Blog
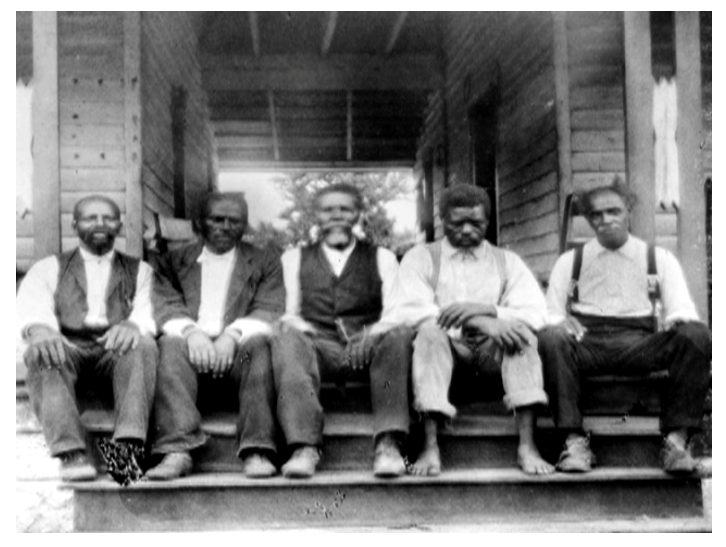


Social History for Genealogy and the Colored Farmers’ Alliance
Social history plays a significant role in successful genealogical research. The events of a particular time-frame shed new light on the lives of our ancestors and ultimately lead us to new finds. In this post, Gems Reader Trisha asks questions regarding her family’s ties to the Colored Farmers’ Alliance.

“The Colored Farmers’ Alliance.” NBC News. NBCUniversal Media. 29 July 2007. NBC Learn. Web. 22 January 2015.
Did a Member of the Family Belong to the Colored Farmers’ Alliance?
Our Genealogy Gems Editor, Sunny Morton, received the following email recently from Trisha:
I am researching my great-grandparents in Northeast Arkansas. The census records I have found so far list that my great-grandfather was a famer. So, I started looking up farming associations hoping that maybe he was a member and I could find out more information about him and possibly any relatives that lived nearby. I came across the Colored Farmers’ Alliance that was in existence from 1886- 1891 in the southern states, but I have only been able to find out basic general public information about this agency. Do you know if, or how, I can find an Arkansas member list or something similar? Any help or advice you can give me would be greatly appreciated.
The History of the Colored Farmers’ Alliance
The Colored Farmers’ Alliance was formed in 1886 in the state of Texas. A group of southern African-American farmers had been barred membership to the other Farmers’ Alliances and hoped by creating this group, they would be able to cooperatively solve the common problems of its members. The group also encouraged African-American farmers to become economically independent by purchasing homes and eliminating debt. [“Colored Farmers’ Alliance,” The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History (https://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-by-era/populism-and-agrarian-discontent/timeline-terms/colore : accessed 28 Oct 2016).]
The organization took off and spread across the Southern United States. It’s peak membership was up to 1.2 million in 1891. However, the organization did not survive long. In 1891, the Colored Farmers’ Alliance called a general strike of African-American cotton-pickers and demanded a wage increase from 50 cents to $1 per hundred pounds of cotton. The strike failed and the group dissolved. [“Colored Farmers’ National Alliance and Cooperative Union,” Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colored_Farmers%27_National_Alliance_and_Cooperative_Union : accessed 28 Oct 2016).]
Pulling Together Some Answers
“Little detail is known about individual members of the Colored Farmers Alliance, including its leadership.”
Google Books
A search of colored farmers alliance delivers several results on the topic. Use search operators to help Google deliver even better results, by putting quotation marks around the search phrase “colored farmers alliance.” This instructs Google to return only web pages that contain that exact phrase. You’ll find more Google search strategies in my book The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox, which also includes an entire chapter on using Google Books for genealogy.
Here’s an example of one book I found called The Agrarian Crusade: A Chronicle of the Farmer in Politics by Solon J. Buck (1920).
Click here to see the entire search results list for the search query Colored Farmers Alliance in Google Books.
