Genealogy Gems Podcast Episode 214
The Genealogy Gems Podcast
Episode #214
with Lisa Louise Cooke
In this episode, Irish expert Donna Moughty joins host and producer Lisa Louise Cooke to talk about Irish genealogy to help you get a jump on yours before everyone starts talking about their Irish roots on St. Patrick’s Day next month! Also in this episode:
- Your DNA Guide Diahan Southard has DNA news
- Other listeners write in with inspiring successes
- Michael Strauss musters in with tips on finding your ancestors in the five branches of the U.S. military.
NEWS: MYHERITAGE DNA MATCHING UPDATE

The MyHeritageDNA test matching algorithm has gotten better?AND they’ve added a chromosome browser. Time to test with MyHeritage DNA or upload your results from another company for free? Click here to read all about it!
MAILBOX: LISTENERS ON FAMILY HISTORY VIDEOS

Muffy in Seattle sent this link to her family history video. Great job!
Melissa asked about finding copyright-free music to add to family history videos. Lisa’s tips:
Unfortunately, free royalty-free music sites are few and far between.
You’re smart to be cautious because if you were to put your video on YouTube they have the technology to identify any song that is used that is a violation of copyright.
YouTube does make free music available:
- Sign into YouTube with your Google account
- Click on your picture in the upper right corner and go to your Creator Studio.
- Upload your video (you can keep it private if you wish) and then on the video page click “Audio” (above the video title).
- Choose among the many music tracks there.
- Once you’ve added a track and saved it, you should be able to download the video with the music included.
The other source of music I use is music that comes with the programs I use (Animoto and Camtasia).
GENEALOGY BUSINESS ALLIANCE
GBA Buzz game for RootsTech 2018; Play the game. See websites for complete rules.
Lisa Louise Cooke uses and recommends RootsMagic family history software. From within RootsMagic, you can search historical records on FamilySearch.org, Findmypast.com and MyHeritage.com.

