by Lisa Cooke | Nov 18, 2016 | 01 What's New, Adoption, Native American, Records & databases
Adoption of Washington State Native Americans records are now available for genealogical research. Also this week you can fill up on North Carolina school books, California land dockets, Florida newspapers, Canadian Aboriginal Peoples records, Lower Canadian census for 1825, and new additions to historic British newspapers.

United States – Adoption of Washington State Native Americans
Washington, Applications for Enrollment and Adoption of Washington Indians, 1911-1919 is now available at FamilySearch.org. This collection consists of records created during the creation of the Roblin Rolls of Non-Reservation Indians in Western Washington. The enrollment and adoption proceedings of Indian tribes in Western Washington that were not on tribal census records makes this collection unique. It is arranged by tribal name claimed by the applicant, and then by applicant’s name.
Records may contain:
- English name of the primary individual or family members
- Indian name of the primary individual or family members
- Birth, marriage, or death dates
- Birth, marriage, or death places
- Place of residence
- Ages
- Number of children in the family
- Occupation
- Other biographical details about the family or individuals such as migrations
- Tribal affiliation
- Religious affiliation
- General information about the tribe
United States – North Carolina – School Books
North Carolina Digital Heritage Center features highlights from the collections at DigitalNC, an online library of sources from across North Carolina. This week, the archive has added almost 90 years worth of “BlueBooks” from St. Mary’s School in Raleigh. The years covered are 1911-2000.
St. Mary’s School was both a high school and a college. In particular, the Student Blue Books could be especially useful for genealogists or historians, as they document the names, activities, and some addresses of the students.
United States – California – Land Docket
Ancestry.com has
California, Private Land Claim Dockets, 1852-1858 available online. This record collection includes case files regarding private land claims in California. They are based on historical Spanish and Mexican land grants that took place before California became part of the U.S.
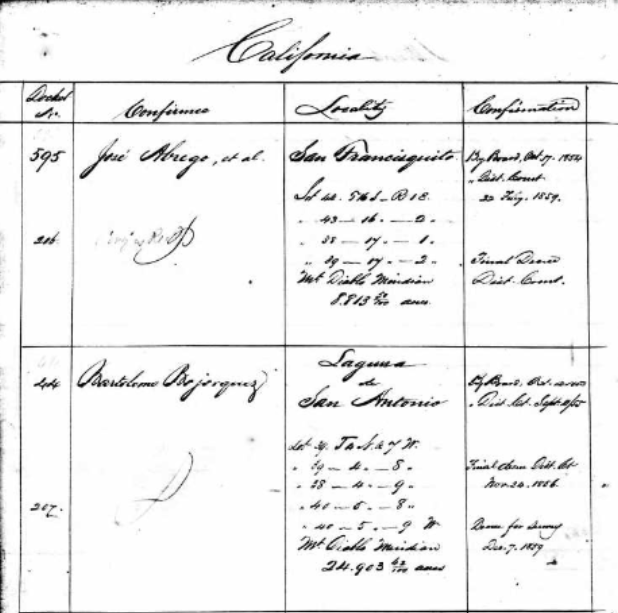
California, Private Land Claim Dockets, 1852-1858 for José Abrego at Ancestry.com
The purpose of these records was to show the actions taken regarding the claims after they were confirmed valid. Additional items within these case files include: notices and evidence of claims, certificate or plats of survey, affidavits, deeds, abstracts of titles, testimonies, appeals, and letters.
Each record in the index usually includes the name of the landowner, their docket number, and the record date.
United States – Florida – Newspapers
Do you have ancestors from Florida? Newspapers.com now has the Palm Beach Post. With a basic subscription, you can see issues of the Palm Beach Post from 1916 through 1922; or, with a Publisher Extra subscription, access earlier years and additional issues from 1922 to 2016.
Florida’s Palm Beach Post first began publishing in 1908 with the name Palm Beach County, and in 1916 (by this time called the Palm Beach Post) the paper made the switch from running weekly issues to daily.
Canada – Aboriginal Records
Library and Archives Canada added over 600 documents from the Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples recently. These records can be viewed at the Library and Archives Canada website.