While I didn’t discover any references to actual member names beyond some of the leaders, Google Books certainly offers more depth and history on the Alliance.
Digitized Newspapers

Indian chieftain., March 03, 1892, Image 1 at the Library of Congress’ Chronicling America.
(The Indian Chieftan was published in Vinita, Indian Territory [Okla.]) 1882-1902
For more help on researching newspapers for genealogy, listen to my two part podcast series titled “Find Your Family History in Newspapers, Part 1 and Part 2.”

members named
Google Scholar
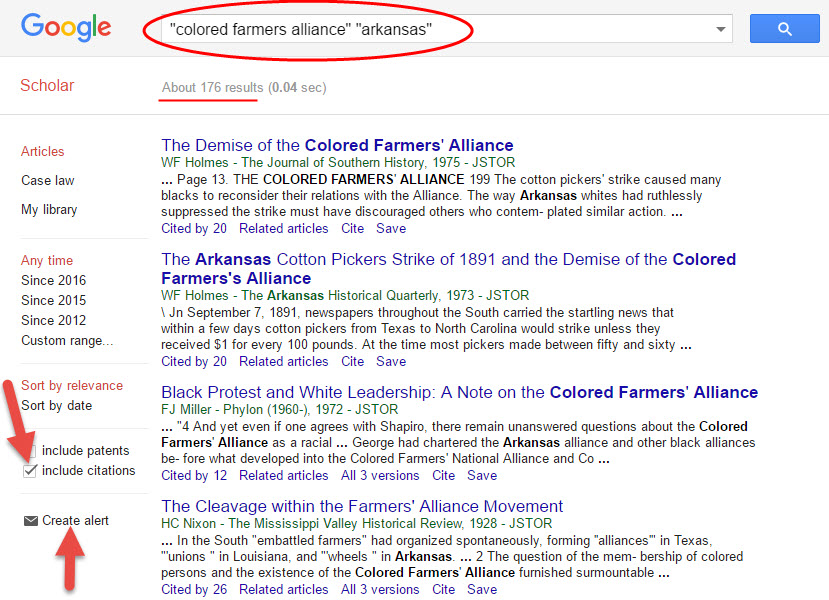
YouTube
It’s amazing what the family historian can discover from the comfort of their own computer. With so many valuable resources discovered through an online search, a well-prepared trip to the library or archive will prove even more fruitful.

Mexican Genealogy: Finding Abuela in New and Updated Genealogical Records for Mexico this week

Mexico – Church Records
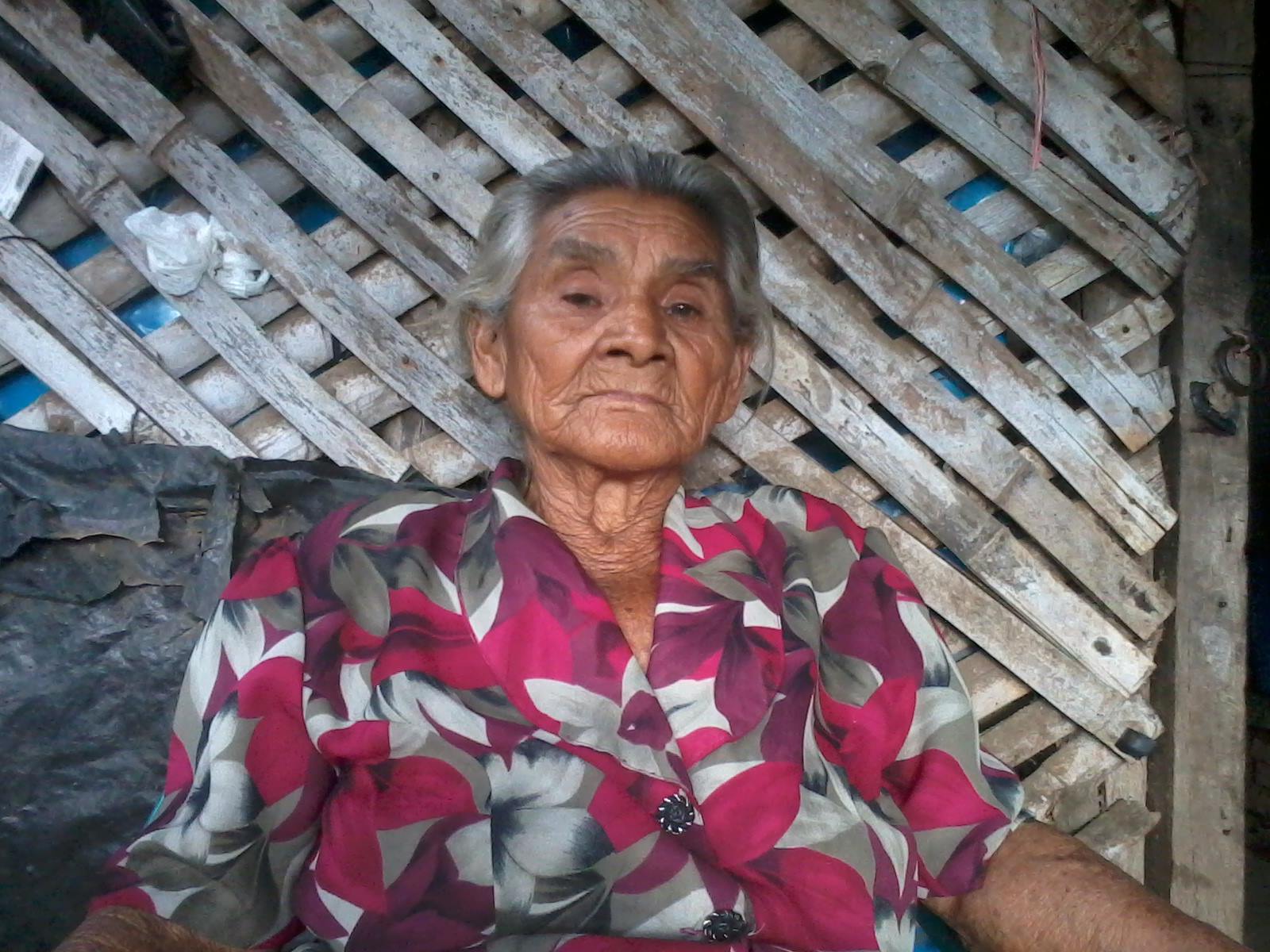

Abuela Francisca Ramos. Photo used with permission from the family.
FamilySearch has updated and added thousands of new Catholic church records in their Mexican genealogy databases. These church records cover many areas of Mexico, but in particular, the Hidalgo, Puebla, Jalisco, and Guanajuato databases have all reached over 1 million records. The years covered will vary, but the earliest records are from the 1500s and as recent as the 1970s.
These Catholic church records include baptismal records, marriage records, deaths, and other miscellaneous records that may contain valuable genealogical data for your ancestors. Check out the following databases for Mexican genealogy below:
England – Norfolk – Church Records
The second database is titled, Norfolk Bishop’s Transcripts Marriages 1685-1941 and contains over 157,000 records. Each record includes a transcript and may include the birth year, date of marriage, place of marriage, and the name of their spouse as well as an image of the original document.
Thirdly, the Norfolk Bishop’s Transcripts Burials 1685-1941 collection will allow you to search over 434,000 Bishop’s transcripts of Norfolk burials to discover your ancestor’s final resting place. Transcripts will also reveal when they died and their age at death. Images of original documents may reveal additional information such as the name of the minister who performed the ceremony, your ancestor’s date of death and, occasionally, their cause of death.
Finally, the Norfolk Electoral Registers 1832-1915 containing over 4.5 million records may be just want you are looking for. Electoral registers were first created in 1832. Every year, a new electoral register was created to list the name of every individual eligible to vote. Voting was closely linked to the possession of property; therefore, the registers described the type of property owned or rented by the individual.
Electoral registers are an invaluable resource to trace your ancestors between the census years. Each entry in the Norfolk Electoral Registers 1832-1915 will include an image of the original register and a transcript of the facts listed. Transcripts will list your ancestor’s name, the place they registered, the district and the year they were registered. Images will provide additional information such as you’re their address and the type of property they owned or rented.
