Blog


The Touching Stories our Heirlooms Hold
Some of us are using heirloom research for genealogy. A new exhibit traces the history of interesting heirlooms using genealogical research strategies. Be inspired by these examples and tips to research heirlooms and more fully discover their stories.

A new exhibit called Heirloom Genealogy: Tracing your Family Treasures has opened at The Star of the Republic Museum in Texas. You better believe it caught our interest! We know our readers are looking for unique and different ways to continue their genealogy journeys. We wanted to find out more about how family historians are using heirloom research for genealogy. Curator Shawn Carlson was kind enough to answer some questions about it and share the touching stories the heirlooms held.
Q: What an unusual exhibit idea! How did you think of it?
A: I had been researching artifacts at the museum for several years by tracing the genealogy of the families who donated the artifacts. The best exhibit text usually comes from real stories about artifacts—and doing the genealogy was where I found the stories. When I started thinking about this latest exhibit, I thought maybe there was a way that I could use the genealogical research I already had, and that’s when I came up with the idea of “heirloom genealogy.”
Q: Who was involved in the research and how long did it take?
A: I did all of the research. Some of it had previously been done, but some was new. I usually spend the summer researching for an exhibit, and then write the text and begin production in the fall for a March opening during the Texas Independence Day celebration at Washington-on-the-Brazos.
 Q: Can you share a couple of examples and images of artifacts and the documents that told their stories?
Q: Can you share a couple of examples and images of artifacts and the documents that told their stories?
A: One of the artifacts I researched was a red-on-white appliqué quilt. It was made in 1805 in Vermont and donated by the quiltmaker’s 3X great-granddaughter who lived in Houston. It should have been easy to figure out the lineage by the inscription on the quilt—but it wasn’t. There were two Cynthia Tuckers and two Pearl Browns in the family and one quilt owner had been married a couple of times and used a nickname. So, it took a bit of sorting out. The research was all done using census data, but it all came back to the inscription on the quilt for final verification.

Another item in our collection is a small buckskin suit that belonged to a little boy named Edward Clark Boylan. He was born in New Orleans in 1840 and died three years later near Galveston, probably from yellow fever. We knew his birth and death dates from his sister’s descendant who donated the suit, but not much else. I found some cryptic notes in our files taken by a previous curator and was able to trace Edward to Captain James Boylan who was captain of the ship Brutus during the Texas Revolution.
I found a passenger list from 1839 with Captain Boylan, his wife, and daughter traveling from Puerto Rico to New York. Mrs. Boylan would have been pregnant with Edward during that voyage:

The year that Edward died, his father was mentioned frequently in the newspapers as he led a flotilla of ships out of Campeche. He was probably not present when little Edward died.
Q: What was an especially interesting story you came across while researching this exhibition?
A: One of the most interesting items we’ve received in recent years is a slave birth record that was part of a family collection:

The donor’s ancestors were early settlers of Washington County. The slave record was interesting because it listed birth dates from 1832 to 1865. Out of curiosity, I tried tracking some of the slaves to see if I could find living descendants. I started with the 1870 census—looking for African-Americans with the surname of the plantation owner and first names that matched the slaves in the birth record. I was able to follow through on one of the names to find a living descendant. She and her family came to visit the museum and see the birth record of their ancestor. While the family was visiting during last year’s Texas Independence Day celebration, the donor of the slave record also visited the museum and the two families were able to meet.
Q: What advice do you have for family historians with heirlooms?
A: Learn about the artifacts you have and match them to their owners. There is plenty of information online that will help you identify and date artifacts. Knowing the date of an artifact helps you determine who had it in the past.
More on Heirloom Research for Genealogy
 Connect your heirlooms with their stories and bring the past to life!
Connect your heirlooms with their stories and bring the past to life!
Get Denise Levenick’s popular book How to Archive Family Keepsakes: Learn How to Preserve Family Photos, Memorabilia and Genealogy Records. This book will help you sort, identify, and preserve your own treasured family artifacts and memorabilia.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

FDA Authorizes Genetic Health Risk Tests by 23andMe
If you have ever wondered if you or your loved ones are at higher risk for diseases such as Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, read on to learn about big changes that are happening. Health history is just one of the ways in which genealogy research can benefit your family.

