by Lisa Cooke | Oct 22, 2015 | 01 What's New, Evernote, FamilySearch, Listeners & Readers, Source Citation
Here’s how can you add family history documents you’ve grabbed with the Evernote web clipper to your tree on FamilySearch!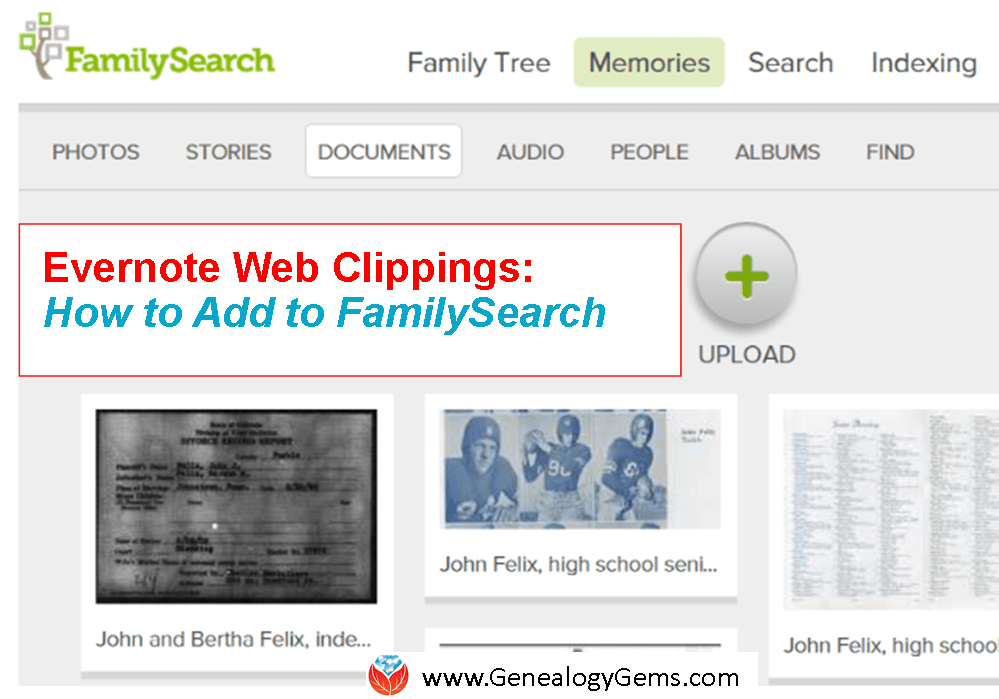
Recently Zooey wrote in with this question: “I’ve clipped numerous things for my ancestors [with the Evernote web clipper] that I want to put in FamilySearch. How do I do it under Documents?”
Good for Zooey for having her genealogy sources organized in Evernote–and for wanting to cite her sources on her FamilySearch family tree. Here’s how to do it:
FamilySearch Documents support the following file types: .pdf, .jpg, .tif, .bmp, and .png. Since it doesn’t currently have an “import from Evernote” feature, you’ll need to export the web clippings from Evernote and then upload them to FamilySearch.
Earlier this year I wrote an article on our blog entitled “Here’s a Cool Way to Export a Web Clipping from Evernote.” The article will walk you through exporting your Evernote web clippings as pdf files, which FamilySearch Documents can then accept as uploads.
More Evernote for Genealogy Tips on the Genealogy Gems Website:
You can find all our past articles on using Evernote for genealogy (including the one I mentioned) at the home page of our website. On the left, just under the main red menu, you will see a drop down menu called “Select Content by Topic.” Click the down arrow and select “Evernote” from the list. This will display all our past Evernote articles on your screen starting with the most recent. Or get started with these great how-tos:
How to Use Evernote for Genealogy: The Ultimate Education
Evernote for Genealogy: What It Is, and Why You Would Use It (FREE VIDEO!)
How to Use Evernote for Genealogy and Family History: Handwriting, OCR, Video and Upload Answers (FREE VIDEO!)
 Thank you for sharing this post with others. We would all love our online trees to be better sourced–and for others’ trees to be better sourced, too.
Thank you for sharing this post with others. We would all love our online trees to be better sourced–and for others’ trees to be better sourced, too.
by Lisa Cooke | Mar 15, 2014 | 01 What's New, Beginner, Organization, Source Citation
 I recently heard from a NEW podcast listener named Judie. As a beginning genealogist she excitedly dove into family history awhile back. However, she soon became overwhelmed by boxes full of uncited, unorganized information having made the biggest mistake beginning genealogists tend to make. Read her story below. Does this sound familiar? Then my answer to her may help you, too, whether you are a beginning genealogist or you need start over with a few things.