Keep your family history research, photos, tree software files, videos and all other computer files safely backed up with Backblaze, the official cloud-based computer backup system for Lisa Louise Cooke’s Genealogy Gems. Learn more at https://www.backblaze.com/Lisa.
INTERVIEW: DONNA MOUGHTY ON IRISH RESEARCH
The following review appeared in the January 2018 newsletter of the Midwest Genealogy Center, Mid-Continent Public Library:
“If you want a quick guide on how to get started on Irish research, this short, four-page guide is an excellent resource. This guide will help you start your research in the United States, so you can figure out where in Ireland your ancestor came from. It is organized into 12 steps with helpful websites added. This guide is the first in the Irish Research Series by Donna M Moughty.”
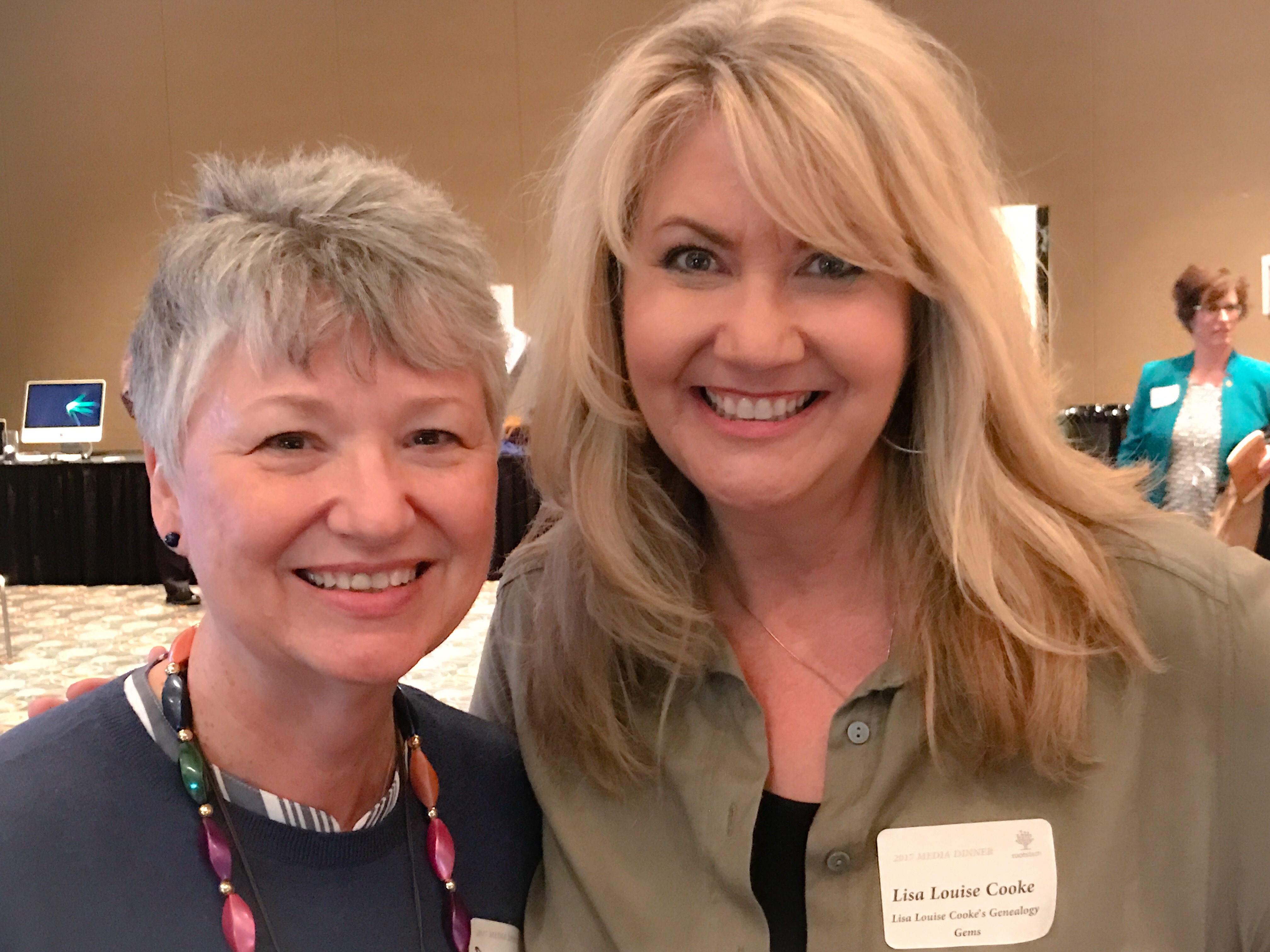

Donna Moughty, shown left with Lisa Louise Cooke, is a professional genealogist and former Regional Manager for Apple Computers. She has been conducting family research for over 20 years. She teaches classes for beginners and lectures on a variety of subjects including Internet, Irish research, and computer topics. In addition, she provides consultations, research assistance, and training. She is a member of Association of Professional Genealogists and the Genealogical Speakers Guild.
Websites mentioned in their conversation:
Donna’s Irish guide series

Preparing for Success in Irish Records Research – Guide #1 (reviewed above): Without the right preparation, researching in Ireland can be frustrating! Before you jump the pond, start your research at home to determine a place in Ireland, as well as details to help differentiate your person from someone of the same name. This research guide will walk you through the process of identifying records in the US to set you up for success in your Irish research.
Irish Civil Registration and Church Records – Guide #2. Civil Registration for all of Ireland began in 1864, with Protestant marriages dating back to 1845. Even if your ancestors left before that date, they likely had relatives that remained in Ireland. Prior to Civil Registration, the only records of births (baptisms), marriages or deaths (burials) are in church records. This Reference Guide will explain how to use the new online Civil Registration records as well as how to identify the surviving church records for your ancestors in Ireland.
Land, Tax, and Estate Records – Guide #3 (NEW!). Had the Irish census records for the 19th century survived, Griffith’s Valuation, a tax list, would not be one of the most important resources for Irish researchers. Without any context, however, it can just seem like a list that includes lots of people of the same name. This Guide explains how and why Griffith’s Valuation was done, and how to use it to glean the most information about your family. Once you know your ancestor’s locality in Ireland, Griffith’s Valuation can place them on a specific piece of land between 1846 and 1864. After Griffith’s Valuation, the Revision Books allow you to follow the land and in some cases, to the 1970s, possibly identifying cousins still living on the land.

