and business, stories of early settlement and pioneers, colleges and universities, military history, geography, and plenty of other details.”
Reminder: you can’t search this database by an ancestor’s name. Instead, look for places, and then start reading.
Historic Land Ownership and Reference Atlases, 1507-2000
A collection of maps and atlases detailing land areas that comprise the present-day United States and Canada, as well as various other parts of the world. It contains a variety of maps and atlases created for different scopes and purposes, including land ownership atlases and bird’s-eye view maps.
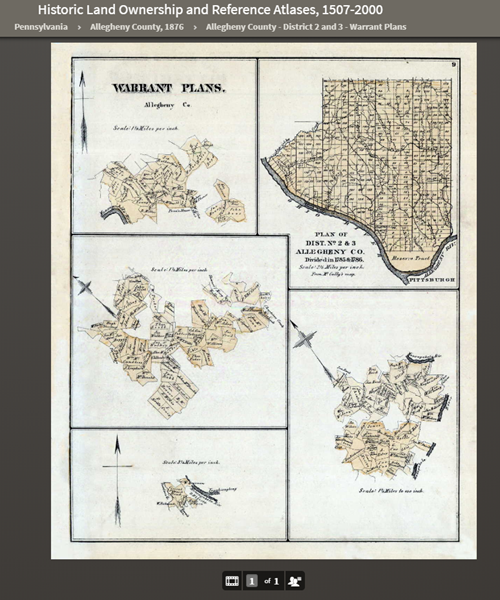
Warrant Plan Records in the Historic Land Ownership and Reference Atlases, 1507-2000 Collection at Ancestry
Land ownership atlases usually show the names of contemporary owners or occupants of land and structures.
Some of the maps depict countries and wider geographical areas, while others depict counties, cities, towns, and smaller geographical areas.
4. Expand your search to the other Ancestry resources on the Web
Ancestry owns a lot of other web resources. Search these too!
Nancy says, “They include Find A Grave, Fold3, and RootsWeb, one of the oldest online genealogy communities around. Don’t give up! Keep looking in other places for the information you want to find.”
Find A Grave
Search results from Ancestry.com do include Find A Grave entries. Many of these contain additional information about the deceased and links to their relatives. As always, be sure to confirm the information you find here.
Fold3
Fold3 is home to millions of U.S. military records. Ancestry.com subscribers can upgrade their subscription to include Fold3 access, or you can subscribe separately.
RootsWeb
RootsWeb is a free and long-lived family history web resource, now hosted by Ancestry.
“The primary purpose and function of RootsWeb.com is to connect people so that they can help each other and share genealogical research,” says the site. “Most resources on RootsWeb.com are designed to facilitate such connections.” You can use RootsWeb in a variety of ways: search it, contribute records, upload your family tree, post your family surnames on a board others can see, and more.
Ancestry has changed one of the ways RootsWeb users have traditionally connected: Mailing Lists. According to the website:
“Beginning March 2nd, 2020 the Mailing Lists functionality on RootsWeb will be discontinued. Users will no longer be able to send outgoing emails or accept incoming emails. Additionally, administration tools will no longer be available to list administrators and mailing lists will be put into an archival state. Administrators may save the email addresses in their list prior to March 2nd. After that, mailing list archives will remain available and searchable on RootsWeb. As an alternative to RootsWeb Mailing Lists, Ancestry message boards are a great option to network with others in the genealogy community. Message boards are available for free with an Ancestry registered account.”
Learn More about Using Ancestry
Nancy Hendrickson’s Book
Nancy shares many more Ancestry tips and treasures in her Unofficial Ancestry.com Workbook. To get the most out of this book read the section on using the Ancestry.com Catalog. Nancy does 95% of her research in the catalog. The workbook is divided into topics, such as military records, so choose a chapter that fits your current goals. It’s also important to not just read the workbook, but also do the exercises. They teach you Nancy’s thought processes for how she finds specific answers or approaches certain types of problems. Then you can apply the same concepts to your own research. Don’t miss the chapter on social history. That’s where you’ll dig into everyday life. And finally, take advantage of the forms that are included. They will help you log your findings and analyze what you’ve learned.
Genealogy Gems Article
Browse-only collections at Ancestry and other genealogy websites are sometimes viewed as inaccessible, but they are actually a hidden treasure. Click here to read How to Find and Browse Unindexed Records at Ancestry – The Better Browsing Checklist. In this article you’ll learn how to access these browse-only collections at Ancestry and expand your family history research.