These records include transcripts of more than 175 days of public hearings, consultations and roundtables; research studies by academics and community experts; and submissions by non-governmental organizations. Until now, patrons could only access this collection in person at LAC’s downtown Ottawa location, or by submitting a reprography request. This is a wonderful asset to the many helpful collections online for Canadian researchers.
Lower Canada – Census
The Lower Canadian Census of 1825 from Findmypast contains over 74,000 records covering modern day Labrador and southern Quebec. Each search result will provide you with an image of the original document and a transcript. Information may include the language your ancestor spoke, where they lived, and with how many people they lived. It does not name each of the inhabitants in the home by name, but they are marked by age.
1.2 million Irish immigrants arrived from 1825 to 1970 according to Wikipedia. The peak period of entry of the Irish to Canada in terms of numbers occurred between 1830 and 1850, when 624,000 arrived. Quebec was a port of entry. So, if you have Irish immigrants who you think may have come to Canada by 1825, this might be a great census for you to look at.
Britain – Newspapers
Over 1.5 million new articles have been added to the military publications available at Findmypast in their historic British Newspapers. The Naval & Military Gazette and Weekly Chronicle of the United Service are two of the new titles added. Additional articles come from the Army and Navy Gazette.
More on Native American Research Collections
This week’s records featured Adoption of Washington State Native Americans. But whether you are searching for your Native heritage in Canada, the Western United States, or the Southeastern United States, we know you want the best in education and helpful tips. We have created a three-part series regarding how to use the Native American collections on Fold3.com here:
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting Genealogy Gems!
by Lisa Cooke | Jul 3, 2015 | 01 What's New, Australian, British, Canadian, Census, Digital Archives, FamilySearch, Findmypast, images, Immigration, Memory Lane, Military, Photographs, Records & databases, United States

Every Friday, we blog about new genealogy records online. Do any of the collections below relate to your family history? Look below for early Australian settlers, Canadian military and vital records, the 1925 Iowa State Census and a fascinating collection of old New York City photographs.
AUSTRALIAN CONVICT RECORDS. Now Findmypast subscribers can access several collections on early settlers. Among them over 188,000 Australia Convict ships 1786-1849 records, which date to “the ships of First Fleet and include the details of some of the earliest convict settlers in New South Wales.” You’ll also find “nearly 27,000 records, the Australia Convict Conditional and Absolute Pardons 1791-1867 list the details of convicts pardoned by the governor of New South Wales and date back to the earliest days of the colony” and New South Wales Registers of Convicts’ Applications to Marry 1825-1851, with over 26,000 records.
CANADIAN WWI MILITARY RECORDS. As of June 15, 162,570 of 640,000 files are available online via the Soldiers of the First World War: 1914–1918 database on the Library and Archives Canada website. This is the first installment of an ongoing effort to digitize and place online records of the Canadian Expeditionary Force service files.
IOWA STATE CENSUS. About 5.5 million newly-added records from the 1925 state census of Iowa are now free to search at FamilySearch,org. Name, residence, gender, age and marital status are indexed. The linked images may also reveal parents’ birthplaces, owners of a home or farm and name of head of household.
NEW YORK CITY PHOTOGRAPHS. About 16,000 photos of old New York City from the New York Historical Society are free to view on Digital Culture of Metropolitan New York. According to the site, “The extensive photograph collections at the New-York Historical Society are particularly strong in portraits and documentary images of New York-area buildings and street scenes from 1839 to 1945, although contemporary photography continues to be collected.”
ONTARIO, CANADA VITAL RECORDS. Nearly a half million birth record images (1869-1912), nearly a million death record images (1939-1947) and over a million marriage record images (1869-1927) have been added to online, indexed collections at FamilySearch.
 Today’s list of new records has a LOT of Canadian material! If you’re researching Canadian roots, here’s a FREE video for you to watch on our YouTube channel: Lisa Louise Cooke’s interview with Canadian research expert Dave Obee, who shares 10 tips in his effort to help one RootsTech attendee break through her brick wall. This post and tip and brought to you by The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox by Lisa Louise Cooke, newly-revised and completely updated for 2015 with everything you need to find your ancestors with Google’s powerful, free online tools.
