by Diahan Southard | Jan 17, 2015 | 01 What's New, DNA
(Update 2020) When genealogists take an ancestry DNA test, they are looking for more than just their ethnicity results. They are also very interested in receiving information on other people who have tested who closely genetically match them. They want to know who the closest matches are, and if those matches have family tree information that they can share.
However, with all the people testing these days, (some being genealogists and some not) the volume of matches can become overwhelming very quickly.
Are you one of those people who have way too many genetic “4th cousins or closer” among your DNA matches? Have you ever wondered “What do I do with all these matches?!” If so, keep reading. We’re going to explore some of your options, and most importantly, how to determine how genetically close your cousins really are.
Doing the DNA Math on Your Cousins
Math can provide us with a degree of certainty in genetic genealogy. Each of us has two biological parents. We have four biological grandparents, and eight great-grandparents.

However, the farther back we go the less we can rely on math.
For example, on paper you should have sixty-four 3rd great grandparents. However, many of us find that the same person occupies more than one slot on our pedigree chart. While this significantly decreases the workload for traditional genealogy, it adversely impacts your genetic genealogy. Especially when it comes to that long long list of 4th cousins you have in your match list at any of the three major DNA testing companies.
Depending on how intermarried your lines are, you may be seeing individuals on your match list that genetically look like your fourth cousins, but they are genealogically your sixth cousins – EIGHT TIMES! So how can you tell the difference?
There are two parts to that answer: one you can control, and the other you can’t.
Distinguishing DNA Matches with Genetic Tools
While your fourth cousins and your eight-time-sixth cousins may look similar genetically, there are often small clues in the genetics that can help you tell the difference. This distinction can sometimes be detected by a testing company who, through research and validation, has been able to fine-tune their algorithms to detect these subtle differences.