I recently heard from a NEW podcast listener named Judie. As a beginning genealogist she excitedly dove into family history awhile back. However, she soon became overwhelmed by boxes full of uncited, unorganized information having made the biggest mistake beginning genealogists tend to make. Read her story below. Does this sound familiar? Then my answer to her may help you, too, whether you are a beginning genealogist or you need start over with a few things.
A Beginning Genealogist’s Confession:
Dear Lisa,
“Just found The Genealogy Gems Podcast and love it. I started my family tree research several years ago by joining Ancestry.com. My tree grew quickly with all the information there but after a couple of years of making every mistake possible including merging everyone’s tree with mine, I ended up with thousands of names without documentation. Another mistake was visiting a couple of historical societies and libraries where I printed lots of information but failed to note where it came from. Ok, I’m sure you got the picture.
After a couple of years of doing everything wrong, and several “dead ends” I became so overwhelmed with so many names and unorganized papers that I packed everything in boxes that would most likely end up in a dumpster when I’m gone (sad but true). That was a year ago. After discovering your site I am ready to get back into the search but don’t really know where to begin. Do I ignore all that has been done and start over or is it possible salvage some of what I have? Do you have any suggestions – Thanks, Judie
My Fix It Advice for the Beginning Genealogist
Start fresh. Get yourself a good genealogy database on your computer and start with a more methodical process like I talk about in the step-by-step series Family History Podcast (Episode 1 is on databases) as well as the Genealogy Gems Podcast. Not sure which database to use? I blogged about that here.
Organize. Once you have a good set of habits, have made some progress, and feel comfortable with your database and citing your sources, then you can start dipping back into the box and “processing” each piece of paper.
If it were me I would toss all those merged trees. The stuff from the historical societies and libraries may be valuable, but without documentation, will have limitations. I would only keep the most obviously applicable items, and toss the rest or at least file it away for now. If you stay focused on all that paper it will direct you, rather than you directing the research process. It may cause you to get off track and lose valuable time.
As you review the “keeper” items and deem them worthy of adding data to your database, you will need to make note that the source is unknown. Use the info gleaned as clues, but realize you’ll still need primary documented sources to back it up.
Cite your sources from this point forward. Beginning genealogists often feel like citing their sources is boring and tedious, and can find it hard to see the long term benefits. Believe me, benefits abound and this is one of the most important things you can do for the health of your family tree! Benefits include:
- avoiding going after the same record twice
- creating a bread crumb trail that helps you retrace your steps
- A foundation for future generations to confidently build upon your research
- adding authority to your research and helping you defend it when challenged
Get a quick start with Elizabeth Shown Mills’ Quicksheet Citing Online Historical Resources.  For a more in depth studying of source citation turn to Mill’s book Evidence Explained:Citing History Sources from Artifacts to Cyberspace 2nd Edition
For a more in depth studying of source citation turn to Mill’s book Evidence Explained:Citing History Sources from Artifacts to Cyberspace 2nd Edition .
.
Bottom line: Put yourself in charge by following a logical research process. Don’t worry about time or paper having been wasted. The point is you jumped in and gave it a shot, and that’s a good thing. I’m just glad you’ve found Genealogy Gems and I’ve got lots of advice and info on the site, podcasts and videos to help you be successful.
Here’s to success!
Lisa
by Diahan Southard | Feb 25, 2014 | Certification, Family History Podcast, Research Skills, Source Citation
Originally published 2009. Republished February 25, 2014
[display_podcast]
Download the Show Notes for this Episode
Welcome to this step-by-step series for beginning genealogists—and more experienced ones who want to brush up or learn something new. I first ran this series in 2008-2009. So many people have asked about it, I’m bringing it back in weekly segments.

Episode 20: The Genealogical Proof Standard
In this episode we are going to cover a powerful process for doing your genealogy research. It’s called the Genealogical Proof Standard or GPS.
If you’re new to research you may hear some terms that you’re not familiar with. This is the ideal time to start getting familiar with them because it may save you going back and re-doing some of your hard work later down the road.
If you’re an experienced researcher, you may already have had some experience with the GPS. But even if you have, you likely haven’t heard it quite like this. My very special guest is Mark Tucker, a software architect by day and an avid genealogist evenings and weekend. And it’s safe to say Mark has a passion for genealogy and he brings his computing expertise to genealogy in some pretty exciting ways, most recently by process mapping the Genealogical Proof Standard – the GPS – into a visual aid that will help you navigate your way to a successful family tree. (Update: Mark’s Think Genealogy blog is no longer available.)