Today’s list of new records has a LOT of Canadian material! If you’re researching Canadian roots, here’s a FREE video for you to watch on our YouTube channel: Lisa Louise Cooke’s interview with Canadian research expert Dave Obee, who shares 10 tips in his effort to help one RootsTech attendee break through her brick wall. This post and tip and brought to you by The Genealogist’s Google Toolbox by Lisa Louise Cooke, newly-revised and completely updated for 2015 with everything you need to find your ancestors with Google’s powerful, free online tools.
by Lisa Cooke | Aug 22, 2019 | 01 What's New, Brick Wall, Research Skills |
Two of my favorite things, cookies and genealogy, have more in common than you might think! Follow me down this genealogy rabbit hole and discover how you can take you family tree further!

Cookies for My Descendants!
My grandson loves Super Mario games and specifically the mascot Mario. (Actually both of my grandsons do!) So, when it came time to create a sweet treat for his birthday, I opted for sugar cookies decorated as Mario.
Normally I would use a cookie cutter to create a decorated character cookie. Unfortunately, the local craft stories didn’t carry the Mario cutter, and I didn’t have time to get it ordered and delivered.
I hit a cookie decorating brick wall.
But brick walls, whether in genealogy or cookie decorating can often be overcome.
When we come face to face with a brick wall, we need to assess the situation, seek additional advice, and assemble the appropriate tools.
In the case of ole Mario, I first found a drinking glass just slightly larger than the size I wanted the cookie to be. It worked well as a cookie cutter, but I later decided to improvise a cookie cutter of my own.
To create the cookie cutter, I copied an image of his face into a Word document, and then enlarged it to the size of a cookie and printed it out on a sheet of paper. I carefully cut the image out, and then placed the cut-out on a sheet of wax paper, drawing around the edges and then cutting it out.
Next I found a good, sharp paring knife. I placed the wax paper template on the rolled-out cookie dough and carefully cut around it with the paring knife. Brick wall busted!

The finished cookies for my grandson’s birthday
Are you a cookie cutter genealogist?
All this cookie cutting and problem solving got me thinking about genealogy. (Ok, I admit it – I’m always thinking about genealogy!) It brought to mind an email I received just the other day from a listener, Kristine, who described herself as a “cookie-cutter” researcher.

Hi Lisa,
I just retired and guess what is first on my list of things I WANT to do? 🙂 I jumped in with both feet listening to your Premium podcasts and realized a few times that I am the ‘cookie-cutter’ researcher. But, no more. You are the Captain of my ship now. Thank you!
After binging on your podcasts the last two weeks, the first bit of advice I took was changing the way I searched on Newspapers.com. My family’s everyday life’s treasures were buried in the pages of the local news! You made me take a second look after I dismissed the possibility of ever reading about them.
Thank you so much for your dedicated work on behalf of all the genealogists. My Premium subscription will NEVER run out. When a family member says “I don’t know what to get you” I’m prepared to solve that dilemma!
A listener for life
Kristine
I really admire how Kristine took an honest look at her current research techniques. She was open to acknowledging that she had more to learn. It’s just icing on the cake for me that she started listening to the Genealogy Gems Podcast.
It’s easy to become a cookie-cutter genealogist in today’s automated world.
Every day more and more is being done for us automatically. Genealogy record hints and matches on genealogy websites is just one example. These can be very effective tools, but they can also lull you into a false sense that the work is done or correct.
An accepted record hint can in no way be considered as work that is done or correct. It is only the beginning.
In Genealogy Gems Podcast episode #232 professional genealogist and lecturer Elissa Scalise Powell and I discussed the pitfalls of “shallow research,” or as Kristine described it, being a “cookie-cutter” researcher.
Elissa says that while we will find a lot of “low-hanging fruit” in the early days of our genealogical search, there always comes a time when we need to dig deeper. All genealogists will need to stretch and reach for other sources. These types of sources are:
- not straightforward,
- possibly unknown to you at this time,
- not easily accessible,
- time-consuming to explore,
- take study to understand it,
- not self-explanatory.
Moving Beyond Cookie Cutter Genealogy
I also recently I received a question from a reader that provides a great example of a scenario where it’s time to move on to these rich and yet more challenging sources. Harold writes:
I have a totally “back to basics” question.
Since I started seriously doing genealogy about 8 months ago, I’ve learned a tremendous amount about my ancestors…families going back as far as those covered in the 1850 census and since then.