According to a recent FDA press release, “The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today allowed marketing of 23andMe Personal Genome Service Genetic Health Risk (GHR) tests for 10 diseases or conditions. These are the first direct-to-consumer (DTC) tests authorized by the FDA that provide information on an individual’s genetic predisposition to certain medical diseases or conditions, which may help to make decisions about lifestyle choices or to inform discussions with a health care professional.”
The release goes on to say:
Consumers can now have direct access to certain genetic risk information,” said Jeffrey Shuren, M.D., director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “But it is important that people understand that genetic risk is just one piece of the bigger puzzle, it does not mean they will or won’t ultimately develop a disease.”
The GHR tests are intended to provide genetic risk information to consumers, but the tests cannot determine a person’s overall risk of developing a disease or condition. In addition to the presence of certain genetic variants, there are many factors that contribute to the development of a health condition, including environmental and lifestyle factors.
The 23andMe GHR tests work by isolating DNA from a saliva sample, which is then tested for more than 500,000 genetic variants. The presence or absence of some of these variants is associated with an increased risk for developing any one of the following 10 diseases or conditions:
- Parkinson’s disease, a nervous system disorder impacting movement
- Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills
- Celiac disease, a disorder resulting in the inability to digest gluten
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a disorder that raises the risk of lung and liver disease
- Early-onset primary dystonia, a movement disorder involving involuntary muscle contractions and other uncontrolled movements
- Factor XI deficiency, a blood clotting disorder
- Gaucher disease type 1, an organ and tissue disorder
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency, also known as G6PD, a red blood cell condition
- Hereditary hemochromatosis, an iron overload disorder
- Hereditary thrombophilia, a blood clot disorder
You can read the complete article called FDA allows marketing of first direct-to-consumer tests that provide genetic risk information for certain conditions here.
 FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide
FDA and 23andMe – Comments from Your DNA Guide
I look to Your DNA Guide, Diahan Southard for all things genetic genealogy, and here’s what she had to say about the recent news:
23andMe is certainly the outlier among our genetic genealogy companies. It is different because its purpose is not necessarily to help you find your ancestors or determine your ethnic composition, though it can do both, but their goal is to empower your personal health.
In November of 2013 the FDA ordered 23andMe to retract all health reporting from their website in order to better regulate the dissemination of health related information to consumers. 23andMe has slowly crawled back toward that same reporting structure, all the while jumping through the compliant hoops that the FDA has set up.
Now this week they have had a major step forward as they have been able to release the risk assessment for 10 major diseases including Parkinson’s and celiac. This is the first such test available direct to consumers, without first going to your doctor.
This is likely the first of many such developments as 23andMe works to make our own health more accessible via our genetics. If you do pursue this kind of evaluation, it is important to keep in mind the words of Jeffrey Shuren, M.D., director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, “…genetic risk is just one piece of the bigger puzzle, it does not mean they will or won’t ultimately develop a disease.”
Learn More About 23andMe
As with all genetic testing, it’s your decision in the end, so be as informed as you can. Diahan’s quick reference guide Understanding 23andMe (a Companion Guide to Autosomal DNA for the Genealogist) will help you tap into the company’s services from a genealogical perspective. Over 1 million people have had their DNA evaluated by 23andMe. This website has powerful family history tools and this guide will answer the most pressing questions like:
- How can I control how much information is being shared with others?
- How can I enter my genealogical information?
- How do I know when I have a good match?
- Is the YDNA and mtDNA information they give the same as what I see at other places?
- What is the best way to use the ethnicity results presented?