In our first segment Mark tells us how he got started using the Genealogical Proof Standard, why he created the GPS map, and what it will do for you to improve your genealogy research. Then he gives us an overview of the Genealogical Proof Standard and the various tools that go along with it.
In our second segment we talk about how the GPS map can be effectively used for breaking down your research brick walls.
What is the GPS?
The Genealogical Proof Standard speaks to the quality of our genealogy research process, as outlined in the BCG Genealogical Standards Manual. BCG stands for the Board of Certification of Genealogists, and it’s an internationally recognized organization that certifies qualified genealogists who meet their standards.
The idea behind the GPS is that it provides standards generally accepted in the field of genealogy research. Historically the GPS has been thought of in conjunction with professional genealogists. But more and more it is being used by family historians everywhere who want to do a quality job of climbing their family tree.
The Genealogical Proof Standard is really like a process map. It maps out the proven steps that a good genealogist takes to answer their family tree questions.
Proof is a fundamental concept in genealogy. In order for your research to really be accurate and dependable, each conclusion you reach about an ancestor must have sufficient credibility to be considered as proven. To make sure that conclusions you come to about your family are accurate they really need to meet standards of the Genealogical Proof Standard (The GPS). The GPS consists of five major criteria:
- You have to be sure that you have conducted a reasonably exhaustive search.
- You need to have complete and accurate source citations.
- You need to do the analysis and correlation of the information that you’ve found. It’s not just enough to find a fact, you have to look at it within the context of all of the fact and make sure that it fits together in a way that really makes sense.
- If that analysis brings to light the fact that there are conflicts when you put your data together, then your next step is to go back and work to resolve any conflicting evidence. You’ll want to look for additional resources to solve the question at hand.
- You need to be able to write a sound, reasoned, and coherent conclusion. If you can summarize your findings in a way that makes sense and you can show your proof you know that you’re in good shape and your hard work meets the Genealogical Proof Standard.
The GPS is not just a tool for professional genealogists, but it’s also a tool for you and your research. It actually makes a lot of sense, and it’s pretty simple when you break it down into the 5 basic steps:
- Conduct a reasonably exhaustive search;
- Document complete and accurate source citations;
- Analyze and correlate all of the collected information;
- Resolve any conflicting evidence;
- Write a sound reasoned, and coherent conclusion.
GPS Resources
Mark’s Genealogy Research Process Chart and Powerpoint presentation “Navigating Research with the GPS.”
Genealogy Standards by the Board for Certification of Genealogists, now updated in a 50th anniversary released in 2013.
The Historical Biographer’s Guide to the Research Process Quicksheet, a laminated quick reference guide by Elizabeth Shown Mills.
“Genealogy GPS: Keeping Your Family Tree Research on Course” by Genealogy Gems Contributing Editor Sunny Jane Morton for Family Tree Magazine. This is a digital download that includes an interview with Elizabeth Shown Mills.
by | Feb 7, 2014 | 01 What's New, Collaborate, Source Citation
 I’m hearing so much these days about source citation and I love it! Everyone seems to be getting smarter and better at sourcing their research finds. And genealogy websites are making it easier and more collaborative. Here’s just one example, an announcement just made by BillionGraves:
I’m hearing so much these days about source citation and I love it! Everyone seems to be getting smarter and better at sourcing their research finds. And genealogy websites are making it easier and more collaborative. Here’s just one example, an announcement just made by BillionGraves:
“After months of work in response to hundreds of user requests, BillionGraves has added several new features designed to validate and enhance the headstone records found on BillionGraves. The Supporting Record feature now allows users to upload evidence-based documents that support the BillionGraves records that have been collected through our mobile Apps. This means that users are now able to upload headstones, birth/death, burial, marriage, cremation, and many other types of records without needing a smart phone.
Thousands of records are being uploaded every day and are breaking down genealogy brick walls and making connections that once seemed impossible. While working closely with our users and genealogists we found that there were many headstones and burials that just couldn’t be accounted for with our current systems; including unmarked graves, cremation scatterings, destroyed stones, and so on. Our Supporting Records features eliminate this problem while maintaining the validity and accuracy of the BillionGraves database.”


 Thank you for sharing this post with others. We would all love our online trees to be better sourced–and for others’ trees to be better sourced, too.
Thank you for sharing this post with others. We would all love our online trees to be better sourced–and for others’ trees to be better sourced, too.