Start creating fabulous, irresistible videos about your family history with Animoto.com. You don’t need special video-editing skills: just drag and drop your photos and videos, pick a layout and music, add a little text and voila! You’ve got an awesome video! Try this out for yourself at Animoto.com.

MyHeritage.com is the place to make connections with relatives overseas, particularly with those who may still live in your ancestral homeland. Visit www.MyHeritage.com
MyHeritage.com is the place to make connections with relatives overseas, particularly with those who may still live in your ancestral homeland. Click here to see what MyHeritage can do for you: it’s free to get started.
MILITARY MINUTES: 5 BRANCHES OF THE MILITARY

Each of the military branches is listed below, detailing information about when each was organized and resources available to genealogists on your ancestors who served in any of these branches.
United States Army. The largest of the five military branches dates back to June 14, 1775, during the early days of the Revolutionary War. Prior to the formation of the Army, each colony had companies and battalions of Associators and local militia. With the war, the need for a professional standing army to fight the British saw the formation of the Continental Army.
With the end of the Revolutionary War, the Army disbanded in 1783 after the signing of the Treaty of Paris. Later in 1796, two legions formed under the command of General Anthony Wayne would later become the nucleus of the United States Army. The Encyclopedia Britannica published this nice article on the history of the Army from its inception to the present.
A number of excellent genealogical resources are available to search for ancestors who served in the United States Army since the beginning. These databases are found on Ancestry, Fold3, and Family Search. One of the largest collections of records covers the United States Regular Army enlistments from 1798 to 1914 (available by subscription at Ancestry.com). Searching the card catalogs of Ancestry.com, Fold3 and FamilySearch will yield many databases that contain information about soldiers who served, and sacrificed their lives with the Army over the last two centuries.
United States Navy. The United States Navy dates from October 13, 1775 when it was officially established by an Act passed by the Continental Congress. At the end of the Revolutionary War it was disbanded, and again reestablished under the Naval Act of 1794 which created the Navy as a permanent branch of the military.
The history of the Navy and technology can be divided into two major eras. The earlier period, called the “Old Navy,” was the age of wooden sailing ships, and still later came the birth of the ironclads during the Civil War. The later period called the “New Navy” occurred with further innovations in late nineteenth century as the United States transformed into a global power recognized the throughout the world.
The United States Navy website has a nice background history of the service. Numerous databases and searches for records of the Navy covering multiple war period detailing pensions, continental sailors, muster rolls, ships logs, and cruise books are located on Ancestry.com, Fold3 and FamilySearch. Consult each database individually for records of interest.
Another organization related to the Navy is the United States Merchant Marines. Although not officially a branch of the military, the Merchant Marines sacrificed and lost lives since the days of the Revolutionary War, carrying out their missions of supply and logistics during times of war. Here’s an excellent website on the history of the Merchant Marines.
United States Air Force. The modern day Air Force dates from September 18, 1947, when it was formed as part of the Security Act of 1947. The Air Force and aviation history began under the authority of the United States Army, starting on August 1, 1907 when it was organized under the name of the Aeronautical Division of the Signal Corps. Over the next 30 years the service changed names several times:
- Aviation Section of the Signal Corps (1914-1918);
- Division of Military Aeronautics (1918);
- Air Service of the United States Army (1918-1926);
- United States Army Air Corps (1926-1941);
- United States Army Air Forces (1941-1947).
In that final year, it was separated as its own organization as it is known today. Click here for a complete history of the Air Force from 1907 to the present.
Two excellent online sources covering the early history of the Air Force from World War I and World War II are located on Fold3:
- Gorrell’s history when part of the AEF in 1917-1918 and
- Missing air crew reports during the World War II
United States Marines. This elite branch of the military began with the organization of the Continental Marines on November 19, 1775. The mission of the Marines initially comprised ship-to-ship fighting, security onboard naval vessels, and assistance in landing force operations. This mission would continue to evolve over the years. At the end of the Revolutionary War, the Marines were disbanded on October 4, 1783.
Along with the Navy, under the Naval Act of 1794, the United States Marines were again re-established and would serve faithfully in every major war period and in peacetime between conflicts. The Marines will forever remain true to their motto of “Semper Fidelis” or Always Faithful as they continue to live up to their long-running tradition of honor and service. Click here to watch an interesting and accurate history of the Marine Corps is viewable online on You Tube.
Ancestry.com has an excellent online genealogical resource for discovering Marine Corps ancestors: fully searchable Marine Corps muster rolls from 1798 to 1958 for enlistees.
Coast Guard. The history of this seagoing service dates back to August 4, 1790. Established as the Revenue Cutter Marines under the direction of Alexander Hamilton, the name was changed in 1894 to the Revenue Cutter Service until 1915. That year, an Act of Congress was passed and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson called the “Act to Create Coast Guard.” The United States Live Saving Service and Revenue Cutter Service came together. Later, in 1939, the United States Light House Service was added to form the modern day United States Coast Guard.
The complete history of the United States Coast Guard from 1790 is on the Historians Office. It includes information about each of the separate organizations that came together to form the Coast Guard at. Ancestry.com has a collection of casualties of the Navy, Marines, and Coast Guard. Very few additional online sources are available online for this branch of the service. Researchers must access these documents and records onsite at the National Archives in Washington, DC.
Military Minutes Case Study