Free WWI App from the National Archives
The National Archives is marking the World War I Centennial with a new app, as well as programs and exhibits. Here’s the scoop from their press release:
 The United States declared war on April 6, 1917
The United States declared war on April 6, 1917
Washington, DC – The National Archives marks today’s World War I Centennial with a new mobile app, special programs, featured document displays, traveling exhibits, and a special new webpage highlighting all related resources on National Archives News.
Remembering WWI App
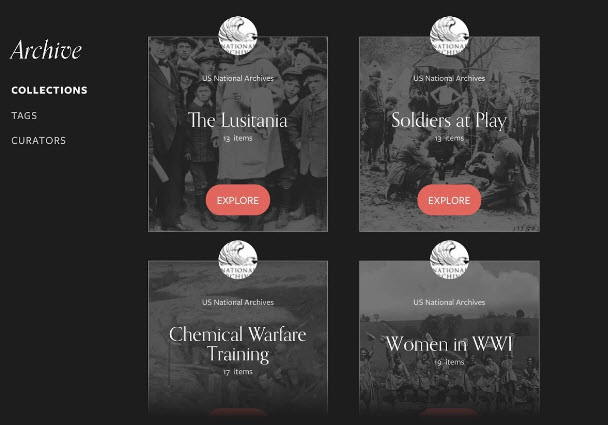 Today, the National Archives launches the Remembering WWI interactive app, now available free of charge through iTunes (iPad only) and Google Play. The app commemorates the 100-year anniversary, in April 2017, of the U.S. entry into World War I.
Today, the National Archives launches the Remembering WWI interactive app, now available free of charge through iTunes (iPad only) and Google Play. The app commemorates the 100-year anniversary, in April 2017, of the U.S. entry into World War I.
The app provides an unprecedented collection of WWI content digitized and preserved as part of the larger Wartime Films Project – much of it never-before-seen by the public – including photos and film shot by the U.S. Signal Corps from 1914 –1920.
National Archives’ partners for the design and testing of the app included: Historypin, Library of Congress, Smithsonian’s Museum of American History, WWI Centennial Commission, WWI Museum, and, American Association of State and Local History. This project is made possible in part by an anonymous donor and the National Archives Foundation.
Saving World War I and II Media through Digitization and Crowdsourcing
Thanks to a generous donation from an anonymous donor, the National Archives embarked on a three-year project to digitize and create public engagement with World War I and II motion pictures and photographs. The project’s original goal was to digitize 70 films and 75,000 photos, and foster engagement on the new digital platform, but by the end of the project, the National Archives had digitized 164 films (337 reels) for more than 65 hours’ worth of content, in addition to more than 100,000 photographs. This is the first time that many of these photos and films will be viewed by the public. All scans are available through the National Archives Catalog or on our YouTube page.
Special WWI-related Exhibits
Featured Document Display: Making the World Safe for Democracy: U.S. Enters WWI
East Rotunda Gallery, National Archives Museum, through May 3, 2017
To commemorate this centennial, the National Archives presents a special display of the Joint Resolution declaring war against the Imperial German Government, April 6, 1917. President Woodrow Wilson signed this declaration of war on April 6, 1917, ending America’s neutral stance on the World War conflict and formally declaring war against Germany. The National Archives Museum’s “Featured Document” exhibit is made possible in part by the National Archives Foundation through the generous support of Ford Motor Company Fund.
Traveling Exhibit: Over Here: Americans at Home in World War I
Over Here: Americans at Home in World War I draws on the unparalleled holdings of the National Archives to capture the patriotic fervor of draft registration, the emotional good-byes of men leaving for training camps, the “hoopla” of Liberty Loan drives, the craze for volunteerism, and the violence of vigilantism. The exhibit is divided into three themes: Mobilizing the Nation, Stirring Patriotic Passions, and Policing Enemies at Home. Over Here is organized by the National Archives, and traveled by the National Archives Traveling Exhibits Service (NATES).
Traveling Exhibit: Over There: Americans Abroad in World War I
After the United States entered World War I, 1917, millions of American men joined or were drafted into the armed services. Some 2 million served in Europe with the American Expeditionary Forces. Over There: Americans Abroad in World War I showcases World War I overseas military photography from the immense photographic holdings of the National Archives. The exhibition includes photographs from the fronts, behind the lines, and the consequences of the war and how it was remembered. Over There is organized by the National Archives, and traveled by the National Archives Traveling Exhibits Service (NATES).
World War I Social Media Day Events in DC, nationwide, and online!
Tuesday, April 11, 2017
Join the National Archives to participate in World War I Social Media Day, hosted by the Smithsonian’s National Museum of American History. Museums, archives, and other educational institutions around the world will share a day of social media activity focused on #WorldWar1 history.
Facebook: World War I in Photos: A Peek inside the Special Media Research Room
10:30 a.m.—Military historian and archivist Mitchell Yockelson showcases his favorite photographs from the war and answers your questions. National Archives on Facebook
Facebook Live with the National Archives at NYC: Online resources for WWI Military Records
2 p.m.—Tune in to Facebook Live for a recap of our Finding Family Genealogy Series, which will be discussing online resources for veterans and military records related to World War I.
National Archives at New York City on Facebook
Twitter: Q&A: U.S. Presidents who served during World War I
11 a.m.—Join archivists from the Presidential Libraries to learn how Presidents Hoover, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Truman, and Eisenhower served during the war.
Presidential Libraries: @OurPresidents, @HooverPresLib, @FDRLibrary, @TrumanLibrary, @IkeLibrary
 Digital Catalog: Tagging mission: World War I posters
Digital Catalog: Tagging mission: World War I posters
All day—Become a citizen archivist and join us to help “tag” World War I posters. By adding keywords of details and features found on the poster in our catalog, you can help make them more accessible to researchers, students, and the public. Educators and classroom teachers, this is a great way to get students involved in doing American history! New to tagging? Get started!
Transcription mission: Fire and Orientation notes by Harry S. Truman
All day—Calling all military history buffs! Help us to transcribe Harry S. Truman’s handwritten notes that he took during his training to learn to fire the French 75 millimeter guns that his artillery unit used while in France. Learn about the future President’s experience during the war. Get started!
World War One Programs
Panel discussion: 100 Years: World War I and The Weight of Sacrifice
Thursday, April 13, at 7 p.m., William G. McGowan Theater, National Archives Museum
Author lecture and book signing: The Hello Girls: America’s First Women Soldiers
Tuesday, April 25, at noon, William G. McGowan Theater, National Archives Museum
Lecture: African American Soldiers in the Great War Through Photographs
Thursday, May 4, at 2 p.m., William G. McGowan Theater, National Archives Museum
The National Archives Museum is located on the National Mall on Constitution Ave. at 9th Street, NW. Hours are 10 a.m. to 5:30 p.m. daily, except Thanksgiving and Christmas.
Related Online Resources at the National Archives
Launching the Beta Program for our Remembering WWI App – post by Archivist David S. Ferriero
U.S. Entry into the War to End All Wars – Pieces of History blog
Joint Resolution of April 6, 1917, Declaring a State of War
World War I Articles in Prologue Magazine
Get Started with the WWI App – National Archives History Hub Post and FAQs