Your Genetic 4th Cousins
You can participate in this double checking process by using some of the genetic tools that are available to you at Family Tree DNA, or at Gedmatch.com. But since you may not be an aspiring geneticist, let’s focus on the genealogical work you can do to determine if a match is truly a fourth cousin.
Use Google Earth to Plot Your DNA Matches
A fourth cousin designation just means that you and your match are separated by between six and twelve degrees (people). So that might be five back on your chart to your common ancestor, and five down to your match, which would make you true fourth cousins. It could also be some other permutation of that.
For our example, let’s assume true fourth cousins. That means that the two of you share one of thirty-two 3rd great grandparents (16 couples). In order to find out which set, you have two genealogical identifiers: surname and location.
Therefore, the first thing you should do is make a list of the surnames and locations of those thirty-two 3X great grandparents.
Now, most of us do not know all 16 of those couples, so you are going to have some holes. Feel free to fill in those holes with surnames on subsequent generations that will carry through to this fifth generation.
A great tool to plot your own list of ancestors geographically is the free downloadable Google Earth software.
Check to see if you have the latest version of Google Earth downloaded to your desktop or laptop computer. On your desktop, look for a grey and white globe. If you see a blue and white globe, you have the older original free version of Google Earth. However, a few years ago, Google made their Google Earth Pro version free to everyone, and it is now the standard.
If you do have Google Earth Pro (the grey globe software) then you’re ready to go.
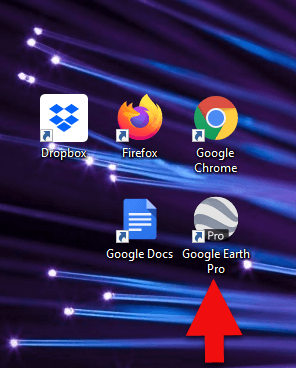
The grey Google Earth globe on the desktop.
If you don’t have it, then you will need to download it.
How to Download the Free Google Earth Software:
- Go to http://www.google.com/earth/download/gep/agree.html
- Click the blue download button
- Read the Terms and Conditions
- If you agree to them, click the Agree and Download button
- Follow the installation guide
- When complete click Run Google Earth
Now that you have Google Earth, you can begin by creating a folder in the Places panel in Google Earth devoted to your 16 couples. Here’s how:
1. In the Places panel, right-click on MyPlaces and select Add > Folder:
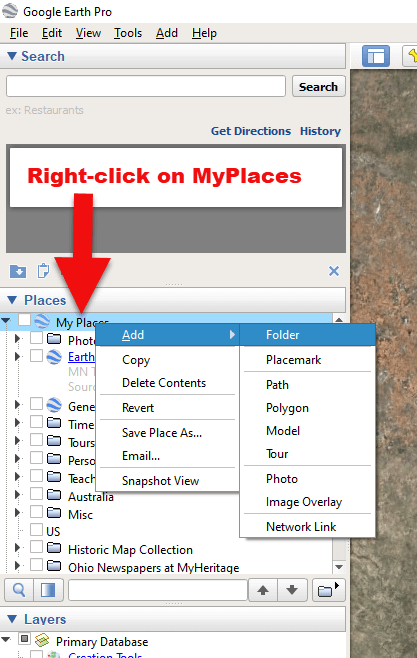
Right-click on MyPlaces > Add > Folder
2. Name the folder and then click OK:
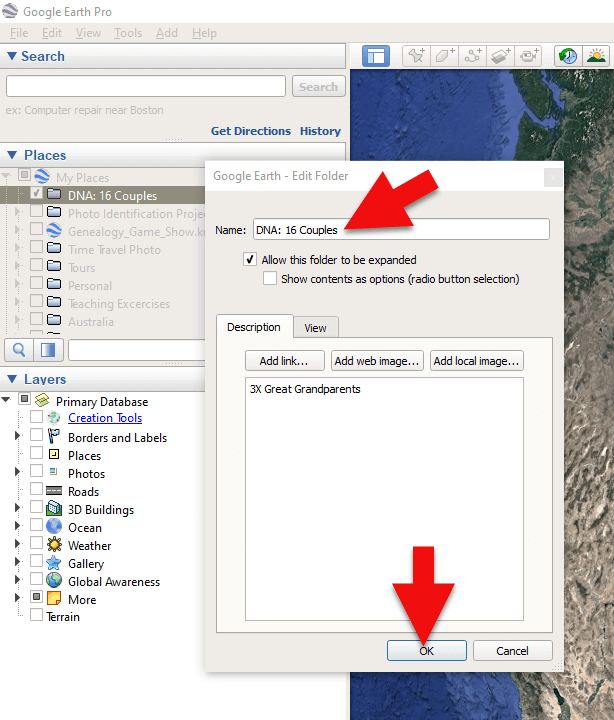
Creating a folder in Google Earth
3. Now you will see your new DNA folder for your 16 couples in the Places panel. If you don’t see it, look toward the bottom of the list. You can move the folder to any location within the list by dragging and dropping it.
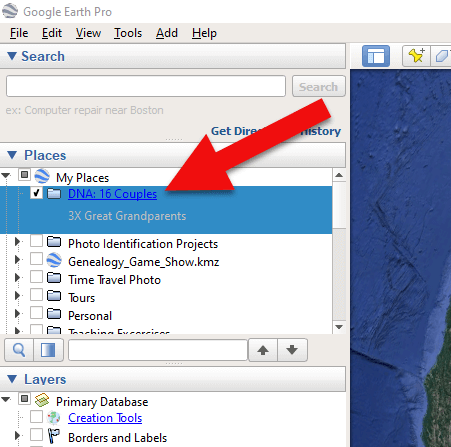
Create a folder in Google Earth for DNA 16 couples
Once you have your DNA folder created fro your 16 couples, you can then easily plot your surnames and locations.
How to Plot Your Surnames and Locations in Google Earth:
1. Click your new DNA folder to select it. This will ensure that the placemark you are about to create will be stored in that folder.
2. In the search box (upper left corner of the Google Earth software) type in the first location and click Search. Google Earth will fly to that location on the map.
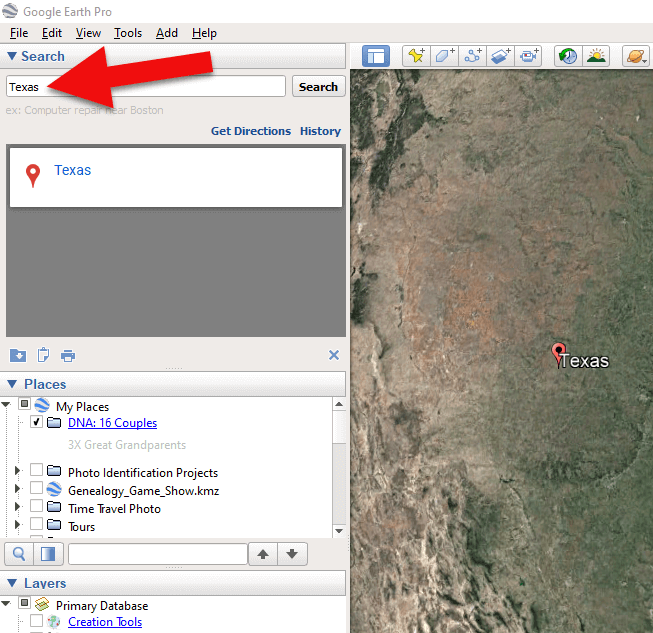
Type the locaton in the Search box and click Search.
3. In the toolbar along the top of the screen, click the placemark button to place a pushpin in that location:
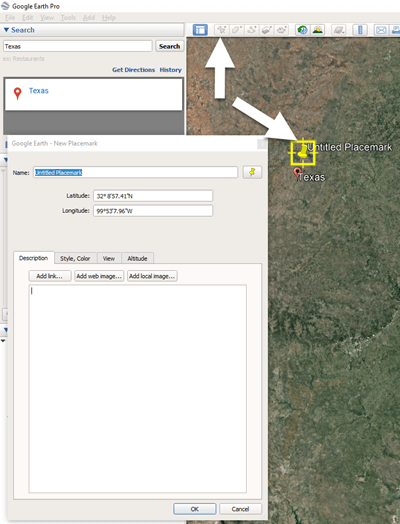
Click the Placemark button in the Google Earth toolbar.
4. In the Placemark dialogue box, enter a title for hte pushpin placemark. Click the OK button to close the box and set your placemark.
5. Repeat the process for all the locations.
Then evaluate the fifth generation of your fourth cousin matches for genealogical information that lines up with any of the items on your list.
You can also plot the surnames and locations of your matches in Google Earth. This is where Google Earth really comes in handy. The free software makes it very easy to see when your ancestral home may be bordering the locations of your matches. Those with whom you find a similarity become your best matches, and your best chance of determining your connection. Those without an obvious connection cycle to the bottom of your pile for a genetic evaluation. You can perform these same kinds of searches for your second and third cousins as well.
As you begin to become more familiar with the fifth generations of your matches, you may also start to see patterns of surnames or locations emerge among your matches. These then become the surnames and locations that might be able to fill the missing spaces in your pedigree chart.
More Genetic Genealogy and Google Earth Gems
If you are new to using Google Earth, I have several suggested resources for you by Lisa Louise Cooke:

Learn more in Premium episode 131.
Here’s a video of the authors discussing three common DNA misconceptions:
Authors: Diahan Southard and Lisa Louise Cooke
by Lisa Cooke | Jan 14, 2015 | 01 What's New, Apps, Canadian, Google Earth, Listeners & Readers
 Awhile back, Barbara from Courtenay, British Columbia, sent me an excellent question about using Google Earth for Canadian genealogy. Then she sent me an excellent answer before I had a chance to answer it myself! Here’s what they were:
Awhile back, Barbara from Courtenay, British Columbia, sent me an excellent question about using Google Earth for Canadian genealogy. Then she sent me an excellent answer before I had a chance to answer it myself! Here’s what they were:
Question: “I live in Canada and a lot of the Google Earth articles involving land plats can’t be applied in Canada. The prairie provinces do have a similar land survey system, with townships, ranges and meridians. I found a website where these can be converted to coordinates that Google Earth will recognize. However, this particular website would like to be paid for providing this information (legallandconverter.com). Do you know of any way these numbers can be converted without paying?”
Answer: “I have some good news! My very smart son found a free website,
prairielocator.com, which will give you the coordinates of Section, Township, Range and Meridian for the Canadian prairie provinces. It doesn’t cover quarter sections, but that’s okay if you know which one your ancestor was on. Please pass this along to your Canadian fans or Americans who have Canadian ancestors (there are many, I know).”

Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research!
Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone: Prairie Locator Mobile – for iPhone, by Lisa Cooke | Dec 19, 2014 | 01 What's New, Google, Google Earth, images, Maps
 If you have experienced frustration managing your genealogy files in Google Earth, you’re not alone. A recent email question from Genealogy Gems Premium Member Linda reminded me what the #1 culprit tends to be: the Temporary Folder. Linda writes:
If you have experienced frustration managing your genealogy files in Google Earth, you’re not alone. A recent email question from Genealogy Gems Premium Member Linda reminded me what the #1 culprit tends to be: the Temporary Folder. Linda writes:
“I have a question for you about Google Earth. I have been trying to play around with it and when I find a place and want to save it, the “Save to My Places” is grayed out and it won’t let me save. My husband said the same thing happens on his computer. I looked on a Google forum and someone posted a question about it not working recently. Do you happen to have any info about this and does the same thing happen to you?”
While Linda didn’t provide specifics as to what kind of “place” she is trying to save, I’ve been at this long enough to have a pretty good ideathat she found something like a Rumsey Historical Map that she wants to add as a permanent fixture to her geographic genealogy files in Google Earth. Fabulous! Or it may be as simple as someone emailed her a map with a single placemark on it. She has clicked to open it and Google Earth magically opened and displayed it on her screen. Awesome!
In both cases, the important thing to notice, is that the item was sent to the TEMPORARY folder in the PLACES panel. That’s because Google Earth doesn’t assume just because you wanted to look at something means you want to save it in your files forever. And this leads me to the answer to Linda’s question…
The only time “Save to My Places” will not be grayed out is when the item that you are looking to Save to My Places is in the TEMPORARY folder. In other words, it is not yet saved to My Places (as in the cases I mentioned above.)
The Temporary folder is the most overlooked feature of Google Earth, and can play havoc with you unless you understand how it works, particularly in conjunction with the menu functions.
Here’s how to save an item in the Temporary folder to be a permanent part of your My Places:
- Click to select and highlight the item in the Temporary Folder
- Go up to the menu click FILE
- Select SAVE
- Select SAVE TO MY PLACES

The item will then jump from your Temporary folder into My Places. You may need to open My Places by clicking the small black arrow next to it in order to see it at the bottom of your list.