Australia – Victoria – Birth Records
Also at Findmypast, over 104,000 records have been added to the Victoria Births collection. These civil registration records may reveal your ancestors birth place, birth year, parent’s names and registration number. The entire collection now contains over 1.9 million records spanning the years 1837 t0 1917.
England & Scotland – Newspapers
Over 1.6 million articles and 13 brand new titles have been added to Findmypast’s collection of historic British Newspapers. The new additions cover the North West and South East of England, a number of Scottish counties, Nottinghamshire, and Bournemouth. The new Scottish titles include the Haddingtonshire Courier, Linlithgowshire Gazette, Ross-shire Journal, Rothesay Chronicle, Kinross-shire Advertiser, Peeblesshire Advertiser, and the Scottish Referee.
Canada – Quebec – Various Record Collections
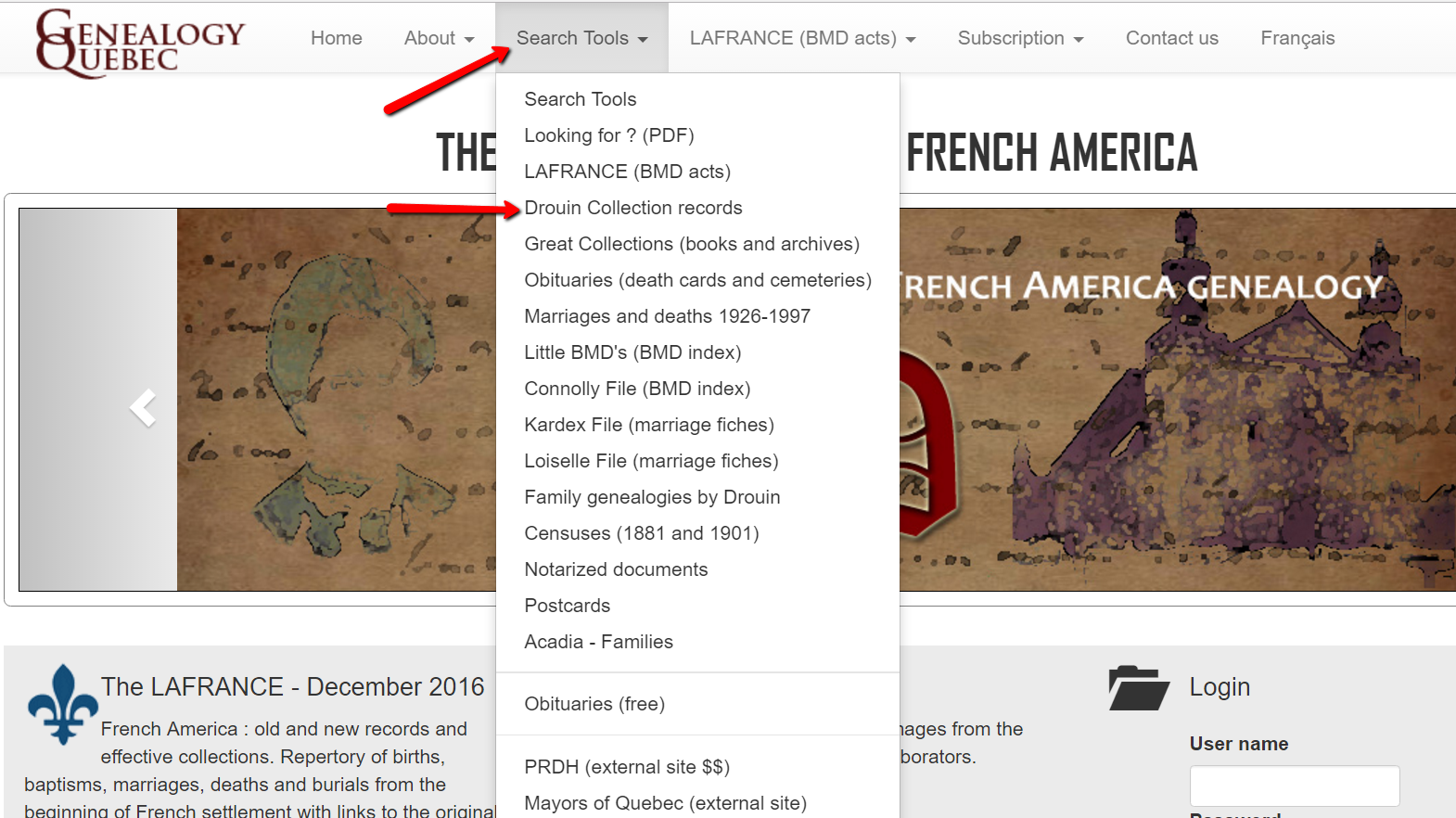
To access the Drouin Institute record collections, you will need to visit GenealogyQuebec.com. It is subscription based website. Subscription information can be viewed here.