But once you get to the 1840 census and earlier, I do not understand how any genealogist can use the meager records in the census, that only identify the head of the family and the number of adults and children living in the household, to any sense prove that they are your ancestors, or to find their predecessors who are likely to have lived in another state.
After all, in those days, often maiden aunts, grandparents, and others stayed with families, so you can never be sure who all the people are.
And they had a dozen kids, not all of whom survived.
So you cannot count on just the “number” of people listed in the 1840 census to prove anything. Even worse, my ancestors, and I think most people’s, seemed to be moving westward every generation from the establishment of the colonies, so there are dozens of states to choose from, and hundreds or thousands of people with the same surnames in them.
I believe I have found the name of my great-grandfather on an 1840 census in Ohio (though it is possible it is just a duplicate name), but there is no telling where he lived in 1830 or earlier.
As far as I can tell, my ancestors were all poor dirt farmers, moved westward every generation, and didn’t have any records of stores or businesses they might have owned that would have those kinds of records. Yet, there are people who claim they can trace their ancestry back to the Mayflower and the like, but I do not understand how anyone can legitimately trace their ancestry back prior to 1840 unless they have something like a family Bible or similar transcription kept in the family.
Sure, you can find names on earlier census, but lots of people have the same name, and lots of names are spelled wrong, etc. and there are a lot of states and territories to choose from.
So how can ANYONE claim they can PROVE their ancestry from 1840 and before?
The “cookie cutter” Harold was using was the U.S. Federal Census. Cookie cutters provide great, consistent results, but over the decades the census cookie cutter shape changes. The check marks don’t provide the same level of details that we find in later enumerations.
For example, the 1850 U.S. Federal Census provided the name, age, and gender of everyone in the family. It also provided valuable and identifying information such as occupations and place of birth.
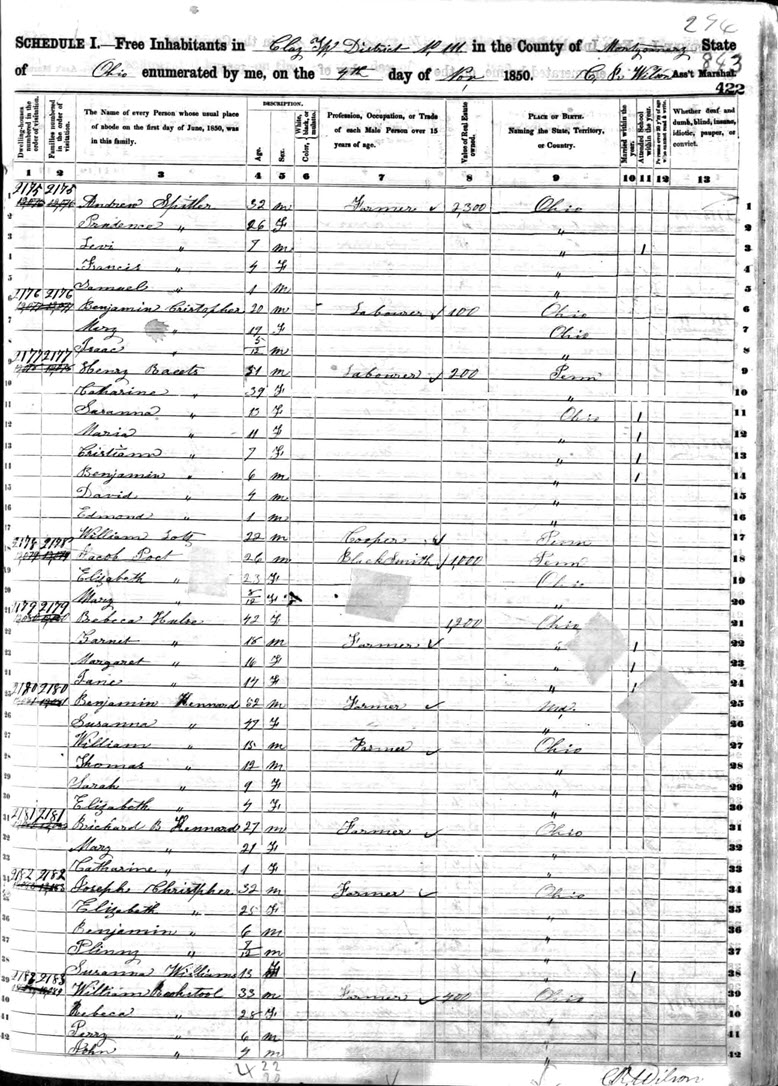
Information provided on the 1850 U.S. Federal Census
Just ten years earlier, the 1840 enumeration looked dramatically different:
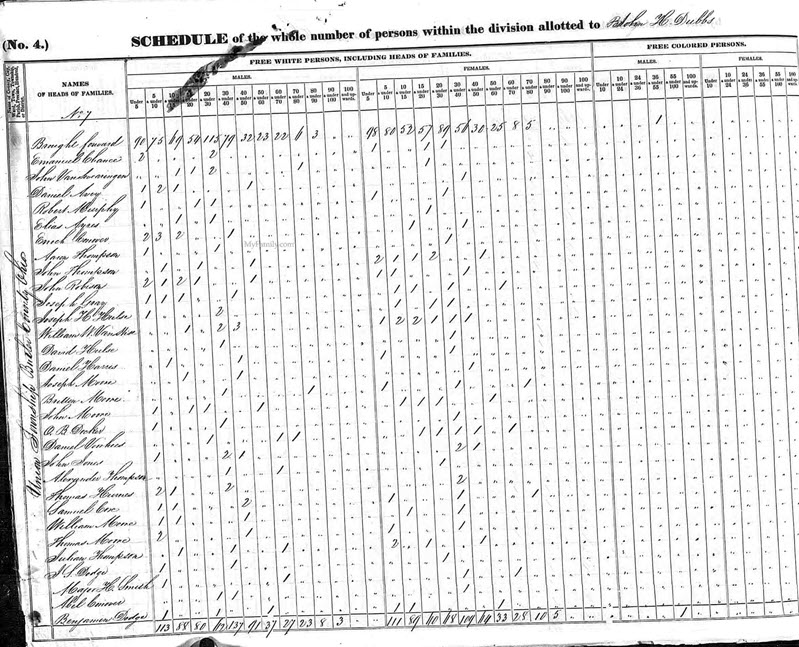
1840 U.S. Federal Census