By Michael Strauss
Subject: Russell Strauss
Died: December 27, 1981-Jonestown, PA
Son of Harry B. Strauss & Agnes S. (Gerhart) Strauss
Over the last 30 plus years doing genealogy research, I’ve discovered that nearly all of my family members who served in the military were in the United States Army. But I have been occasionally surprised to find relatives who served in other branches of the military.
On the paternal family several years ago one of my cousins gave me a box of photographs. One of the images was marked Russell G. Strauss. He wore the uniform of the United States Navy during World War II. I recognized his name and knew that he was my grandfather’s first cousin. I was 16 years old when he died and didn’t know him very well.
His uniform indicated that he was a third class petty officer in the Navy during the war. I looked further at his uniform and noticed a diamond shaped “S” as part of the insignia. This military occupation indicated that he was a specialist that would require further research. I spoke with a couple of my older family members who knew Russell. All of my family interviewed said that he in the military police (M.P.) during the war. With additional research, I discovered that his insignia was that of the Shore Patrol. When I compared what my family said to me and his uniform told me the information matched very closely.
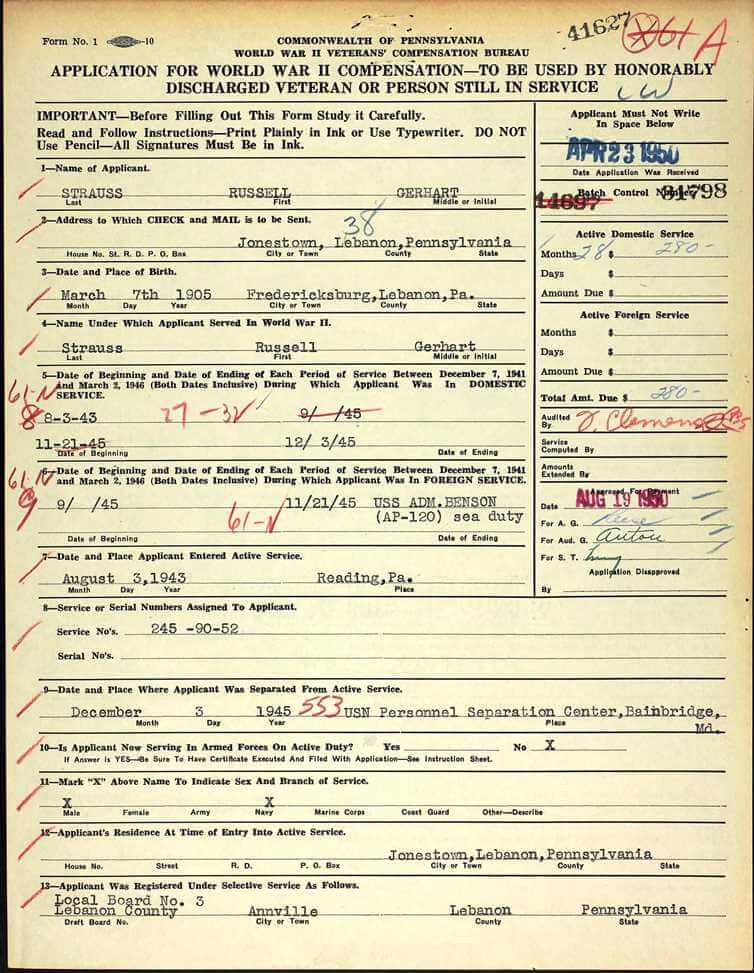
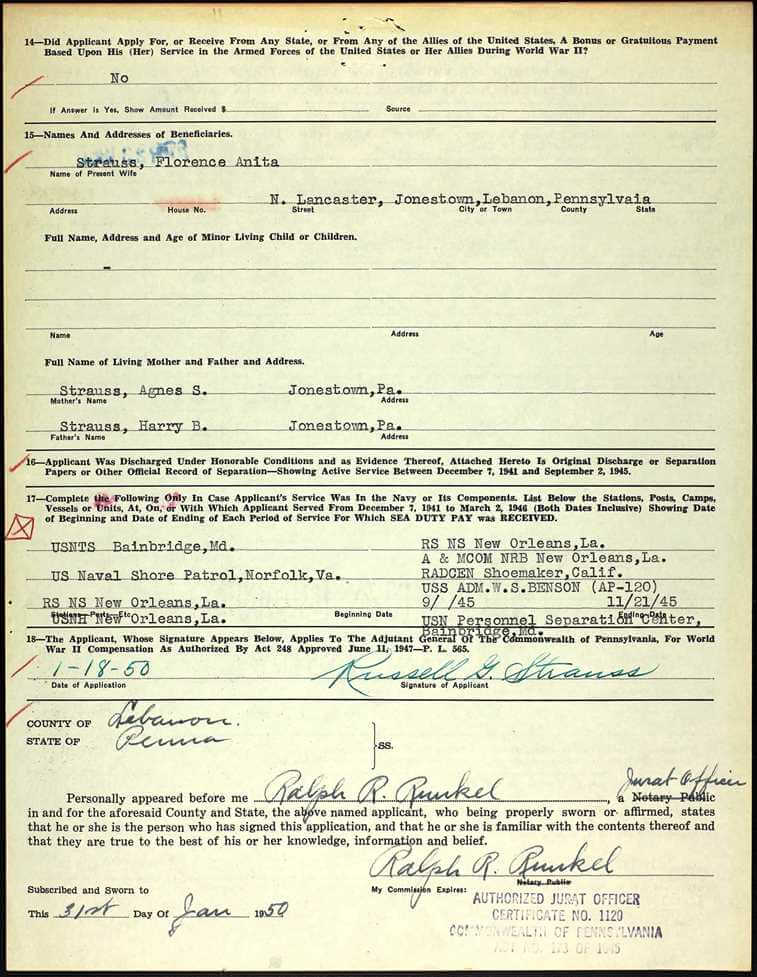
I found on Ancestry his application for compensation from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in 1950 when he served in the Shore Patrol in Norfolk, Virginia as part of his military duty (inserted below). Putting information from his photograph together with what my family members shared with me helped answer questions I had regarding of my relatives.
PRODUCTION CREDITS
Lisa Louise Cooke, Host and Producer
Sunny Morton, Editor
Vienna Thomas, Associate Producer
Hannah Fullerton, Production Assistant
Lacey Cooke, Service Manager
Disclosure: This page contains affiliate links and Genealogy Gems will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on these links (at no additional cost to you). Thank you for supporting this free podcast and blog!