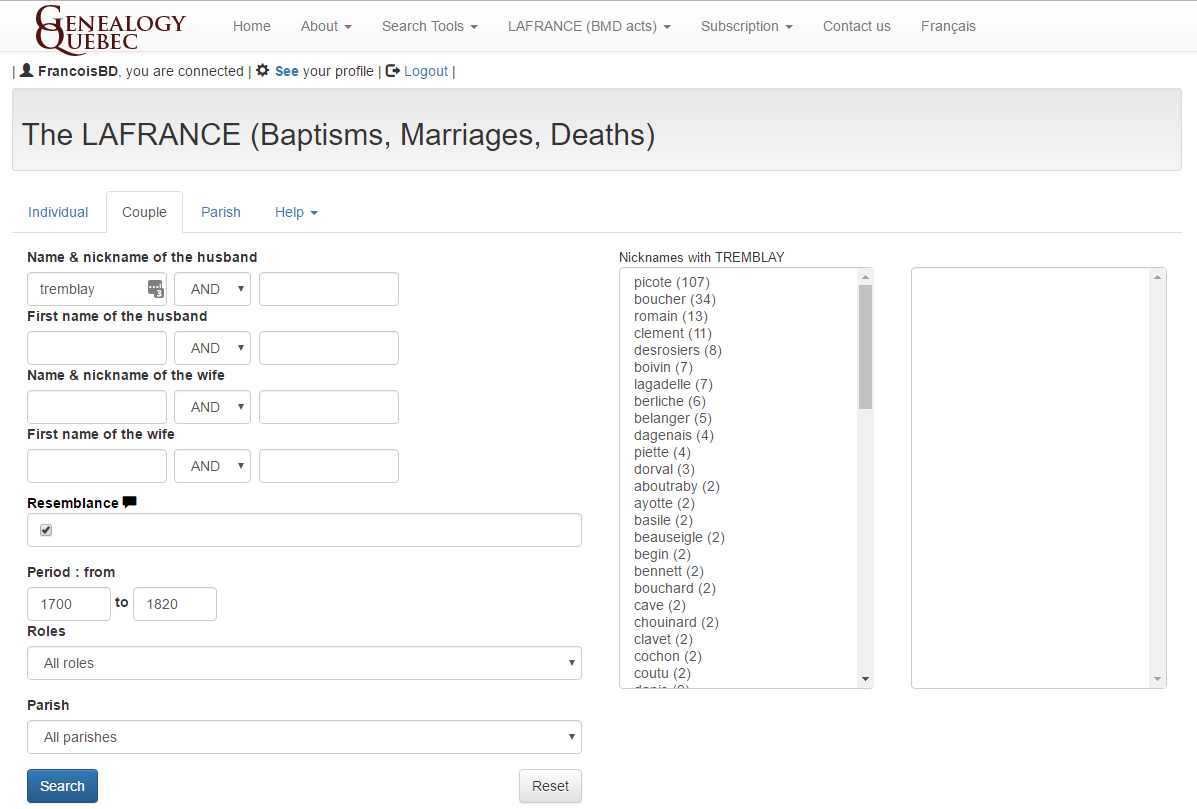
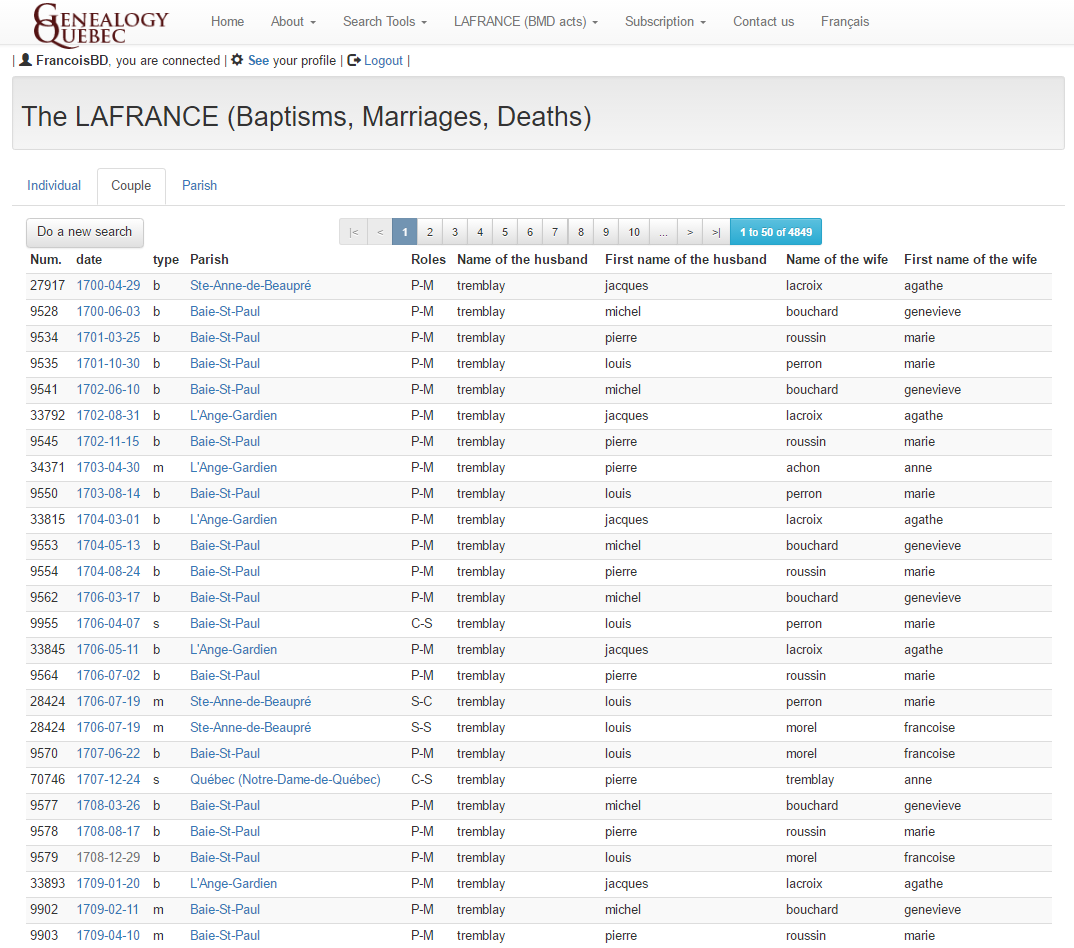
Currently, the LAFRANCE covers the entirety of the 1621 – 1849 period for Catholic baptisms and burials, as well as, the 1621-1916 period for Catholic marriages. In addition, the LAFRANCE covers the 1760 – 1849 period for Protestant marriages.
The LAFRANCE’s index is particularly valuable and appreciated by English speakers, as it negates the need to read and understand French in order to obtain all the relevant information from a record.
WWI Holdings
The Library of Congress has launched a comprehensive portal to its extensive WWI holdings. This one-stop portal is designed to help you search WWI subject material with ease. Search things like propaganda posters, letters, diaries, newspapers, and more. It is a wonderful site for not only the genealogist, but the avid historian as well.
More on Mexican Genealogy
 The Mexican Genealogy Guide by David A. Fryxell from Family Tree Magazine will help you discover the bounty of records in Mexico. This digital download will help you understand naming practices, pinpoint ancestral whereabouts, and how to best navigate church records there.