As Harold lamented, in 1840 we only find the name of the head of household, followed by the number of people in the household who fell within a certain age range. There’s still valuable information here, but clearly not as detailed as later enumerations.
So, the general answer to his question is that he is right, from 1840 on back you typically cannot rely just on census records.
However, it is indeed often possible to reliably take your family tree further back in time.
Genealogical research at this point in history requires deeper cross-referencing of the types of sources that Elissa referred to in the podcast episode. Examples of these sources include wills and probate records, land deeds, homestead records, tax records, marriage records, old newspapers, compiled genealogies and more. They all play a part in piecing together a family tree.
Some of these records are available online. However, in many cases, you will use only the internet to help you determine where the records are held. Then you must access the records in person, by contacting the repository, asking a friend or fellow researcher in the area to copy it for you, or hire a professional genealogist in the area where they are held.
Regarding Harold’s question regarding genealogists who are able to tie their family tree to the Mayflower, this is indeed possible. There is a lot of excellent documentation over the last few centuries on descendants of the Mayflower, so it is sometimes not that difficult to connect up an ancestor in your own tree with the descendant of the Mayflower. This can indeed take your own tree back much further. However, that’s a topic for another article.
A Sweet Tool that Can Help
In addition to discussing the sources and strategies that you can use to avoid being a cookie cutter genealogist, Elissa and I also discuss the Genealogical Proof Standard (also known as the GPS) in Genealogy Gems Podcast episode #232.
The Genealogical Proof Standard was created to help genealogists gain confidence in their research conclusions by providing criteria that can be followed. A genealogical conclusion is considered proved when it meets all five GPS components.
You can learn more about the GPS in episode #20 of my Family History: Genealogy Made Easy podcast.

Sweet Rewards
It’s normal for new genealogists to follow the basic cookie-cutter approach of birth, marriage, death and census records. But these standard sources can only take you so far (as Harold discovered!)
Reaching further back in your family tree by embracing more challenging sources and digging deeper offers a much sweeter reward!