Once an item (such as a place mark) is created, and it appears anywhere in the Places panel other than the Temporary folder (such as in a folder you created, or under My Places,) it is technically already in My Places, and therefore does not need to be Saved to My Places. And that is why that option is grayed out.
Think of “Save to My Places” as “MOVE to My Places”.
Once your item is in My Places, from that point forward you will be saving any changes you make to it by selecting FILE > SAVE > SAVE MY PLACES.

This procedure saves changes made to any and all files in your My Places, including the new file you just added. Anything in your Temporary folder will be lost when you close Google Earth.
Play it Safe!
Be smart and get into the excellent habit of saving My Places every 10 minutes or so, (in case Google Earth, our computer, or internet connection crashes,) and most definitely when you close the program at the end of your work session.
Happy Googling!
Lisa
by | Nov 8, 2014 | 01 What's New, Google Earth
I often wish I had the opportunity to work with each one of you on your individual Google Earth projects, because I firmly believe it’s one of the most exciting ways to tell your family history stories, and to analyze your research data.
So when Family Tree University invited me be your guide to mastering the genealogical benefits of this free software for a special one week workshop, I couldn’t resist. I’ve cleared my calendar for the week of November 17, and I’m all yours!
In this workshop we’re going to cover how to tap into Google Earth’s robust features to bring depth and a new perspective to your family history research, as well as create projects that enhance your genealogy with a “wow!” factor.

Seats are limited and will go fast.
Nov. 17-24, 2014 Online Workshop
Register Here
You’ll have the opportunity to participate in message board discussions with me and your fellow students over the course of the week, plus create your own Google Earth project to showcase your genealogical research.
Here what you’ll get:
Consultations with me in the Message Forum. This is your chance to ask questions and receive my feedback personalized to your Google Earth projectsVideo classes: Genealogy Projects With Google Earth and Best Websites for Finding Historical MapsFive step-by-step lessons from the course Google Earth for Genealogists in PDF format
Lesson from the Finding Your Ancestral Village course on locating your ancestral town
Unlimited viewing: Your all-access pass gets you into the workshop all week-you can even download the videos to watch again later.
I can’t wait to see what you will create!

by | Oct 26, 2014 | 01 What's New, Google Earth, History, Maps

The Abbeville press and banner., October 12, 1892, Image 6/ www.chroniclingamerica.com
When Liberian national Thomas Eric Duncan was diagnosed with Ebola it was unnerving for everyone here in the U.S. As a new Dallas area resident, and someone who was hopping from plane to plane for a Fall series of speaking engagements, it definitely gave me pause.
Epidemics, quarantines, and communities trying to protect citizens have been age old dilemmas, so it makes sense to look back through history at the strategies employed. There is much to be learned.
If we ask the question “what would have happened if Ebola had struck the U.S. 130 years ago?” we don’t have to look much farther than the location of one of the most recent Ebola patient: New York.

from the Humboldt Republican (Humboldt, Iowa) March 31, 1892
Courtesy www.Newspapers.com
In New York’s East River, tucked between the Bronx and Rikers Island lies North Brother Island, where in 1885 Riverside Hospital was relocated from Blackwell’s Island to isolate and treat small pox patients. From there it expanded to include the quarantine of other diseases.
North Brother Island stands idle today, closed to the public. However from 1907-1910 and 1915-1938 it housed the notorious Typhoid Mary, closing shortly after her death.
Although today the island is closed to the public, anyone can visit virtually with the aid of Google Earth. Join me on a 5+ minute tour of North Brother Island featuring the magazine and newspaper articles of the day, and written, audio and video tours of how it stands today a shell of what it once was. Click here to download and play my Google Earth Historic Tour KMZ file on your computer. It will be added to your “Places” panel in Google Earth under “Temporary Places.” Open the folder and click the “click to play the tour” icon. Be sure your speakers are on! And take time to click to watch the video and view the articles in the placemarks.
Don’t have Google Earth loaded yet? Download it free here.
If you would like to learn to create your own Google Earth family history tours watch this free video and then pick up your copies of Google Earth of Genealogy Volume I and Volume II.












 Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research! Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone:
Thank you, Barbara–and a special shout-out to your son for finding that resource to help genealogists use Google Earth for Canada research! Here’s my two-cent’s worth: I just peeked at PrairieLocator.com and I see the site also has an app for the iPhone: 