The Mexican Genealogy Guide by David A. Fryxell from Family Tree Magazine will help you discover the bounty of records in Mexico. This digital download will help you understand naming practices, pinpoint ancestral whereabouts, and how to best navigate church records there.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!

What Was it Like to Land at Ellis Island?
Chalked full of a rich history, Ellis Island was the leading port of arrival for the United States for sixty years. Read more about this historic place and the inspirational stories of immigrants past.

[Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.
Ellis Island: What was it like?
Many of our ancestors first stepped ashore at Ellis Island when they came to America seeking a new life. I can only imagine their first thought might have been, “Get me off this boat!” But then, perhaps there was worry and trepidation. Would they be sent home because they were sick? Would they find work, a place to live, or food to eat?

Immigration Day at Half Day School, Lincolnshire, Illinois. 2010. Courtesy of the author.
The very first immigrant was processed in 1892. Her name was Annie Moore and she was a 15-year-old Irish girl. [1] Can you imagine?
One elementary school in Lincolnshire, Illinois recreates this event with their yearly “Immigration Day.” Immigration Day is for all 3rd and 4th students to participate in what it’s like to come to this country for the first time. They dress up, pack up a few belongings, receive little tickets and passports, and experience in a small way the history of many of their ancestors.
Arriving on land again must have been quite the relief to passengers. Especially those in steerage. Steerage or third class passengers traveled in crowded and often unsanitary conditions near the bottom of the ship. Upon arrival in New York City, ships would dock at the Hudson or East River piers. First and second class passengers would disembark, and pass easily through Customs. They were free to enter the United States. The steerage and third class passengers, however, were transported from the pier by ferry or barge to Ellis Island where everyone would undergo a medical and legal inspection. [2]
If the immigrant’s papers were in order and they were in reasonably good health, the Ellis Island inspection process would last approximately three to five hours. The inspections took place in the Registry Room (or Great Hall). Here, doctors would quickly look over every immigrant for obvious physical ailments.
If the immigrant was found with a minor ailment, broken bone, or found to be pregnant, they would be sent to the “Island Hospital, built to restore the health of people suffering minor injuries [and] broken bones.” [3]
An Ellis Island Myth
The ship’s manifest log, that had been filled out back at the port of embarkation, contained the immigrant’s name and his/her answers to twenty-nine questions. This document was used by the legal inspectors at Ellis Island to cross-examine the immigrant during the legal (or primary) inspection. [4]
There are some genealogical myths regarding Ellis Island. Many believe that their ancestors surnames were changed when they arrived. Some even believe the name change was due to the lack of native speakers of different languages and an overall lack of communication. This is not the case.
Vincent J. Cannato’s book American Passage: The History of Ellis Island explains why this did not happen:
Nearly all […] name change stories are false. Names were not changed at Ellis Island. The proof is found when one considers that inspectors never wrote down the names of incoming immigrants. The only list of names came from the manifests of steamships, filled out by ship officials in Europe. In the era before visas, there was no official record of entering immigrants except those manifests. When immigrants reached the end of the line in the Great Hall, they stood before an immigration clerk with the huge manifest opened in front of him. The clerk then proceeded, usually through interpreters, to ask questions based on those found in the manifests. Their goal was to make sure that the answers matched. (p.402)
A First-hand Look at Ellis Island
The official, award-winning documentary shown today at Ellis Island (more about that here) is available to watch online below. It is a wonderful way to get a first-hand look at what it felt like to land at Ellis Island and the a land of liberty.
 The Genealogy Gems Podcast (get our app) helps you make the most of your family history research time by providing quick and easy-to-use research techniques. Producer and host Lisa Louise Cooke brings you the best websites, best practices, and best resources available! Listen to all of Lisa’s podcast episodes on iTunes for free!
The Genealogy Gems Podcast (get our app) helps you make the most of your family history research time by providing quick and easy-to-use research techniques. Producer and host Lisa Louise Cooke brings you the best websites, best practices, and best resources available! Listen to all of Lisa’s podcast episodes on iTunes for free!



